Testicular pain RCEMLearning
Testis, in animals, the organ that produces sperm, the male reproductive cell, and androgens, the male hormones. In humans the testes occur as a pair of oval-shaped organs. They are contained within the scrotal sac, which is located directly behind the penis and in front of the anus. In humans each.
Testicular Anatomy Structur Testis Diagram Showing Network Semineferous Tubules Stock
The testes, or testicles, are two egg-shaped sex organs that play an important role in the male reproductive system. They are where sperm cells are produced and are also responsible for the production of the sex hormone testosterone . The testes, commonly referred to as "balls," are housed in a pouch of skin beneath the penis called the scrotum.

Structure of the testis Figure 42.2a Diagram Quizlet
A ruptured testicle is a health emergency that happens when the membrane covering a testicle breaks. It can occur when: Something pierces your scrotum. Your testicle is hit very hard. Your testicle gets crushed against abone in your pelvis. Testicles are a pair of organs that make hormones and sperm in people assigned male at birth.
PPT Inguinal , femoral and scrotal regions PowerPoint Presentation ID711110
The testes (testicles) are male reproductive glands found in a saccular extension of the anterior abdominal wall called the scrotum. They are in ovoid shape, sized four to six centimeters in length. Testes develop retroperitoneally on the posterior abdominal wall and descend to scrotum before birth.
Testicular Torsion Urology Surgery Geeky Medics
