Histone Protein Structure
The Trithorax group protein Lid is a trimethyl histone H3K4 demethylase required for dMyc-induced cell growth. Genes Dev. 21 , 537-551 (2007). CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar

Histone H4 Protein Overview Sequence, Structure, Function and Protein Interaction Sino Biological
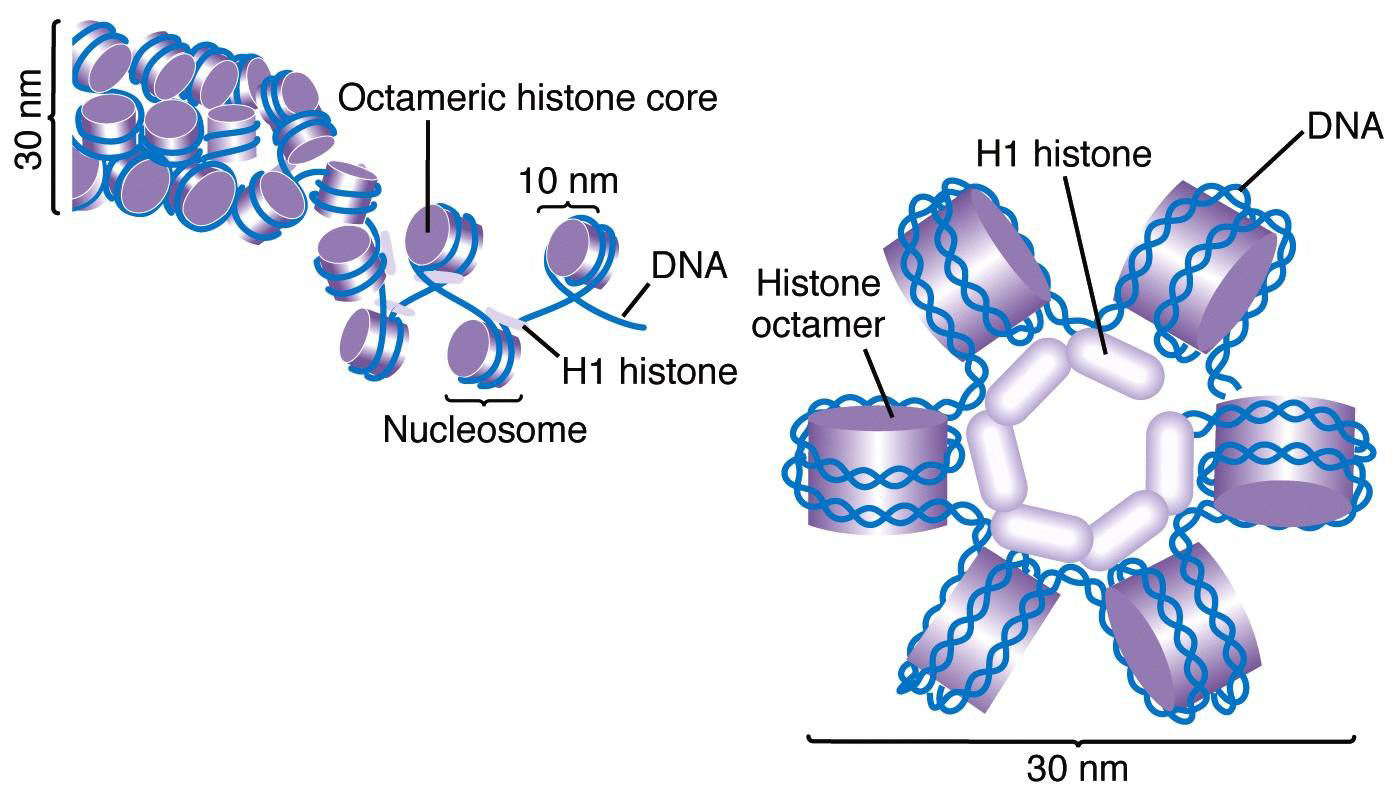
H1 and its homologous protein H5 belong to the linker histone protein family, while H2A, H2B, H3, and H4 are known as core histones. Core histones are the part of the nucleosome; H2A, H2B, H3, and.

