
UndergroundMiningEquipment1 Australian Mining
Underground hard-rock mining accounts for 40 percent of global mining operations but only 12 percent of run-of-mine (ROM) production. 1 Underground mines also tend to be more targeted, more costly, and less productive than open-pit mines. Because the choice of which underground method to deploy is predominantly driven by the geology of the.
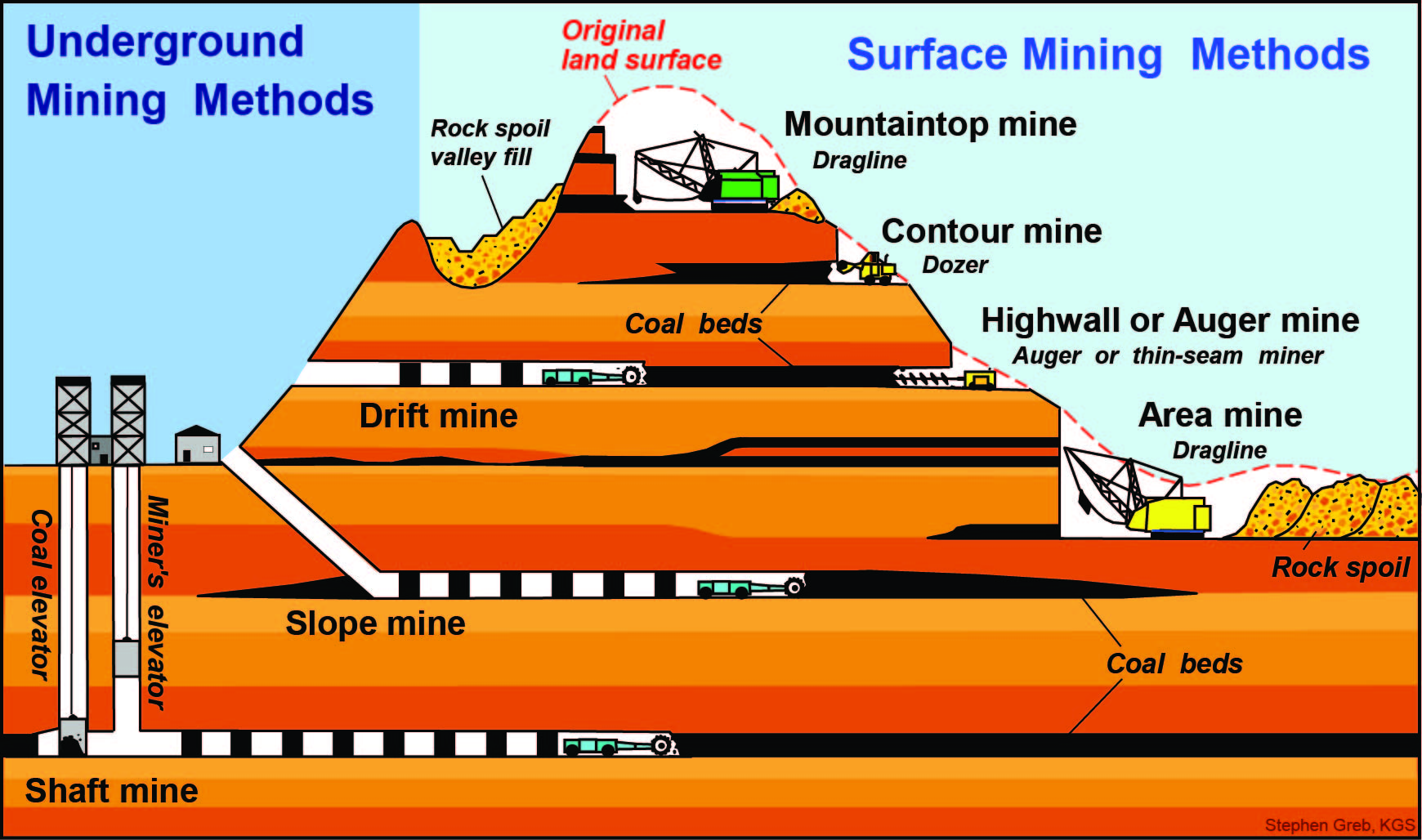
Coal Mining, Kentucky Geological Survey, University of Kentucky
There are four main mining methods: underground, open surface (pit), placer, and in-situ mining. Underground mines are more expensive and are often used to reach deeper deposits. Surface mines are typically used for more shallow and less valuable deposits. Placer mining is used to sift out valuable metals from sediments in river channels, beach sands, or other environments.

