
PPT Trauma PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID3357625
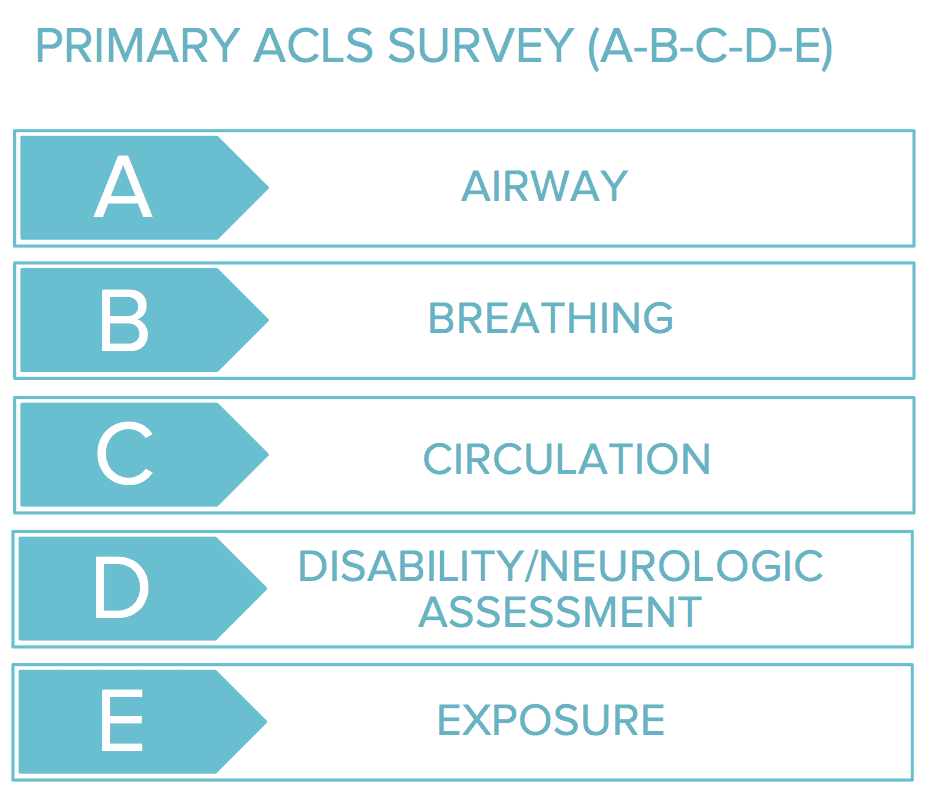
The primary survey is designed to assess and treat any life-threatening injuries quickly. It should be completed very rapidly. The main causes of death in a trauma patient are airway obstruction, respiratory failure, massive hemorrhage, and brain injuries. Therefore, these are the areas targeted during the primary survey. The following are some of, but not all, the specific injuries that may.

Using the ABCDE approach for all critically unwell patients British Journal of Healthcare
Abstract and Figures. Background: The primary survey is the initial assessment and management of a trauma patient. With a systematic method to the immediate assessment and treatment of critically.
Abcde / How to do an abcde assessment when seeing an acutely unwell patient. lembang park zoo
Abstract. Accidents are the primary cause of death in patients aged 45 years or younger. In many countries, Advanced Trauma Life Support® (ATLS®) is the foundation on which trauma care is based. We will summarize the principles and the radiological aspects of the ATLS®, and we will discuss discrepancies with day to day practice and the.