Schematic illustration of the roles that histone protein... Download Scientific Diagram
Histone H2A is one of the five main histone proteins involved in the structure of chromatin in eukaryotic cells. The other histone proteins are: H1,. H2A utilizes a protein fold known as the 'histone fold'. The histone fold is a three-helix core domain that is connected by two loops. This connection forms a 'handshake arrangement.'
Histone Protein Structure
Histone protein are of 2 types. Core histone. Linker histone. Core histone- H2A, H2B, H3 & H4. Linker histone- H1 & H5. Each histone protein gathered to create 1 octameric nucleosome core particle and 147 base of DNA wrap around this core particle. H2A is very important for packaging DNA into chromatin. H2A package DNA molecules into chromatin.

Nucleosome structure. Histone proteins bind DNA forming nucleosomes.... Download Scientific
The term "Histone H3" alone is purposely ambiguous in that it does not distinguish between sequence variants or modification state. Histone H3 is an important protein in the emerging field of epigenetics, where its sequence variants and variable modification states are thought to play a role in the dynamic and long term regulation of genes.
Histone Wikipedia
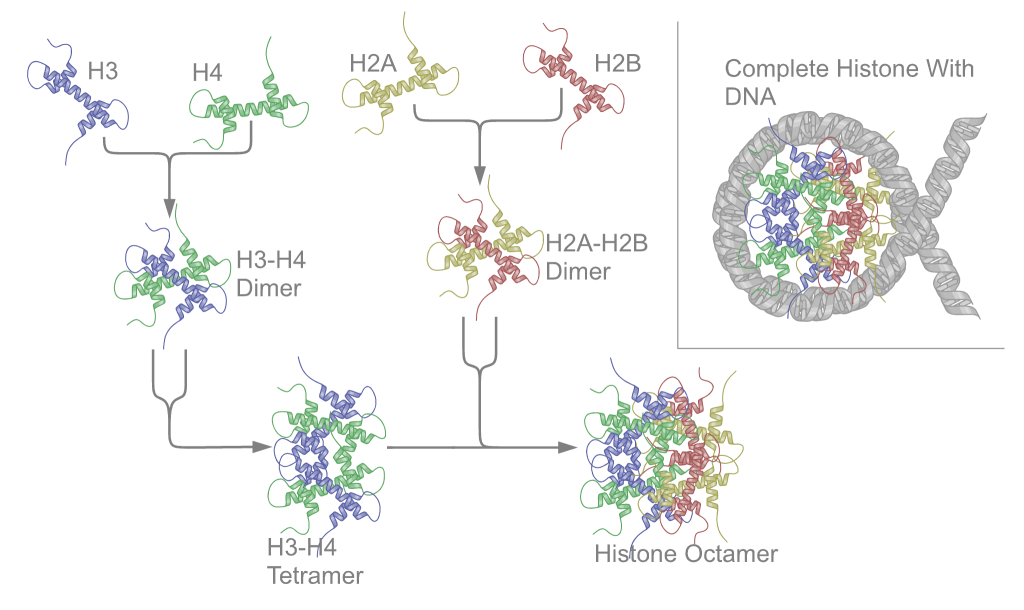
Histone H4 is a 102 to 135 amino acid protein which shares a structural motif, known as the histone fold, formed from three a-helices connected by two loops. Histone proteins H3 and H4 bind to form a H3-H4 dimer, two of these H3-H4 dimers combine to form a tetramer. This tetramer further combines with two H2a-H2b dimers to form the compact.

What Do Histone Proteins Do KWHATDO
Histone methyltransferase G9a promotes the recruitment of heterochromatin protein 1 (HP-1) and inhibits TNF-α expression by catalyzing H3K9 di-methylation of TNF-α promoter in THP-1 macrophages . Another research showed that G9a interacts with the NF-κB transcription factor RelB to induce endotoxin tolerance in macrophages.

Histone dynamics across the cell cycle Histone marks and... Download Scientific Diagram
Histone proteins are the major protein components of chromatin, the physiologically relevant form of the genome (or epigenome) in all eukaryotic cells. Chromatin is the substrate of many.