Different Mining methods Different mining operations Underground
Bulk mining methods are fully mechanised allowing the excavation of large volumes of ore. These techniques enable high production rates in underground mines, but are less effective in separating ore and waste so are preferentially used in extracting massive ore bodies. 2.1 Underground Selective Mining Methods

Primary underground mining methods in Australia
Underground mining is practical when: 1. The ore body is too deep to mine profitably by open pit. 2. The grades or quality of the orebody are high enough to cover costs. 3. Underground mining has a lower ground footprint than open pit mining. The underground mining methods we use include room and pillar, narrow vein stoping and large-scale.

4 Things To Know About Underground Mining Methods And Techniques
5) Shrink age Stoping. Shrinkage stoping may be termed a " classic" mining method, having been perhaps the most popular mining. method for mos t of the past century. It has largely been.

underground mining processes and types AMS
Underground mining methods: Blast mining - drilled holes are filled with explosives to remove, loosen, and open the area. Each hole is drilled either by a handheld drill or drilling machine. Room and pillar mining - uses the construction of pillars to support ceiling weight while a team clears out the surrounding rock from around the pillars.

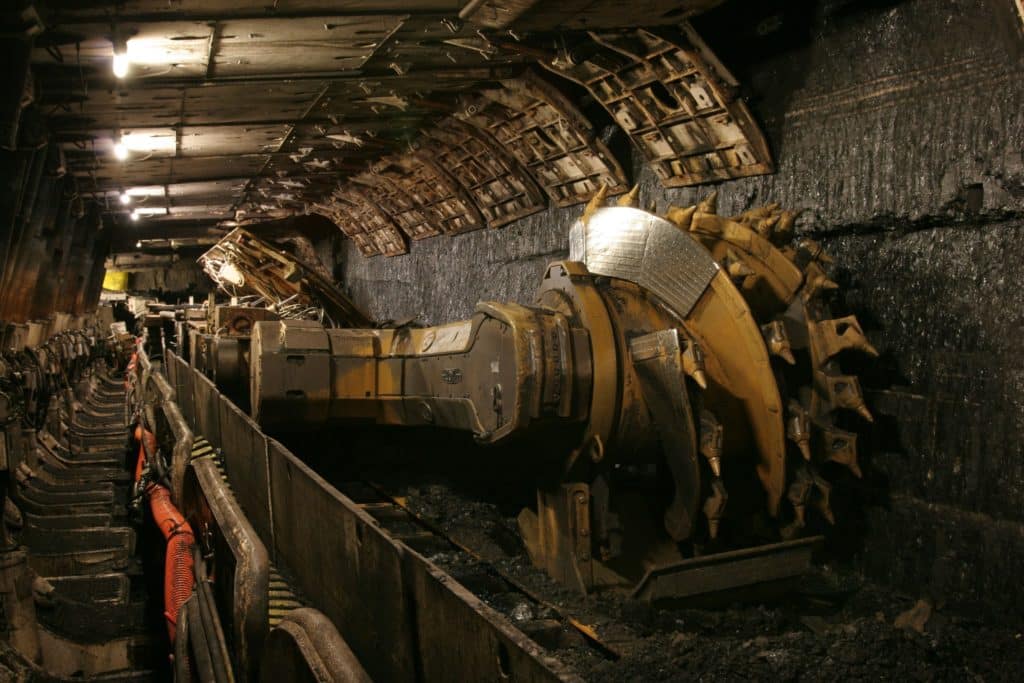
How a Continuous Miner Works in 2023 Underground Mining
Different mining methods are designed to produce different types and magnitudes of displacements, in the near-field and far-field domains of an orebody. For example, the mining method illustrated schematically in Figure 12.2 is designed to restrict rock displacements in both the near field and the far field of the orebody to elastic orders
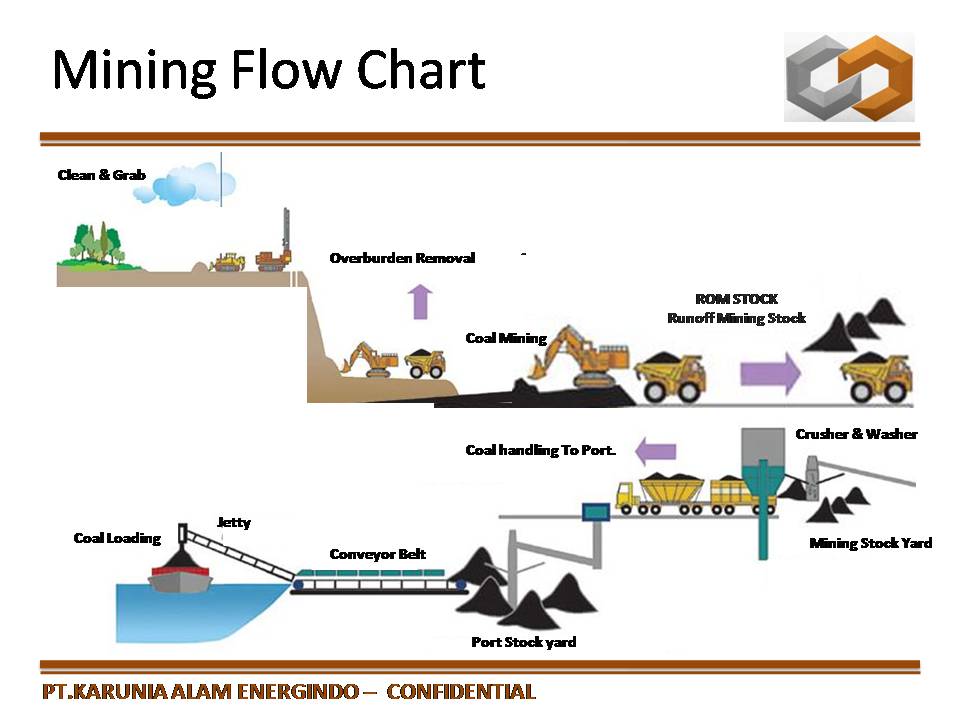
Prasindo Consulting Coal is mined by two methods surface or
Underground mining methods become necessary when the stripping ratio becomes uneconomical, or occasionally when the surface use of the land would prohibit surface mining. Underground methods are traditionally broken into three classes: unsupported, supported, and caving methods. These classes reflect the competency of the orebody and host rock.