A testicle (pronounced "teh-stuh-kl") is part of the anatomy of men and people assigned male at birth (AMAB). Generally, you'll have two testicles. These body parts make sperm and hormones. Other names for your testicles are male gonads or testes (pronounced "teh-steez"). One testicle is called a testis. There are other more casual.
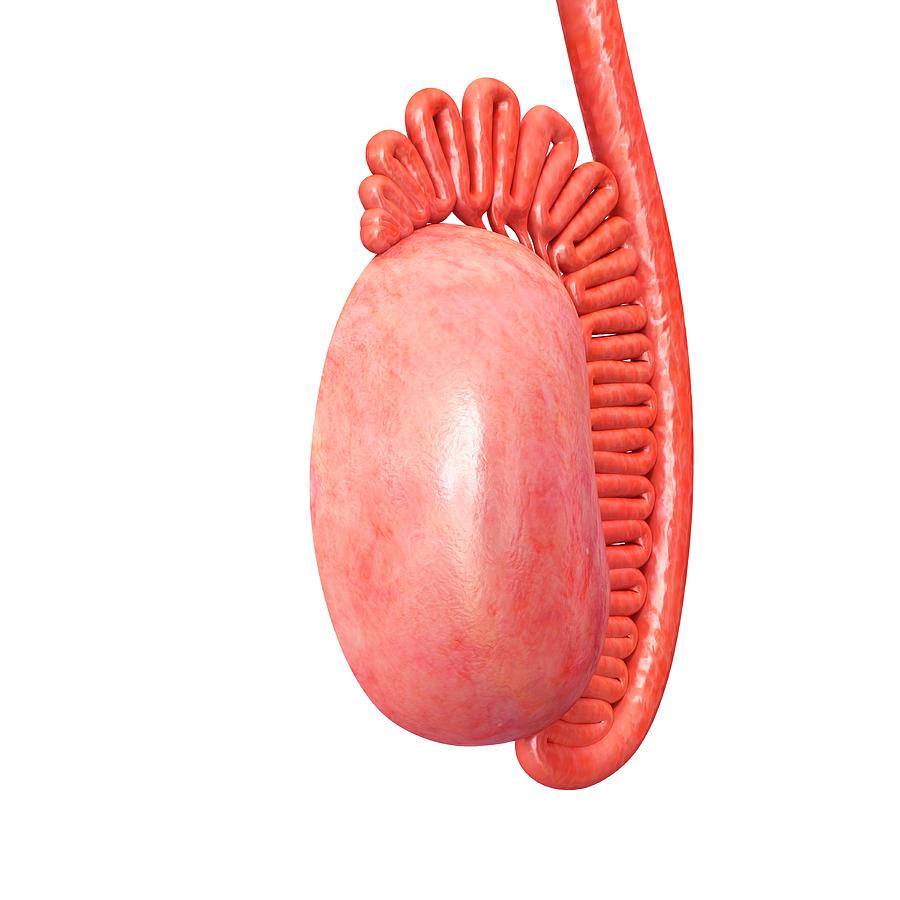
Male Testis Anatomy Photograph by Pixologicstudio/science Photo Library
The testis is the male reproductive gland that is responsible for producing sperm and making androgens, primarily. Testosterone levels are controlled by the release of Luteinizing Hormone (LH) from the anterior pituitary gland; whereas, Follicle-Stimulating Hormone (FSH) levels control sperm production. Go to: Embryology

Traumatic testicular injury a fracture not to miss! Emergency Medicine Journal
1. Epididimitis Epididimitis adalah kondisi ketika terjadi pembengkakan pada saluran belakang testis yang membawa sperma menuju uretra. Infeksi bakteri atau penyakit menular seksual (PMS) biasanya menjadi penyebab kondisi ini. Epididimitis sering menyerang pria berusia antara 19 hingga 35 tahun. Gejala epididimitis meliputi: Demam ringan
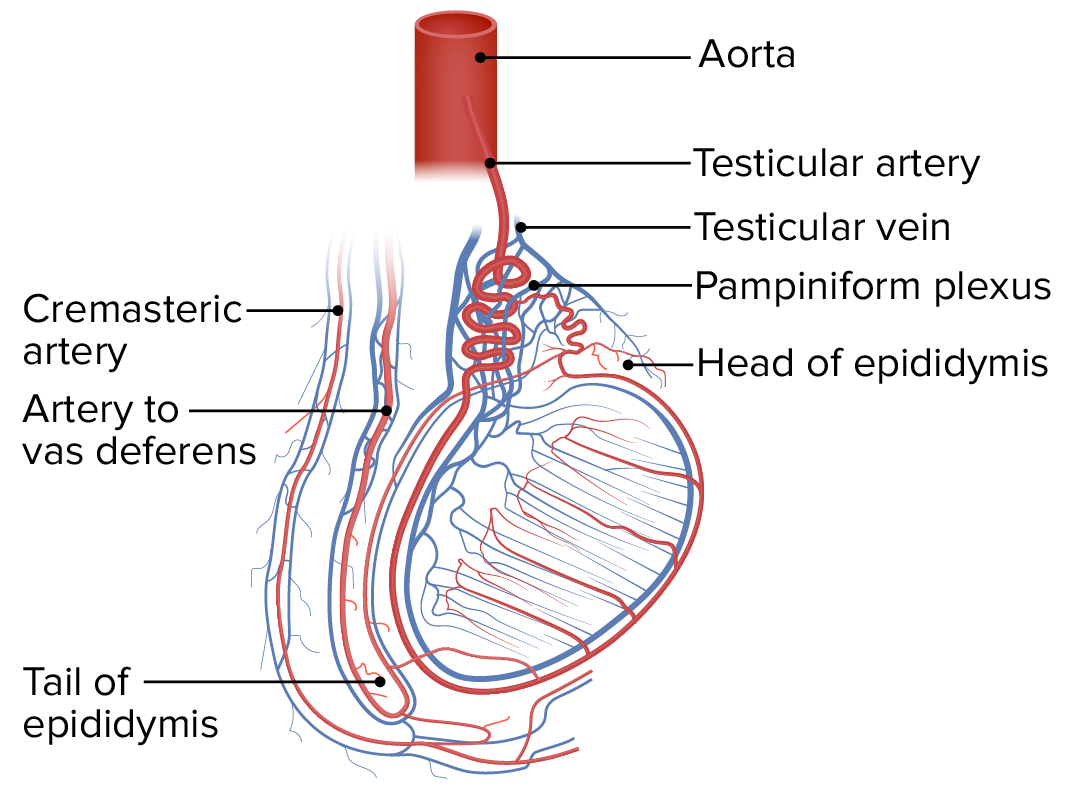
Testículos Anatomía Concise Medical Knowledge
The testes (singular = testis) are the male gonads —that is, the male reproductive organs. They produce both sperm and androgens, such as testosterone, and are active throughout the reproductive lifespan. Paired ovals, adult testes are each approximately 4 to 5 cm in length and are housed within the scrotum (see Figure 27.3 ).