DNA with histone protein stock illustration. Illustration of biology 4649056
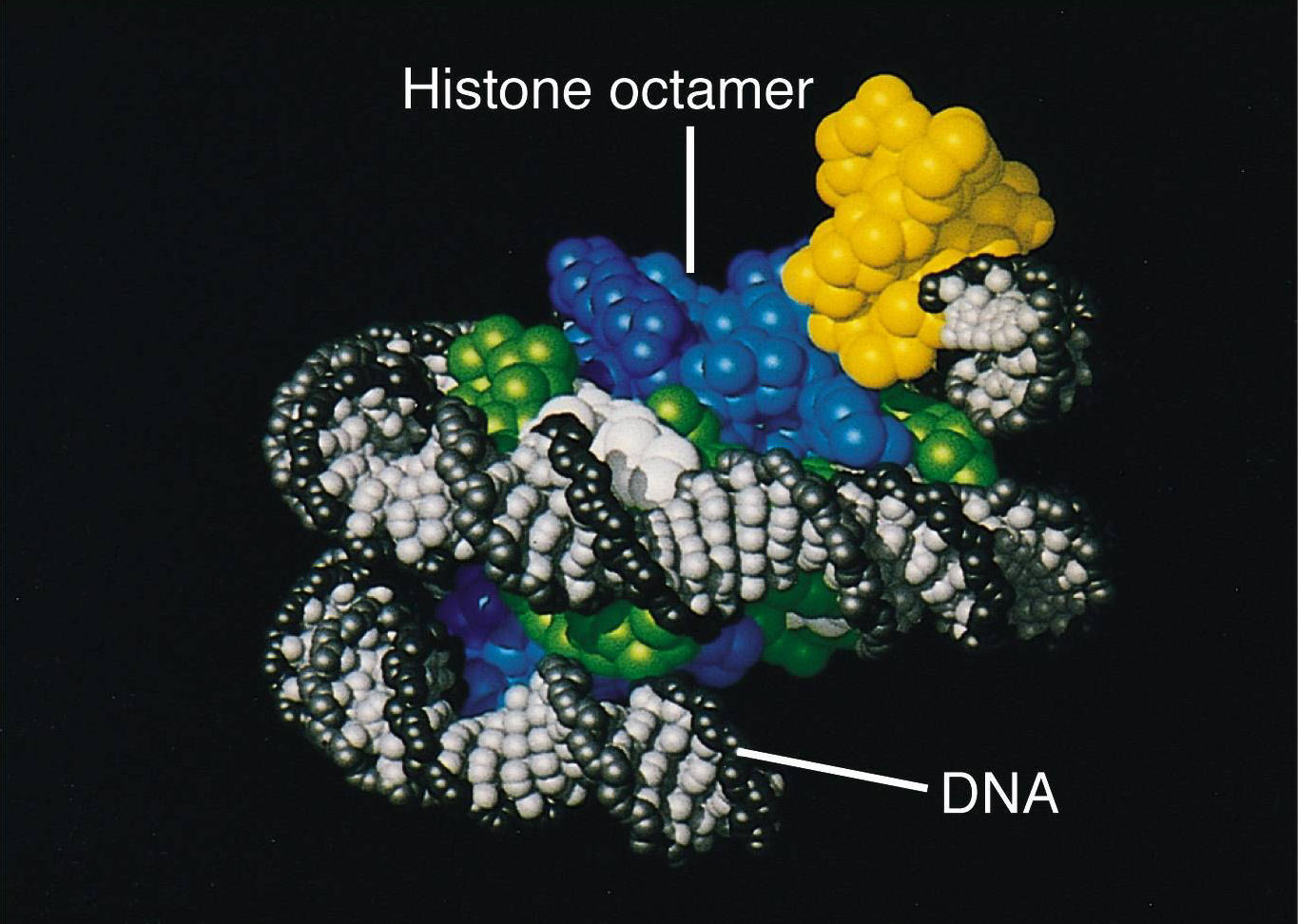
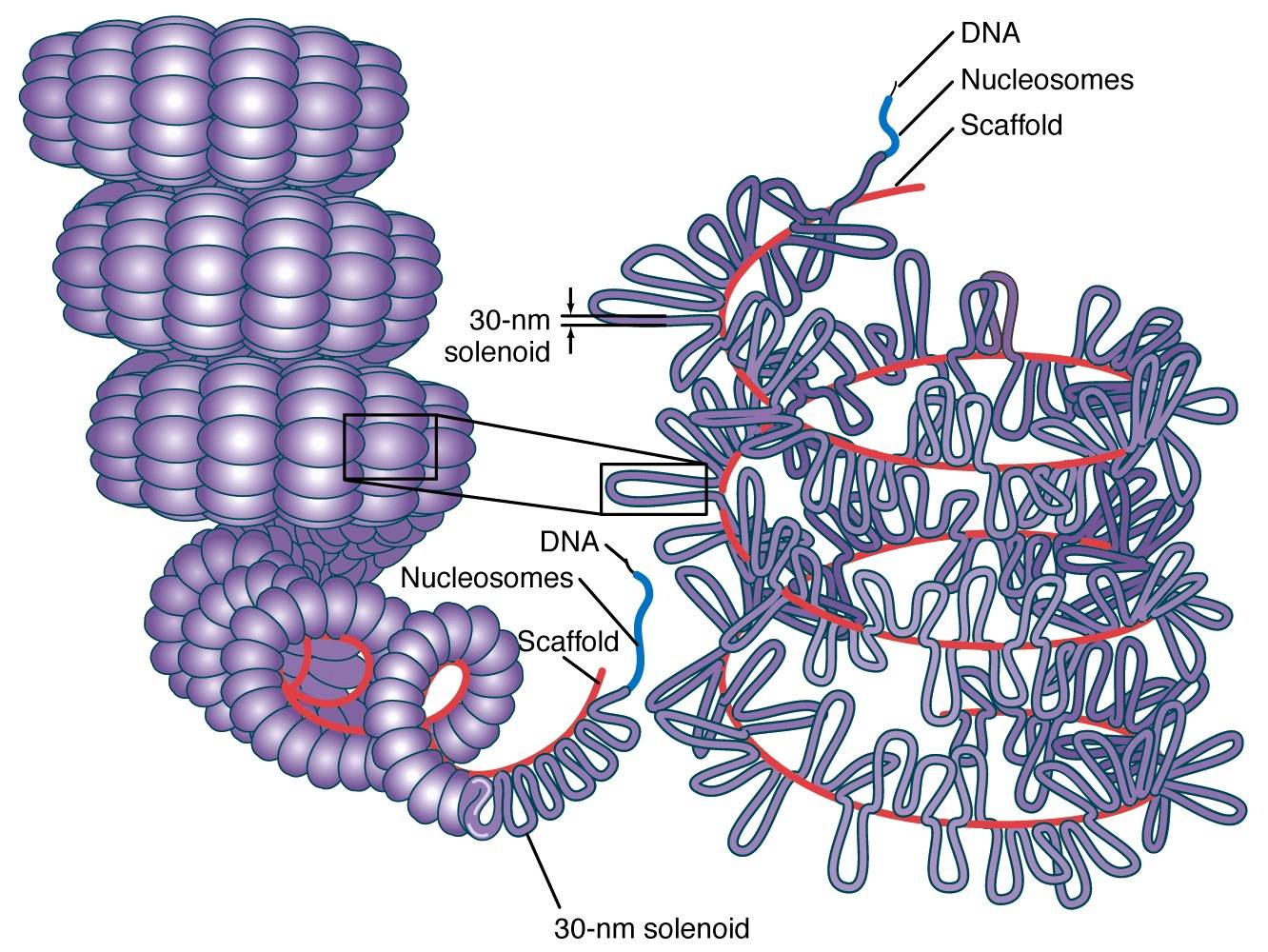
A nucleosome consists of a protein core of basic histone proteins, around which the DNA is wound 1.65 times. The core is an octamer that comprises two copies of each of the canonical histones: H3.
Histone Protein Structure
In addition to core histones, there is also a fifth histone protein called H1, which is involved in the regulation of chromatin structure. Recent studies have shown that histone proteins play a crucial role in gene expression and regulation. Modifications to histone proteins, such as acetylation and methylation, can affect the accessibility of.

