
List of all Pythagorean Triples where a, b, and c are less than 1,000.
PYTHAGORAS KELAS 8 - PEMBAHASAN TABEL TRIPLE PYTHAGORAS HALAMAN 69 - BUKU PAKET MATEMATIKA KELAS 8 KURIKULUM MERDEKAAyo Menggunakan TeknologiHumam diberikan.
Pythagorean Triples Definition, Formula, Examples
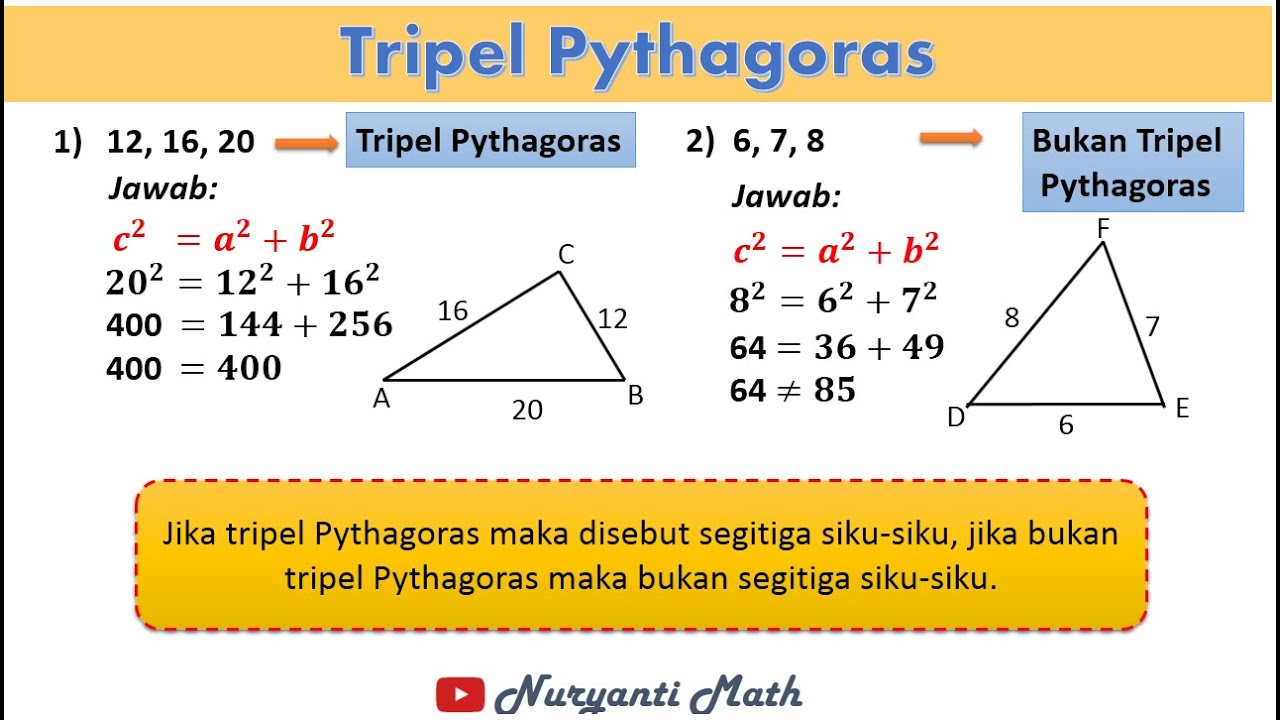
By Pulpent. Triple Pythagoras. Tabel Triple Pythagoras Dan Contoh Soalnya - Pythagoras merupakan sebuah rumus yang berlaku pada segitiga siku-siku. Dimana kuadrat sisi miring sama dengan jumlah kuadrat sisi lainnya. Tiga angka yang membentuk segitiga siku-siku itulah yang dinamakan tripel pythagoras. Segitiga siku-siku memiliki tiga buah sisi.

PPT Pythagorean Triples PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID492892
Tabel Rumus Triple Phytagoras. Rumus Triple Phytagoras. Jika sisi miring pada segitiga siku-siku dituliskan dengan huruf c dan kedua sisi lainnya dituliskan dengan huruf a dan b, maka rumus teorema phytagoras adalah c² = a² + b². Dan berikut merupakan tabel yang berisi beberapa contoh bilangan triple phytagoras. sisi a.