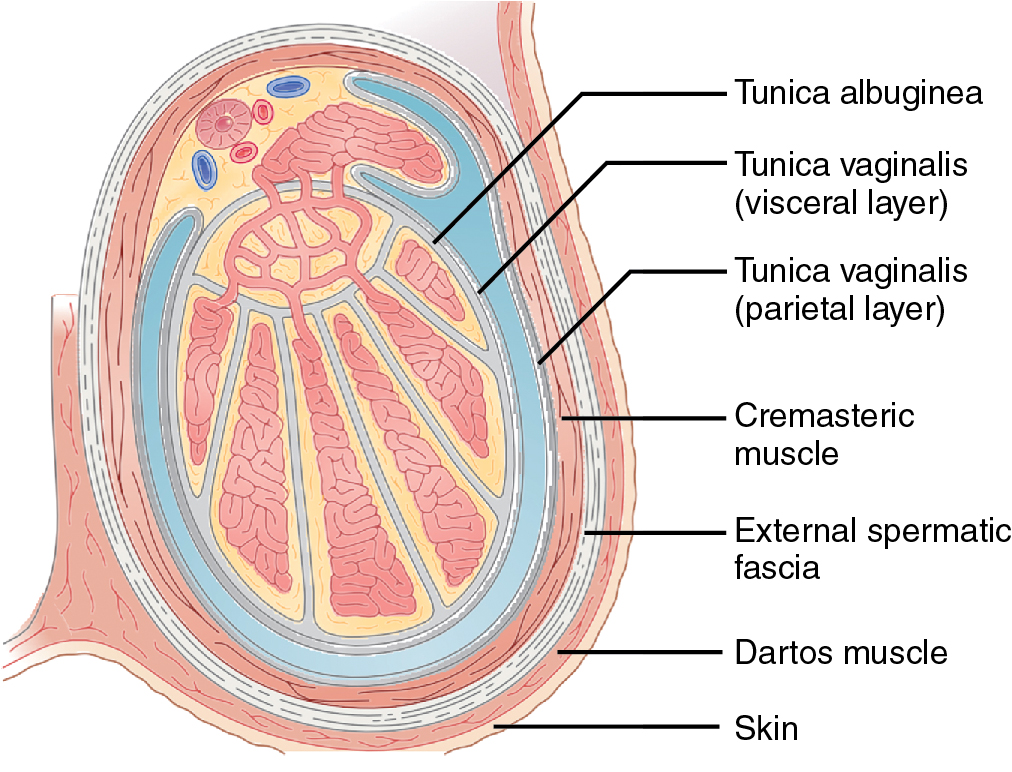
Testicular lesions Radiology Key
Symptoms of epididymitis might include: A swollen, discolored or warm scrotum. Testicle pain and tenderness, usually on one side, that often comes on slowly. Pain when you pass urine. An urgent or frequent need to urinate. Discharge from the penis. Pain or discomfort in the lower abdomen or pelvic area.