Eukaryotic Gene Regulation Biology for Majors I
A protein that is part of the histone family of basic proteins which associate with DNA in the nucleus and help to condense the DNA into a smaller volume.. Each histone octamer is composed of.

1 Chromosomes are made of DNAhistone protein complexes. Chromosomal... Download Scientific
Role of histone citrullination in physiological regulation. Although PAD is considered a transcriptional regulatory protein that affects gene expression, the exact biological function of citrullination remains unclear [].Citrullinated histones account for approximately 10% of all histone molecules in HL-60 granulocytes, highlighting the significance of PTM in many nucleus-related processes [].
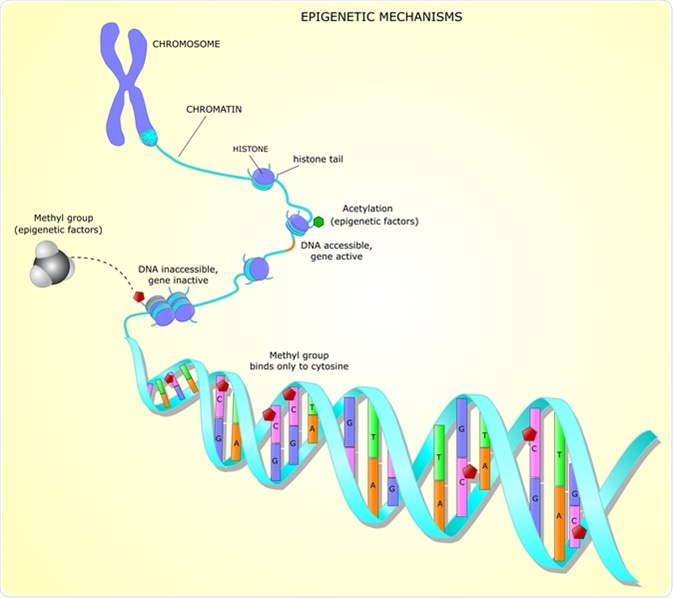
Histones and the Cell Cycle
Nuclear protein Ataxia-Telangiectasia (NPAT), also known as nuclear protein coactivator of histone transcription, is a transcription factor which activates histone gene transcription on chromosomes 1 and 6 of human cells. NPAT is also a substrate of cyclin E-Cdk2, which is required for the transition between G1 phase and S phase.