Pythagorean Triples List from 1 to 100 in Maths
Contoh Soal 3. Jika x, 61, 11 merupakan tripel Pythagoras dan 61 bilangan terbesar maka tentukan nilai x. Penyelesaian: 612 = 112 + x2. 3721 = 121 + x2. 3600 = x2. x = √3600. x = 60. Jadi nilai x yang memenuhi adalah 60.

Pythagorean Triples Chart
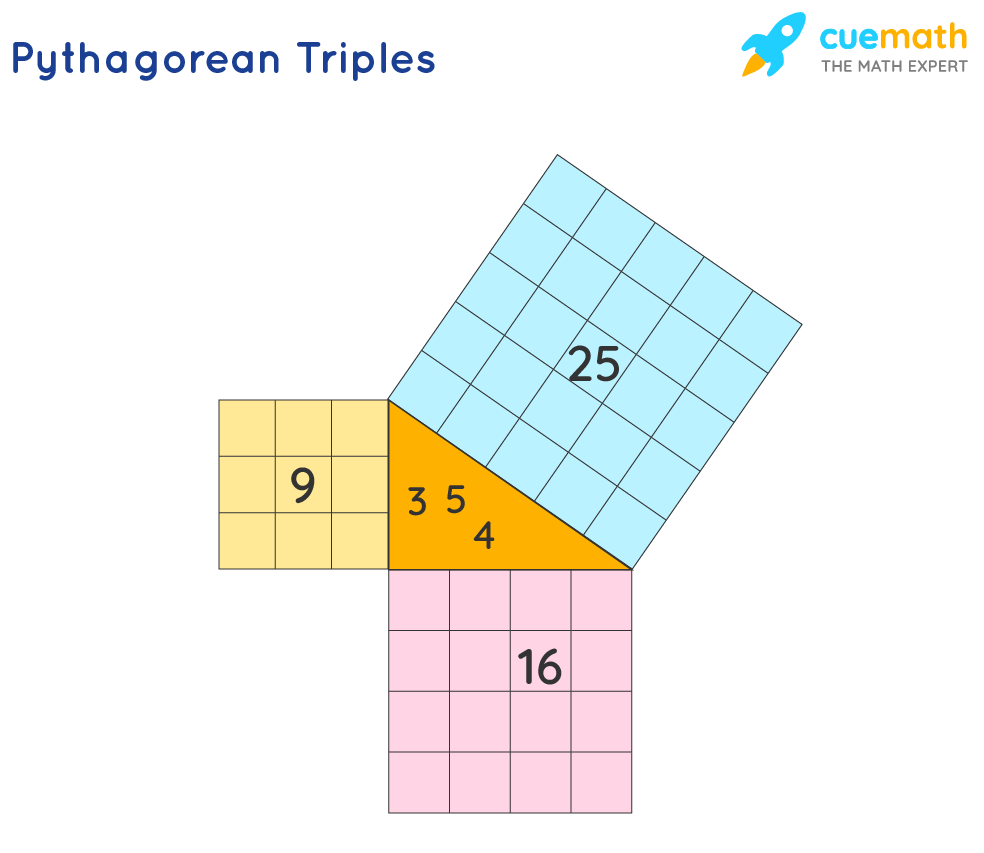
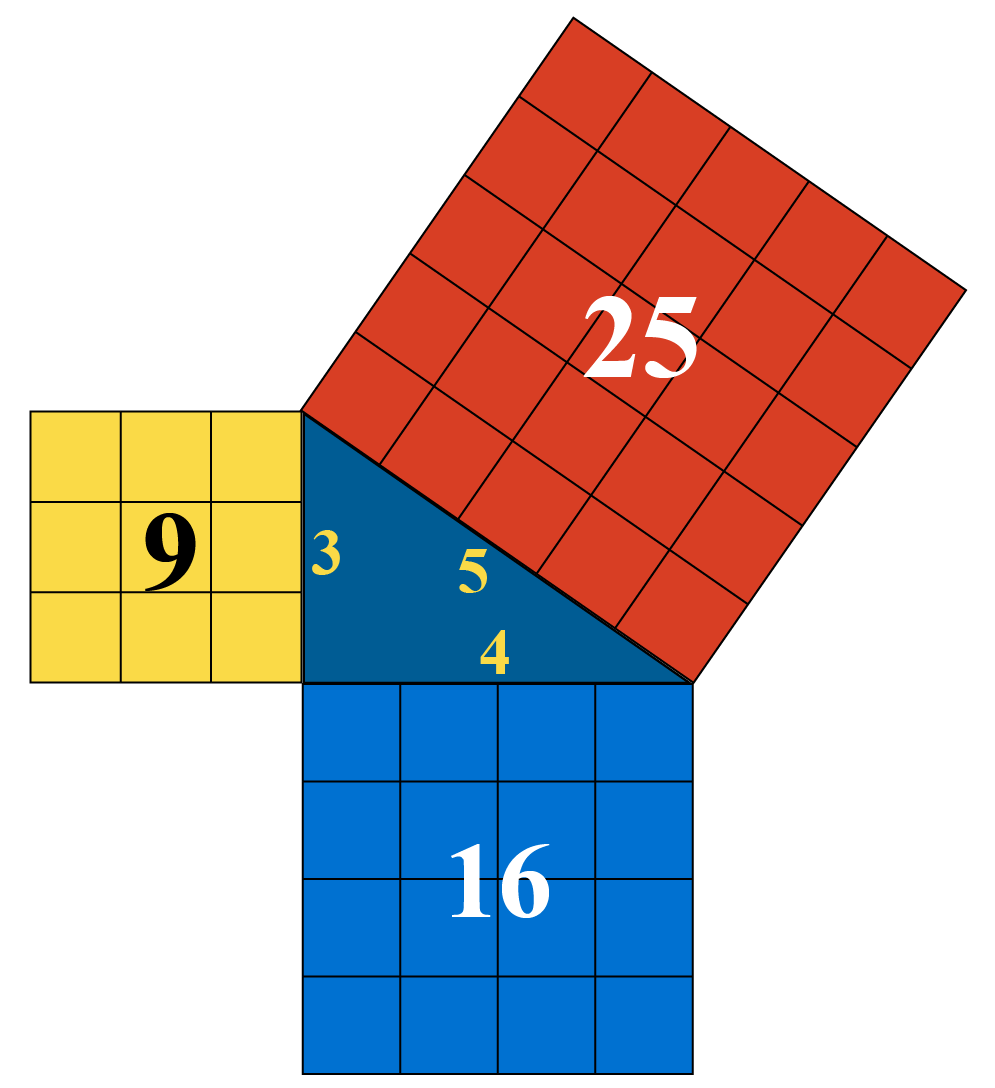
The Pythagorean triple definition says it is a set of three positive integers a, b, c that satisfy the relationship:. a² + b² = c². If you have already learned about the Pythagorean theorem, you surely recognize this formula. Three integers constitute a Pythagorean triple if they are the sides of a right triangle: c is the hypotenuse (the longest side of the triangle), while a and b are the.

Pythagorean Triples Definition, Formula, Examples
Conclusion: Pythagorean triples are sets of three natural numbers that follow the equation a^2 + b^2 = c^2. The theorem is named after Pythagoras because he discovered the formula and it is sometimes called "Pythagoras' Theorem.". The theorem is important in geometry and architecture because it helps us calculate distances and angles.