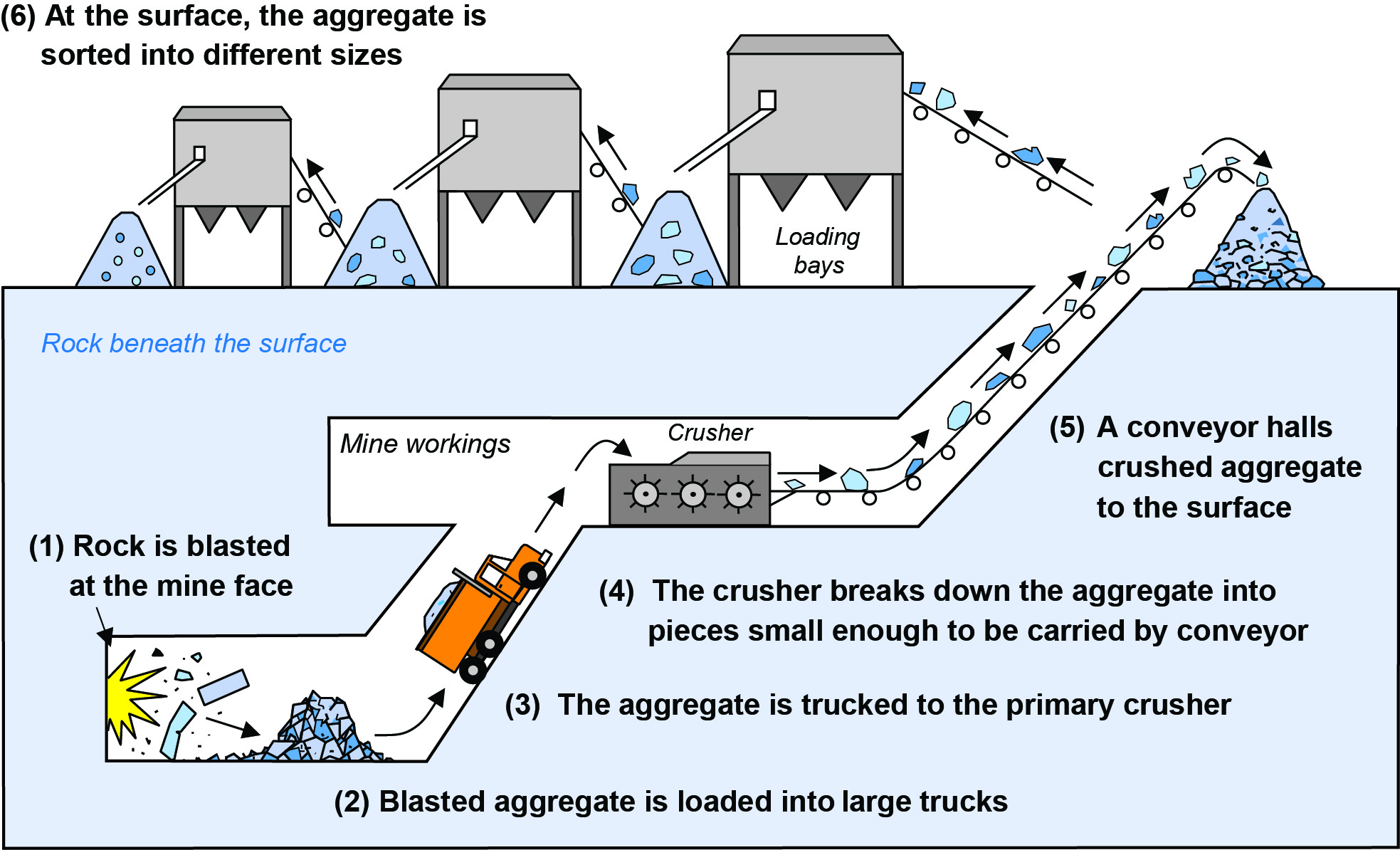
Underground Mining Diagram
A 3D diagram of a modern underground mine with shaft access. Underground hard-rock mining refers to various underground mining techniques used to excavate "hard" minerals, usually those containing metals, [1] such as ore containing gold, silver, iron, copper, zinc, nickel, tin, and lead. It also involves the same techniques used to excavate.