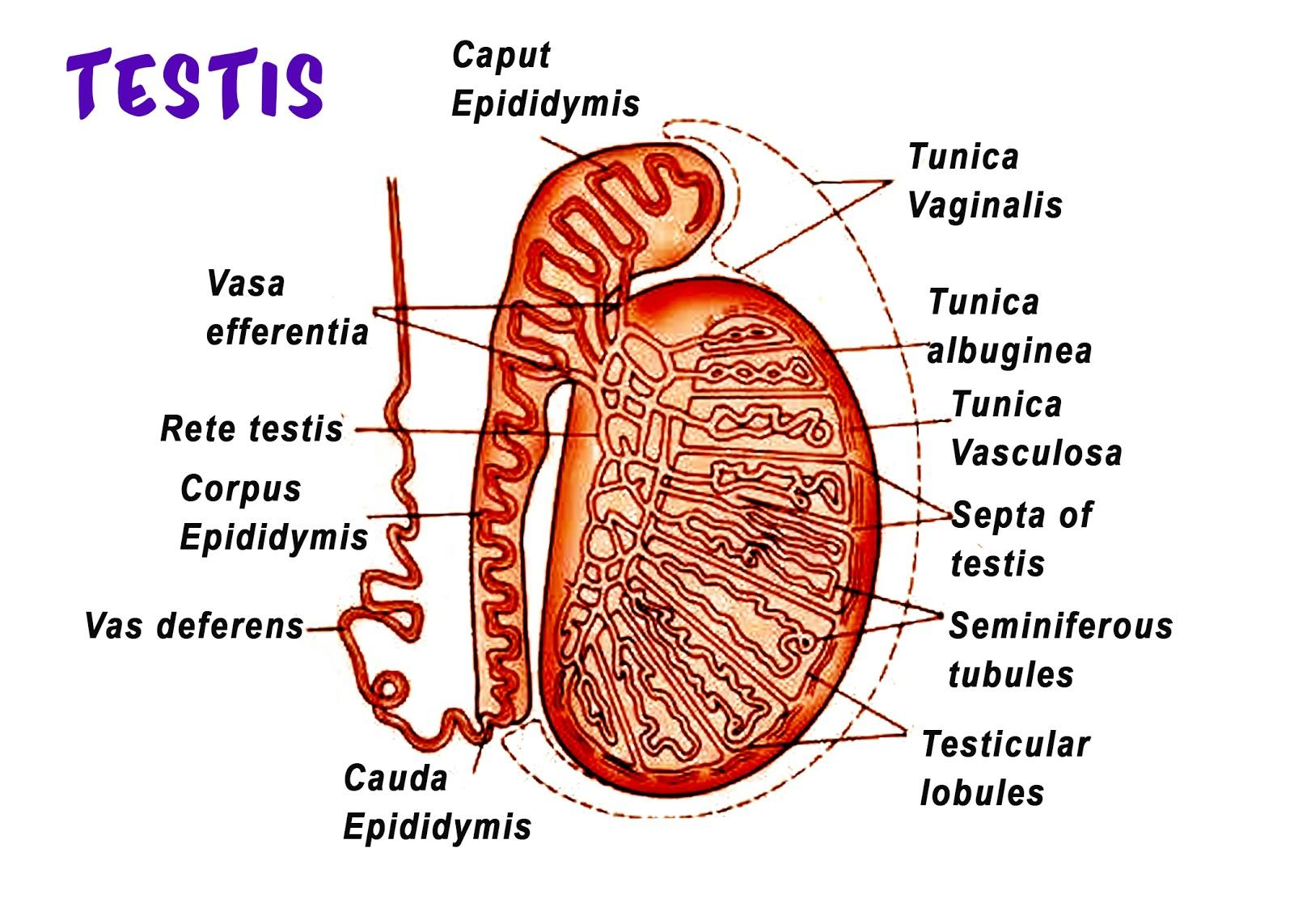
The part of the male reproductive system which connects testis with epididymis is?
Testes (testicles). The testes are 2 small organs that are found inside the scrotum. The testes are responsible for making sperm and are also involved in producing a hormone called testosterone. Testosterone is an important