Pythagorean Triples Definition, Formula & Examples Cuemath
The Pythagorean Triples here are also called Primitive Pythagorean Triples because the Greatest Common Divisor ( GCD) or the Greatest Common Factor ( GCF) of the three positive integers is equal to 1. where the GCD of [latex]a,b,c [/latex] equals [latex]1 [/latex]. It also implies that [latex]a,b [/latex] and [latex]c [/latex] are relatively.
Pythagorean Triples Definition, Formula, Examples
Untuk mencari a dan b pada triple phytagoras, rumusnya dapat dibalik sebagai berikut: a² = c² - b². b² = c² -a². Biasanya, nilai b lebih besar daripada nilai a. Maka secara berurutan, panjang sisi segitiga siku-siku dari yang paling besar ke yang paling kecil adalah c, b, dan a (c > b > a).
Tripel Pythagoras, Menentukan Jenis Segitiga Matematika Kelas 8 SMP/MTs YouTube
A Pythagorean triple consists of three positive integers a, b, and c, such that a2 + b2 = c2. Such a triple is commonly written (a, b, c), and a well-known example is (3, 4, 5). If (a, b, c) is a Pythagorean triple, then so is (ka, kb, kc) for any positive integer k. A triangle whose sides form a Pythagorean triple is called a Pythagorean.