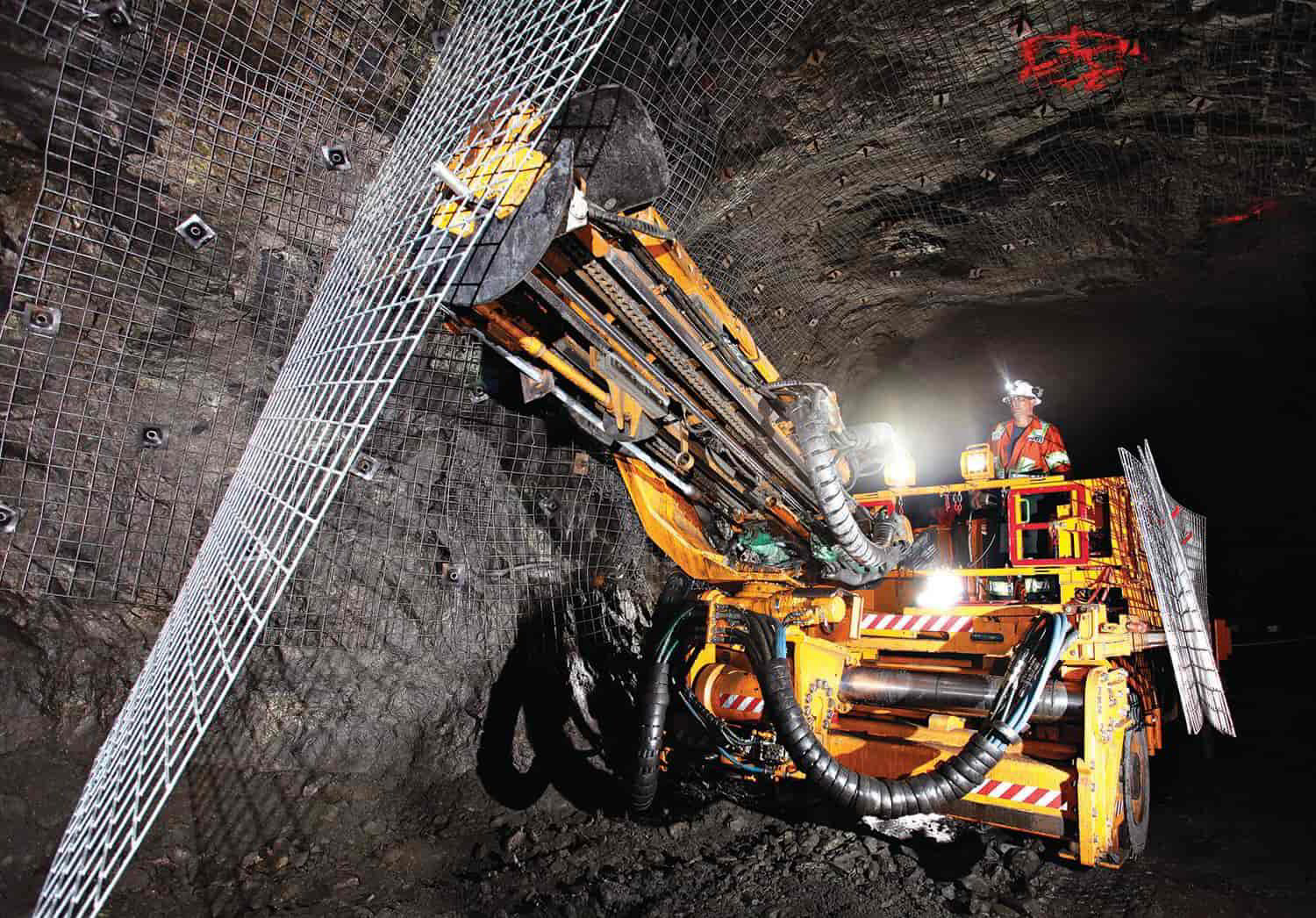

The Four Main Types of Mining An Underground Miner
Mining - Underground, Safety, Techniques: When any ore body lies a considerable distance below the surface, the amount of waste that has to be removed in order to uncover the ore through surface mining becomes prohibitive, and underground techniques must be considered. Counting against underground mining are the costs, which, for each ton of material mined, are much higher underground than on.