hormone during male development and maturation for developing muscles, deepening the voice, and growing body hair. Epididymis.
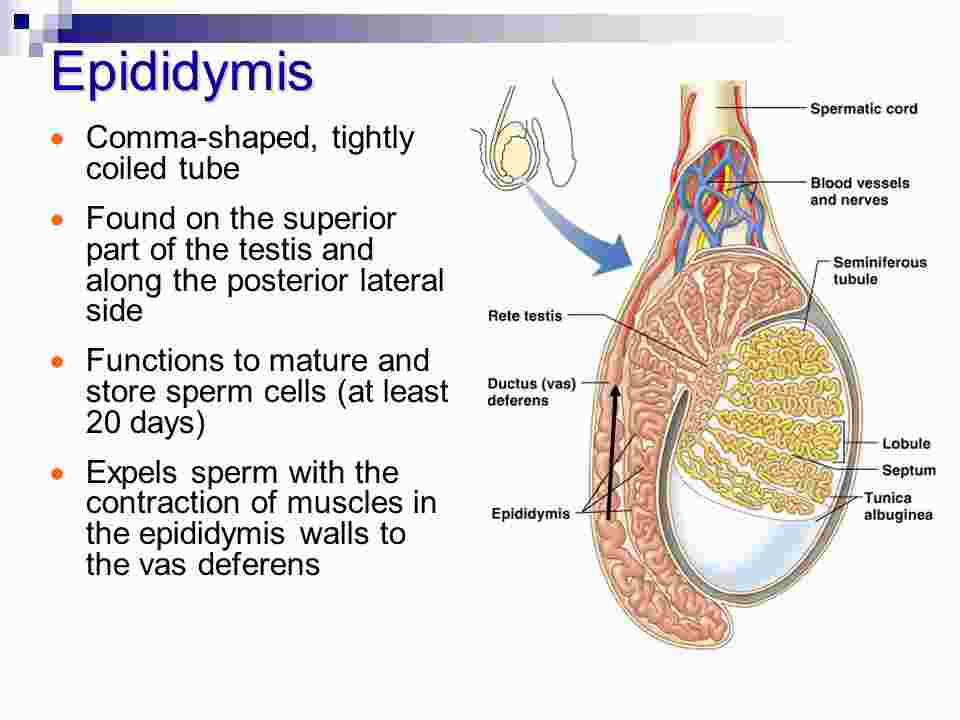
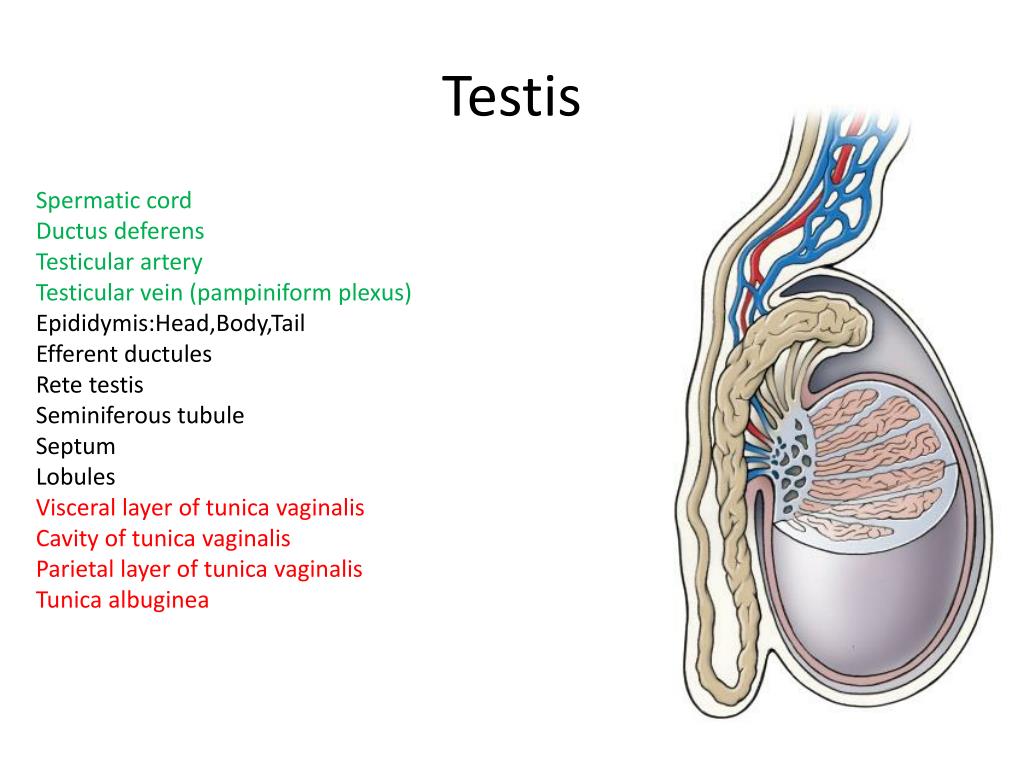
Contents of the scrotum Epididymis, vas deferens, spermatic cord and cremaster muscle
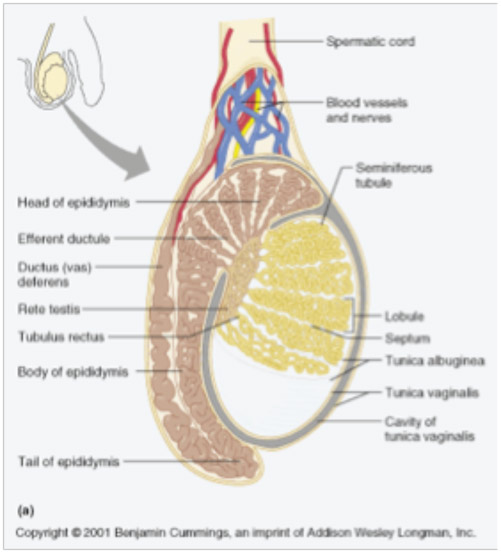
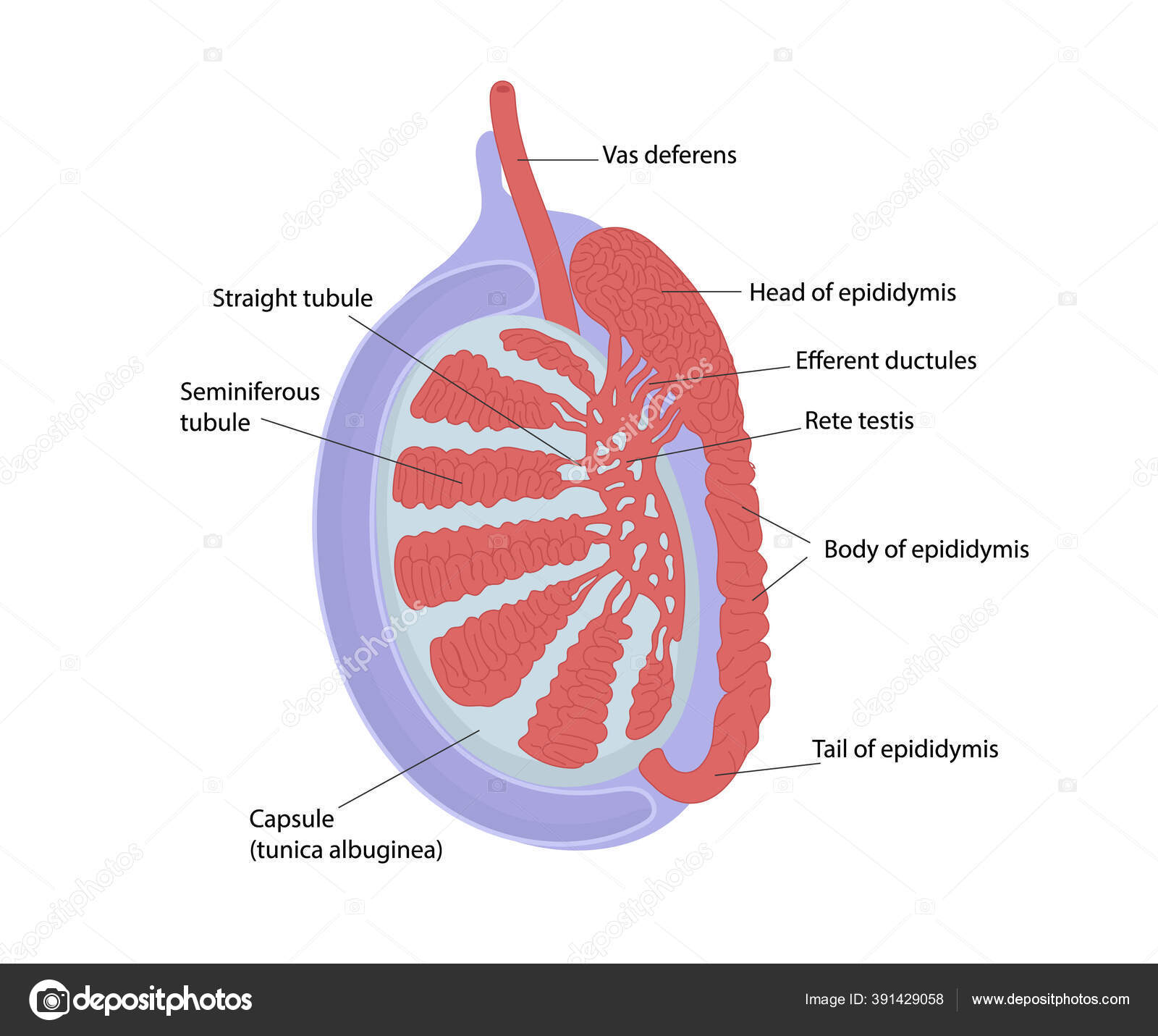
Testicular Anatomy. The human testis is an ovoid mass that lies within the scrotum. The average testicular volume is 20 cc in healthy young men and decreases in elderly men. In Asian men, testes tend to be smaller. Normal longitudinal length of the testis is approximately 4.5 to 5.1 cm. The testicular parenchyma is surrounded by a capsule.