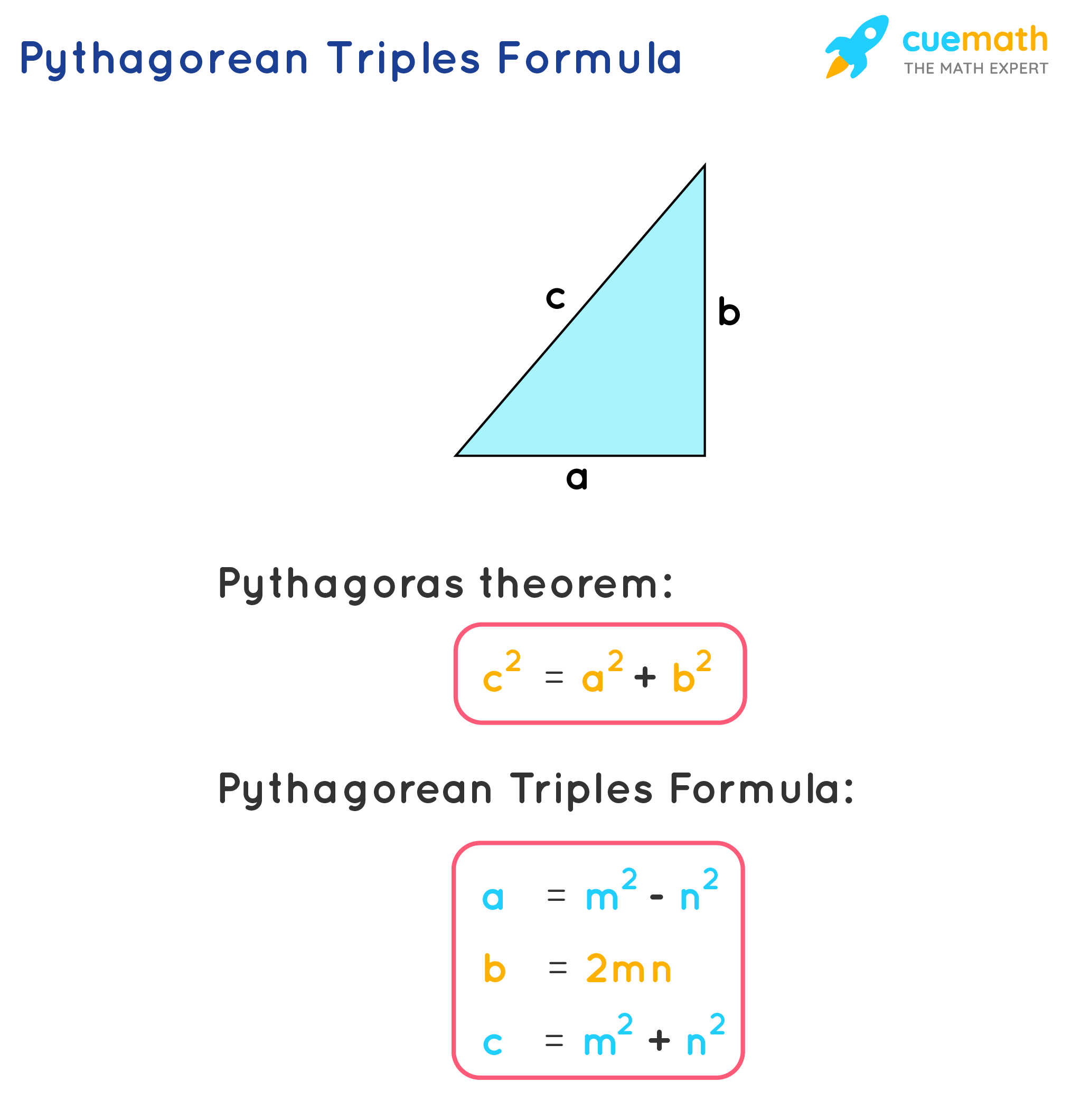
Pythagorean Triples Formula Learn the Formula to Find Pythagorean Triples
A Pythagorean triple is a triple of positive integers a, b, and c such that a right triangle exists with legs a,b and hypotenuse c. By the Pythagorean theorem, this is equivalent to finding positive integers a, b, and c satisfying a^2+b^2=c^2. (1) The smallest and best-known Pythagorean triple is (a,b,c)=(3,4,5). The right triangle having these side lengths is sometimes called the 3, 4, 5.