World’s Most Modern Underground Mine Silibrain Medium
Fig. 2: Examples of the underground machineries and equipment: (a) two beams Jumbo; (b) air leg; (c) LHD truck; (d) underground working supported by meshing and rock bolting (RB) 2.0 UNDERGROUND MINING METHODS 2.1 Selective mining methods Narrow steeply dipping veins are usually mined using cut-and-fill and shrinkage stoping methods, which.

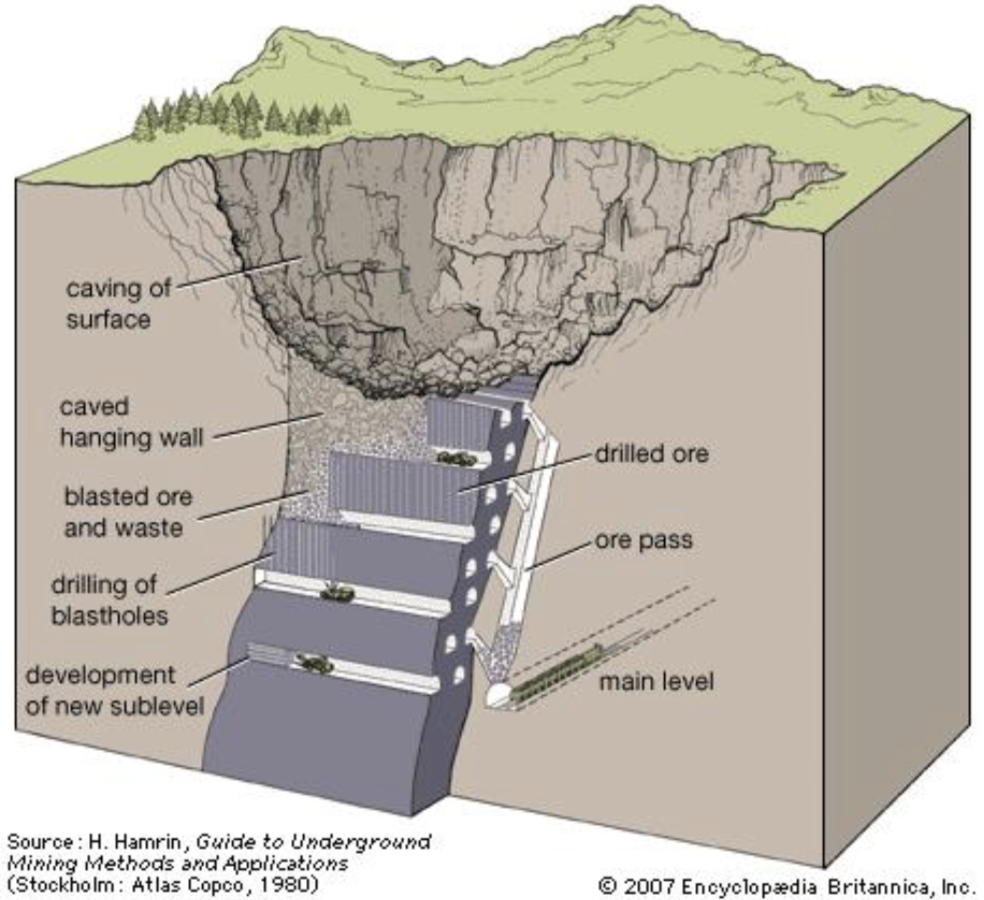
Schematic view of underground mine (source H. Hamrin, Guide to
Modern underground coal-mining methods can be classified into four distinct categories: room-and-pillar, longwall, shortwall, and thick-seam. Room-and-pillar mining. In this method, a number of parallel entries are driven into the coal seam. The entries are connected at intervals by wider entries, called rooms, that are cut through the seam at.