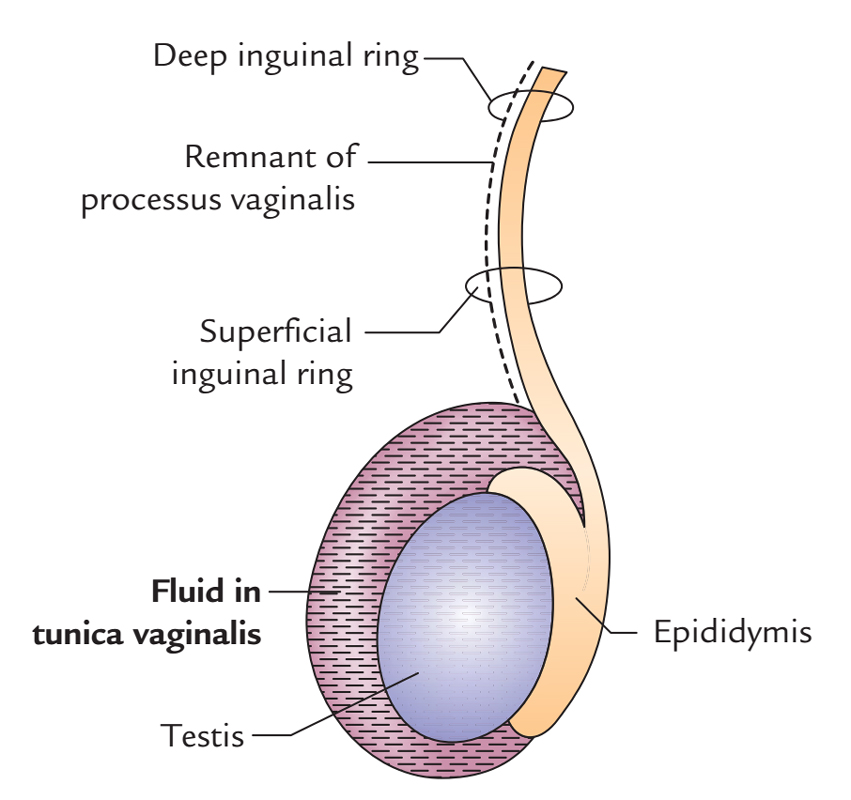
Testis and Epididymis Anatomy Earth's Lab
The testis (from the Greek word orchis) is the male gland important for both reproductive (exocrine) and endocrine functions. [ 1] Initially, it begins as an undifferentiated gonad in the retroperitoneal area. Transcription of the SRY gene (testis-determining factor region) on the Y chromosome ultimately leads to sex differentiation.
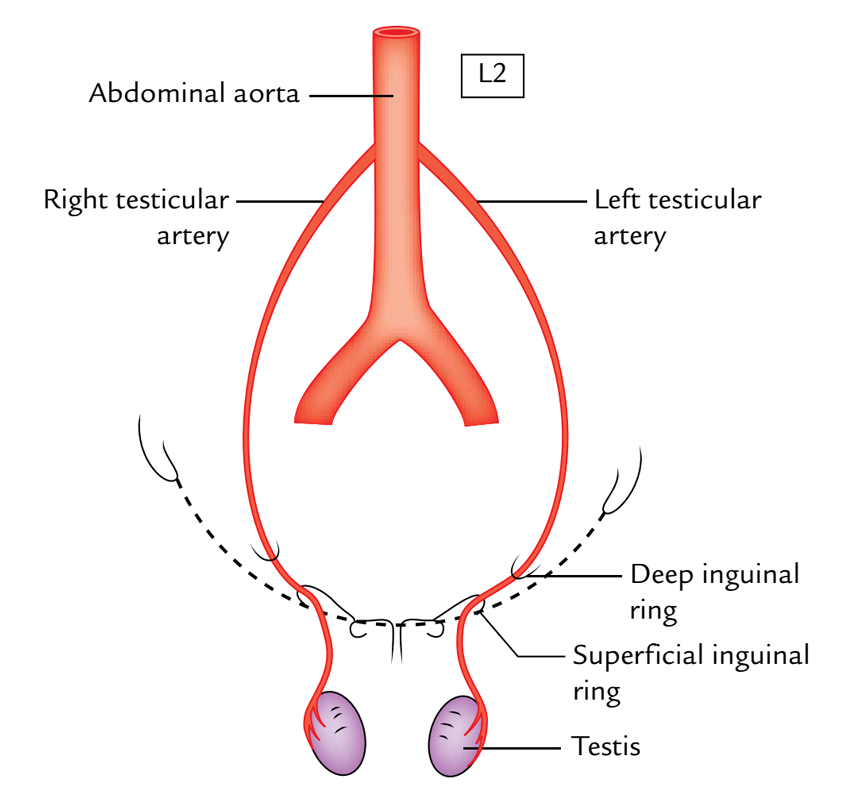
Testis and Epididymis Anatomy Earth's Lab
Beberapa penyakit mungkin juga menyebabkan sensasi bergetar di bawah skrotum, misalnya varikokel (pembengkakan vena testis), hernia skrotalis (turunnya usus ke skrotum melalui celah dinding perut yang melemah), dan banyak lagi kemungkinan lainnya. Masturbasi berlebihan juga bisa membuat area skrotum dan penis Anda terasa bergetar terus menerus.

Gubernaculum testis définition et explications
Pengaruh posisi/postur tubuh. dll. Umumnya selama kondisi ini tidak diiringi dengan gangguan seperti nyeri, gangguan BAK, gangguan ereksi atau gangguan fungsi lainnya, maka seharusnya tidak perlu terlalu dikhawatirkan, sementara ini Anda bisa mencoba: Mencukupi istirahat. Senantiasa menjaga kebersihan organ tubuh.