Triple Pythagorean Triples MooMooMath and Science
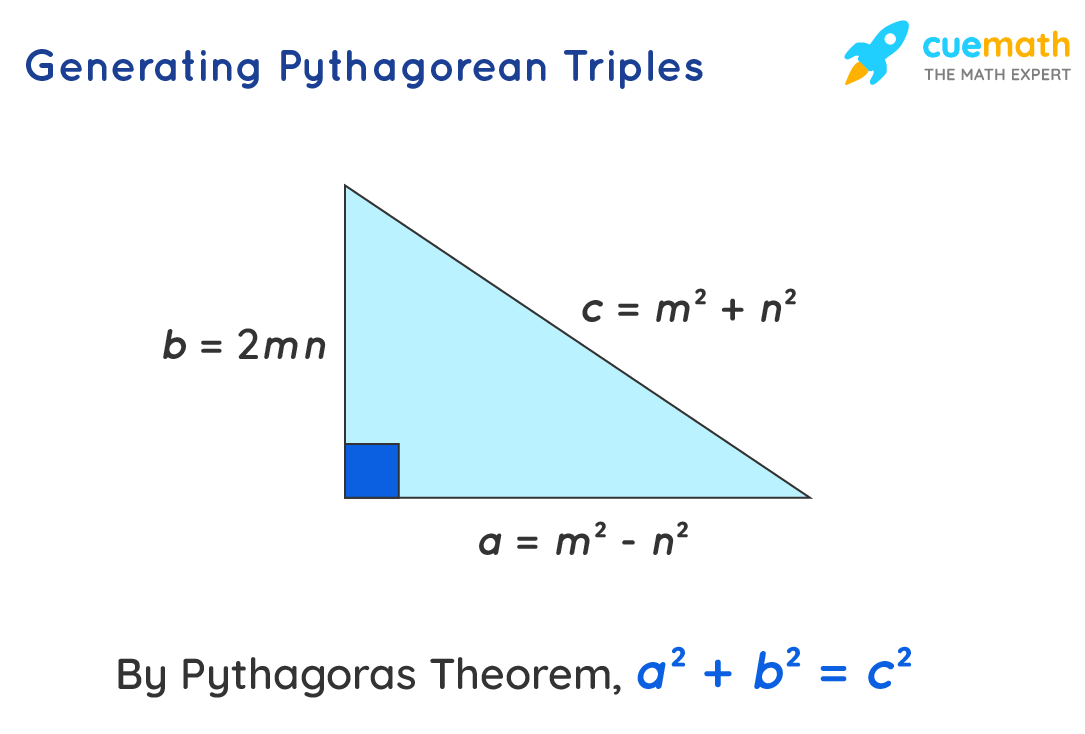
Examples on Pythagorean Triples. Let's look at some examples of how to generate Pythagorean Triples using the formula: Example 1: Choose m = 4 and n = 1: a = 4² - 1² = 16 - 1 = 15. b = 2 × 4 × 1 = 8. c = 4² + 1² = 16 + 1 = 17. The resulting Pythagorean Triple is (15, 8, 17). Example 2:
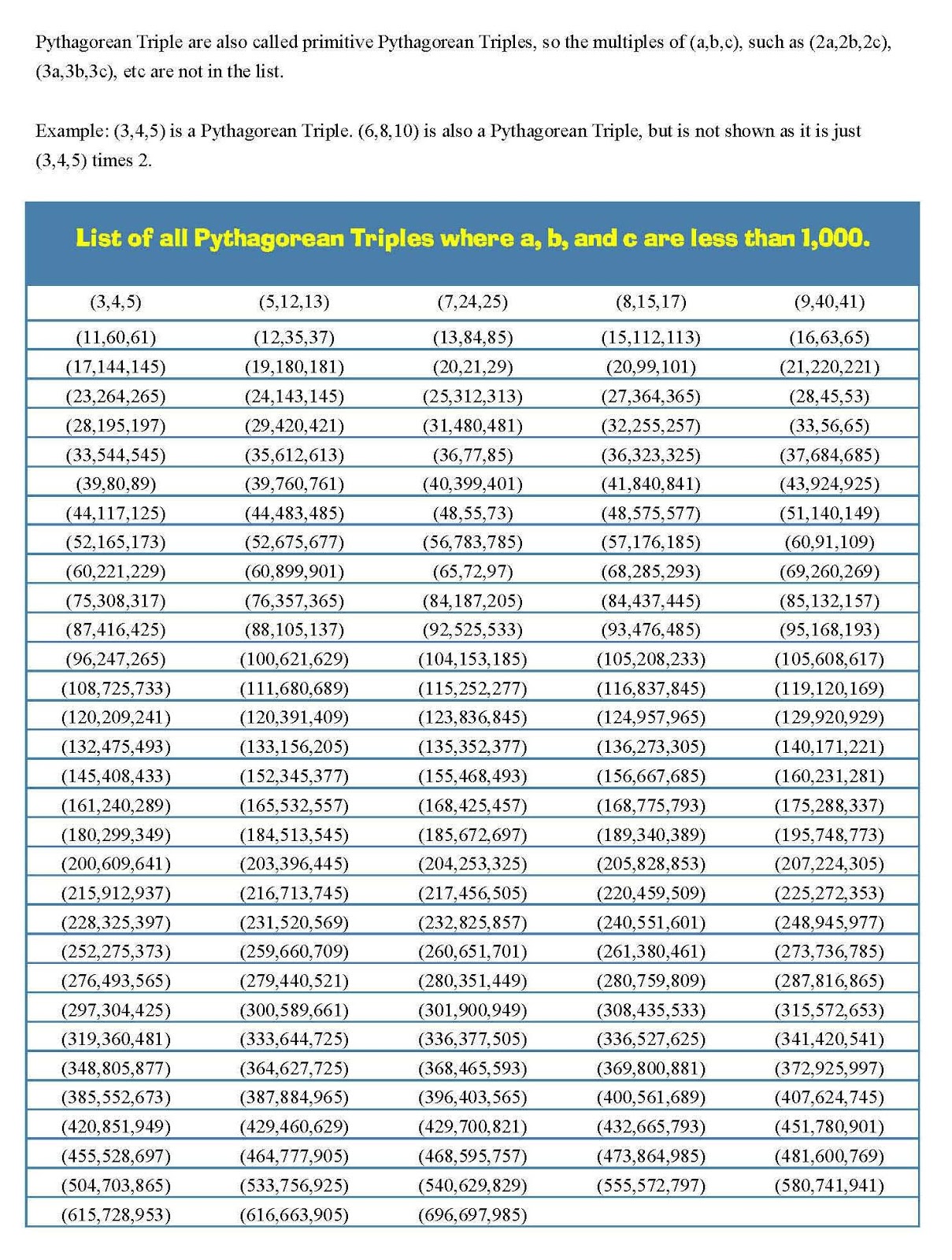
List of all Pythagorean Triples where a, b, and c are less than 1,000.