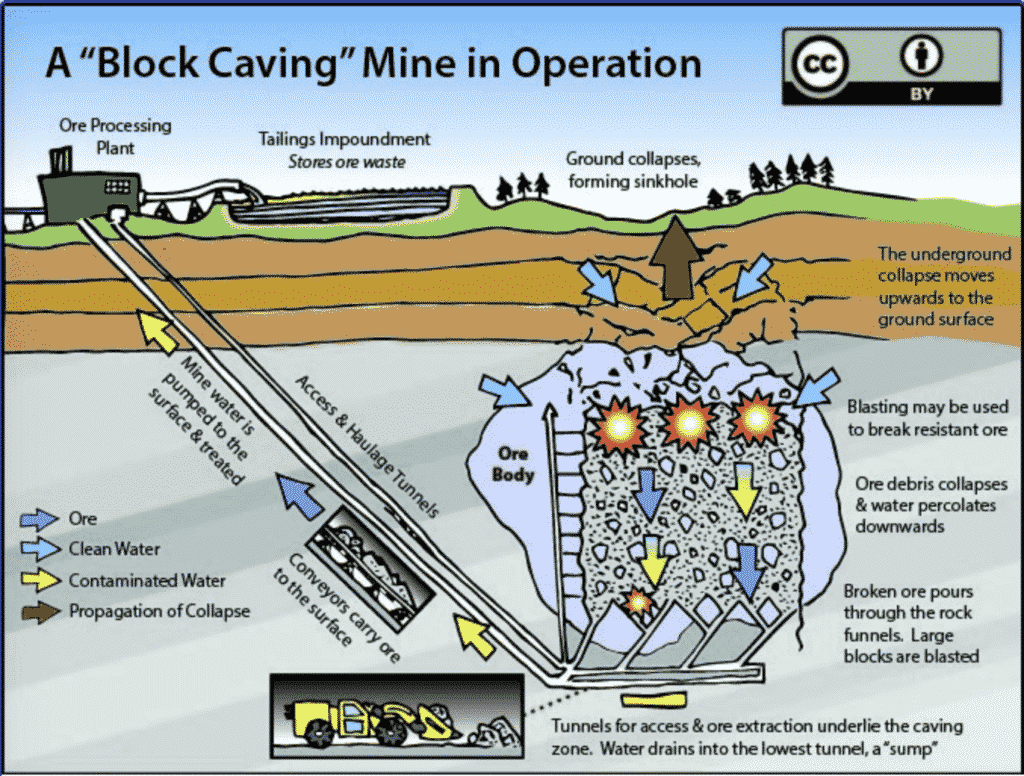
Primary underground mining methods in Australia
In India, open cast and underground mining are the two major coal mining methods. Opencast mining contributes about 95.74% of the total production. In contrast, underground mining contributes to the rest of the production by 4.26% during 2021−22 (provisional).

Beginners Guide to Room and Pillar Mining An Underground Miner
In this method, you must drill a downwards ramp next to the ore deposit. This ramp should run from the surface level down as far as the ore deposit goes. Next, you can drill a horizontal cut from one side of the ore deposit to the other. Miners typically refer to such cuts as drifts.

4 Things To Know About Underground Mining Methods And Techniques
UNDERGROUND Mining Methods Engineering Fundamentals and International Case Studies Edited by William A. Hustrulid and Richard L. Bullock. Society for Mining, Metallurgy, and Exploration, Inc. (SME) 8307 Shaffer Parkway Littleton, Colorado, USA 80127 (303) 973-9550 / (800) 763-3132 www.smenet.org SME advances the worldwide minerals community.