Organization of the testis. A) A crosssection through a testis,... Download Scientific Diagram
The testes are vital organs for male reproduction and health. Learn about their anatomy, function, and common conditions that affect them, such as testicular cancer, torsion, and infection. Find.

Testis Cross Section Anatomy
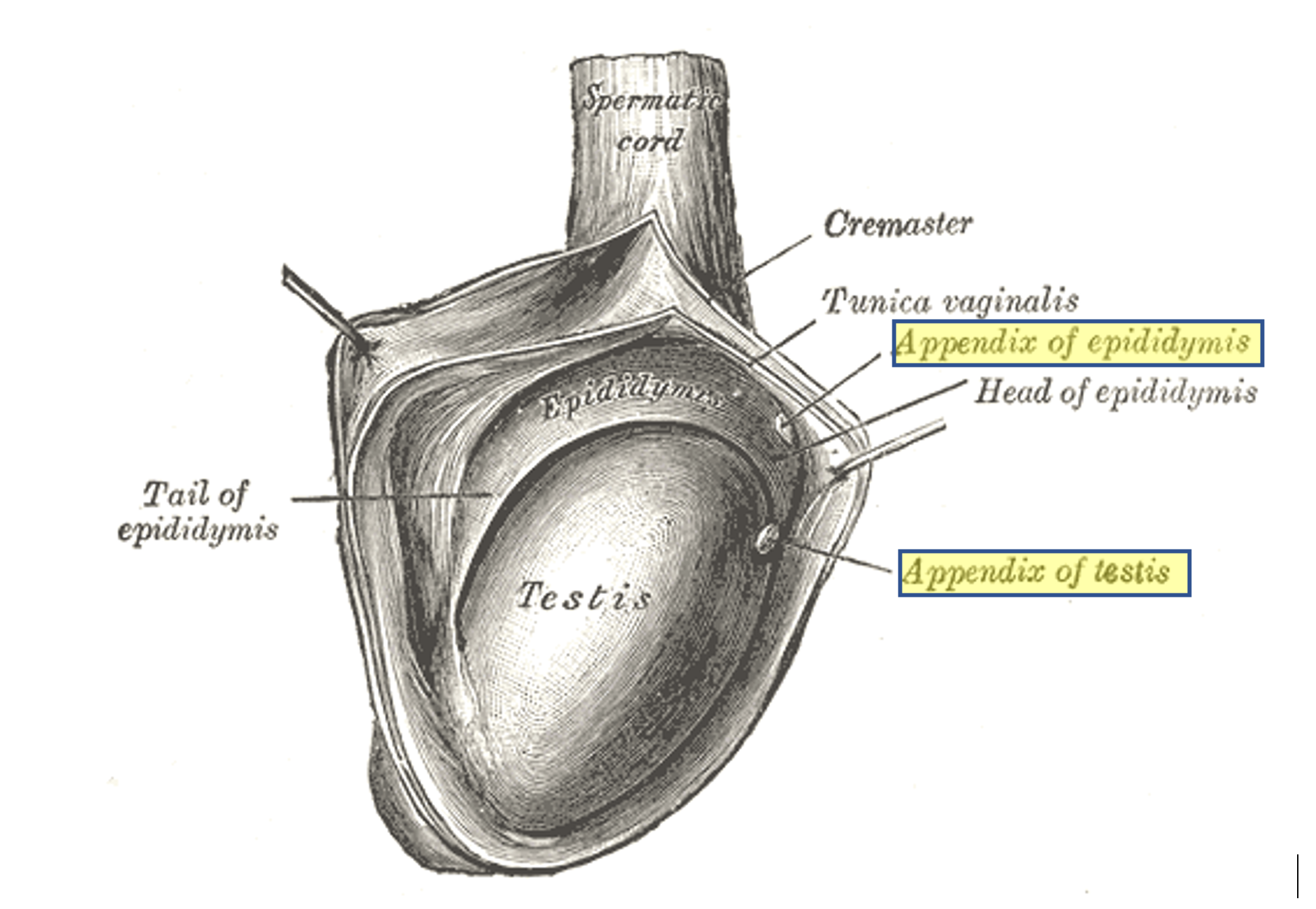
The only potential problem with the hydatid of Morgagni is torsion (twisting). It's a common cause of testicular pain, especially between ages 7 and 12. Appendix testis torsion can cause: Acute (sharp) pain on one testicle. A blue dot visible on the scrotum, due to blood loss to the piece of tissue. Redness.