Pythagorean triples. The most famous example of a Pythagorean triple is the (3, 4, 5) triangle: In this case, the hypotenuse has length 5, and the other two sides have length 3 and 4. 3 squared is 9, 4 squared is 16, which adds up to 25. And, of course, 5 squared is also equal to 25. Another example is the (5, 12, 13) triangle:
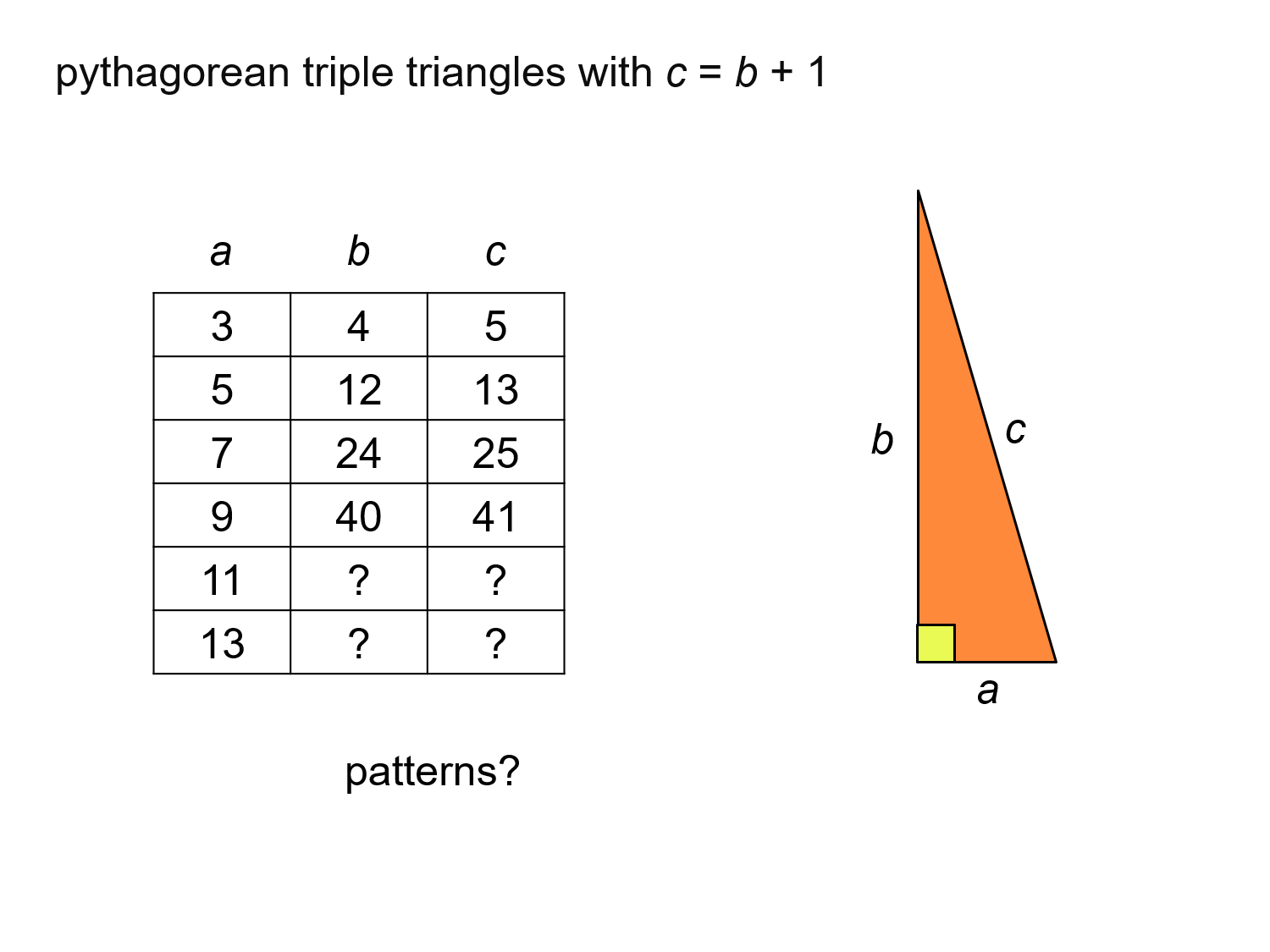
MEDIAN Don Steward mathematics teaching pythagorean triples introduction
Pythagorean Triples. A Pythagorean Triple is a set of three positive integers namely [latex]a, b[/latex] and [latex]c[/latex] that represent the sides of a right triangle such that the equation [latex]{a^2} + {b^2} = {c^2}[/latex] which is based on the Pythagorean Theorem is satisfied.. We can informally describe the equation of a Pythagorean Triple as:.

Pythagorean Triples Definition, Formula & Examples Cuemath
Pythagorean triples are a2+b2 = c2 where a, b and c are the three positive integers. These triples are represented as (a,b,c). Here, a is the perpendicular, b is the base and c is the hypotenuse of the right-angled triangle. The most known and smallest triplets are (3,4,5). Learn Pythagoras theorem for more details.