How Do Histone Proteins Help in the Coiling of DNA
In particular, it discusses three recent examples of structures that illustrate how lysine-methylated histone tails interact with target proteins. The author observes that the recently described interaction modes are more complex than the canonical interaction of a methylated side chain with an aromatic cage in the target protein.

Mapping histone modificationdependent protein interactions with chemical proteomics Trends in
Furthermore, histone modifications provide or remove binding sites for specific protein complexes, including histone-modifying enzymes, chromatin remodeling complexes, and transcription factors.
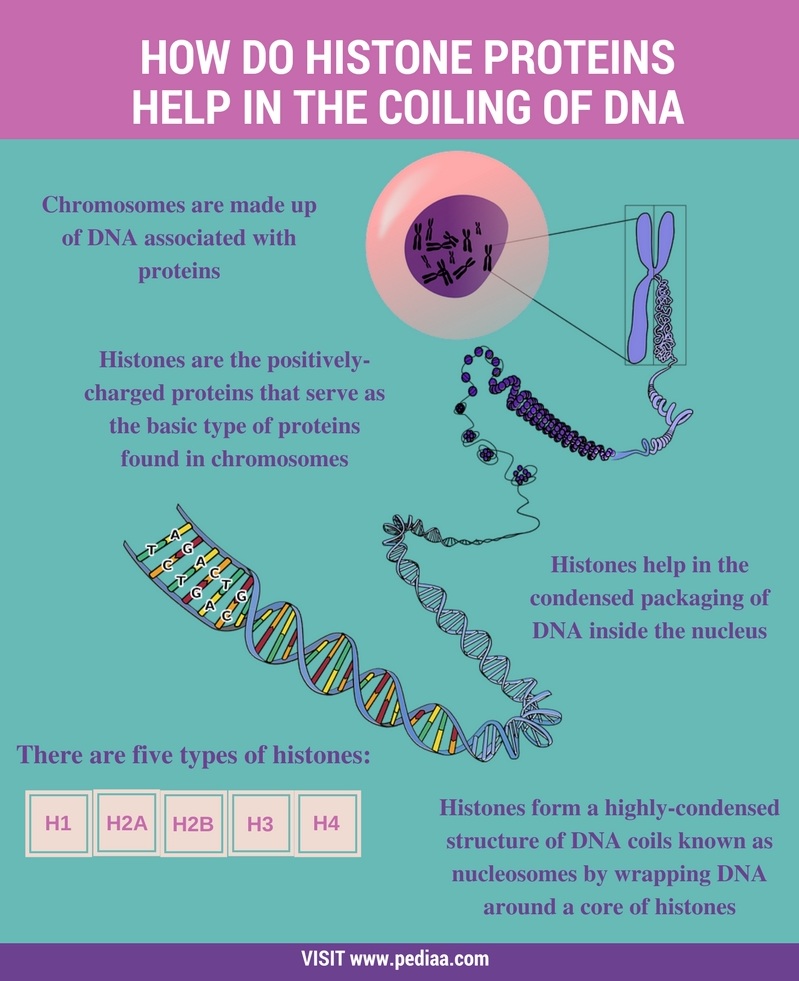
How Do Histone Proteins Help in the Coiling of DNA
Definition. A histone is a protein that provides structural support for a chromosome. Each chromosome contains a long molecule of DNA, which must fit into the cell nucleus. To do that, the DNA wraps around complexes of histone proteins, giving the chromosome a more compact shape. Histones also play a role in the regulation of gene expression.