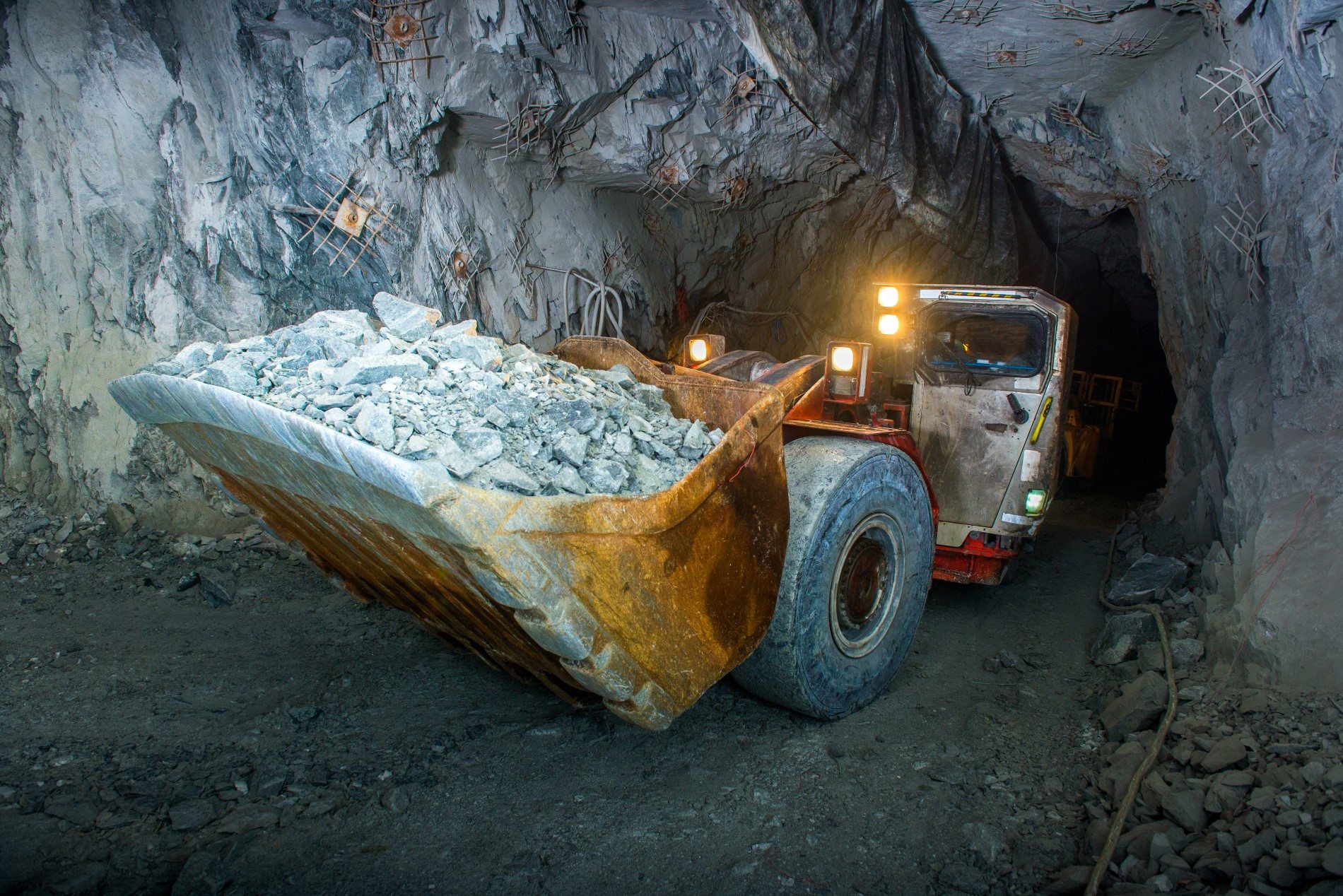

What Is Underground Mining? Groff Engineering & Consulting PLLC
Current underground mining methods can be classified into three main groups, namely: (a) naturally-supported, (b) artificially-supported, and (c) unsupported (Fig. 3; Brady and Brown, 2006). Naturally-supported mining methods leave a portion of unmined ore as pillars, commonly referred to as remnant pillars.