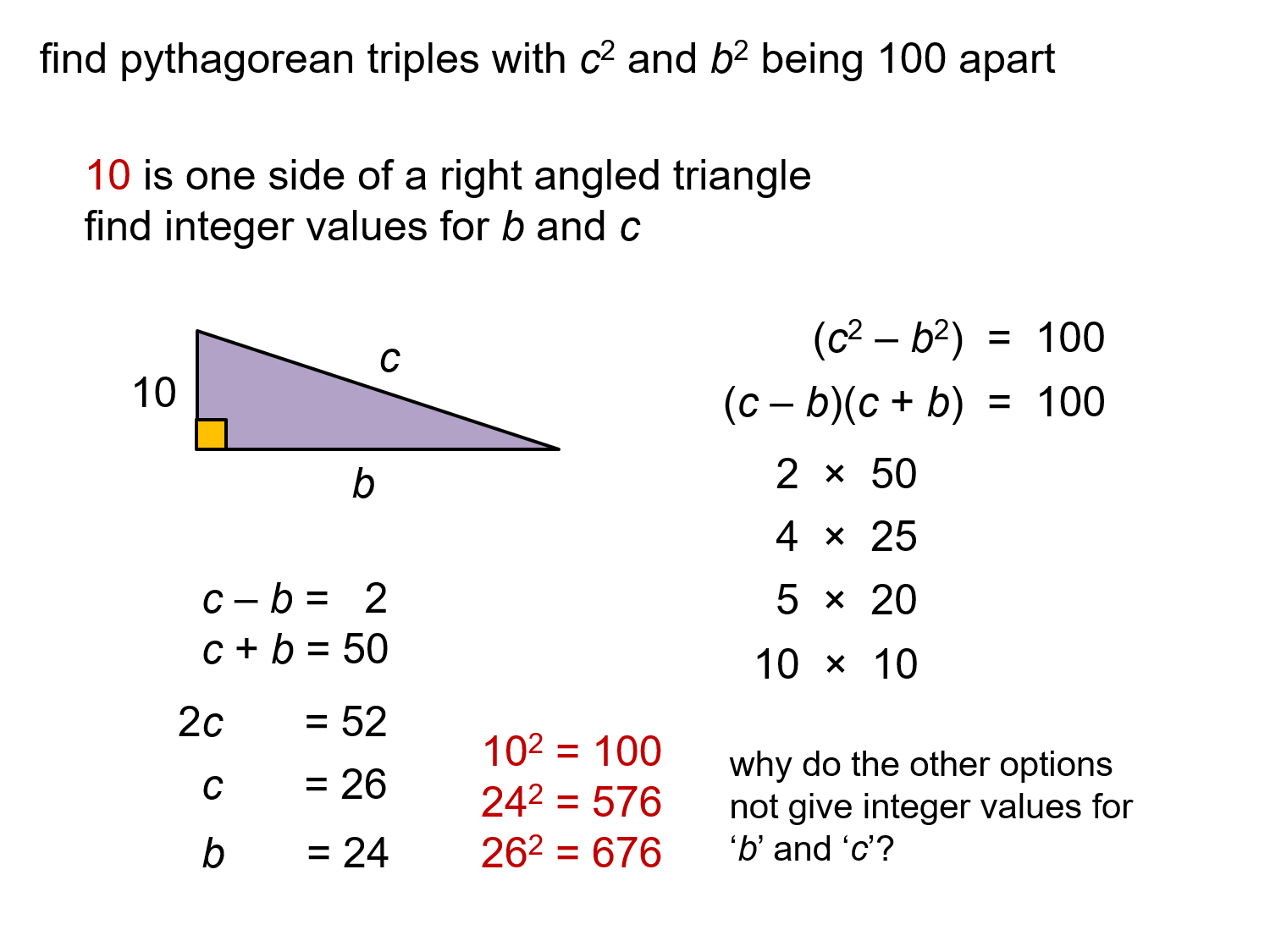
MEDIAN Don Steward mathematics teaching finding pythagorean triples with a property
Pythagorean Triples - Advanced (You may like to read Pythagoras' Theorem and Introduction to Pythagorean Triples first). A "Pythagorean Triple" is a set of positive integers a, b and c that fits the rule:. a 2 + b 2 = c 2. Triangles. And when we make a triangle with sides a, b and c it will be a right angled triangle (see Pythagoras' Theorem for more details):

Tabel Rumus Triple Phytagoras Dan Contoh Soalnya Cilacap Klik
[Chap. 2] Pythagorean Triples 20 We now know that c¡b and c+b have no common factor, and that their prod- uct is a square since (c¡b)(c+b) = a2.The only way that this can happen is if c¡b and c+b are themselves squares.2 So we can write c+b = s2 and c¡b = t2; where s > t ‚ 1 are odd integers with no common factors. Solving these two equations for b and c yields c