Trauma Primary Survey Abcde Assessments Take Home Points Emergency Medicine Lecturio Images
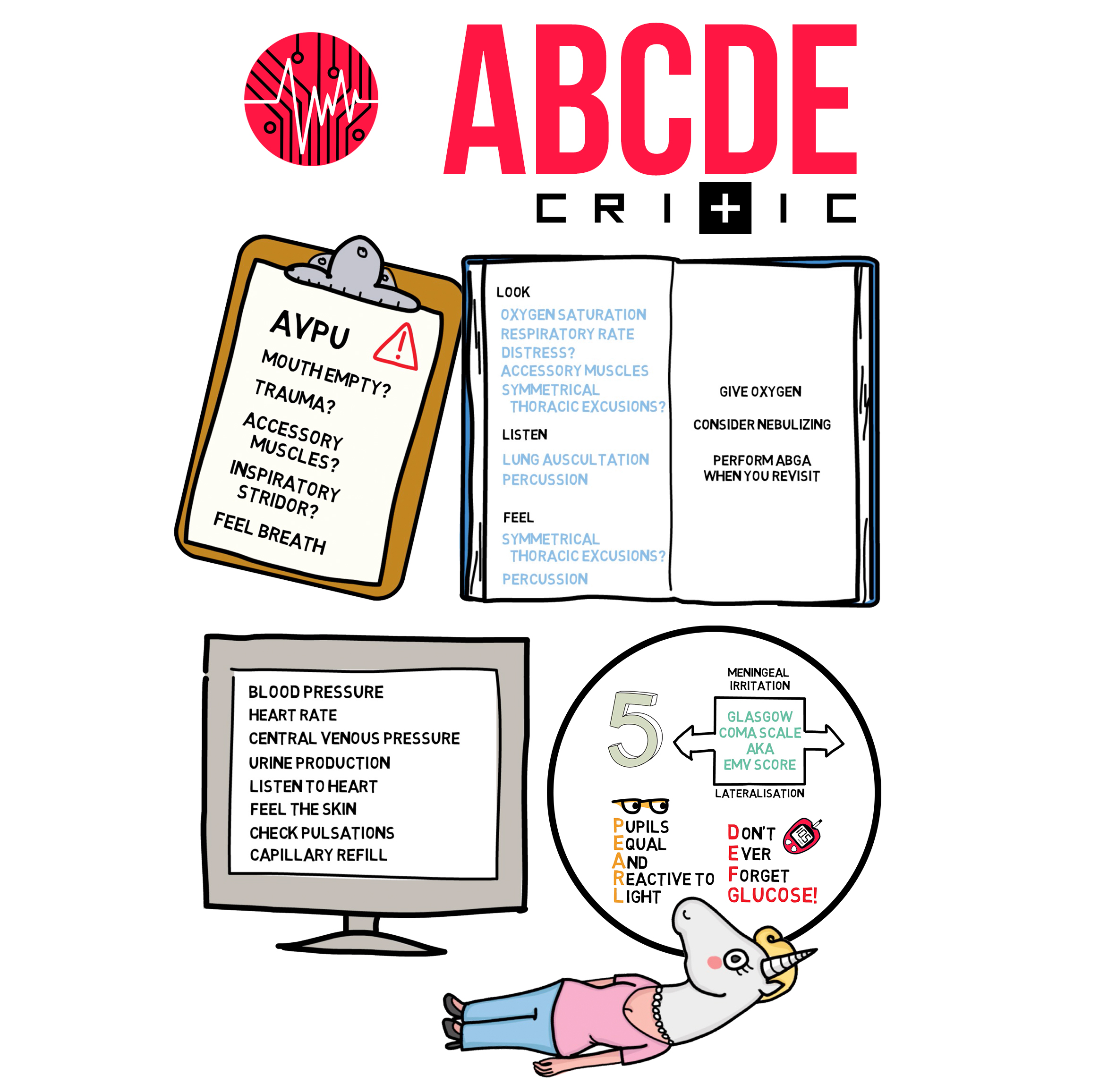
D - Severe head injury - GCS less than or equal to 8, Responds to pain only / Unresponsive (AVPU) D - Impending herniation - Unilateral fixed and dilated pupil, Cushing's triad: ↓HR, ↑BP, irregular respirations • ↑head of bed 30 degrees, head midline • Drug assisted intubation with Manual In-Line Stabilization (MILS), maintain ETCO 35.
Abcde / How to do an abcde assessment when seeing an acutely unwell patient. lembang park zoo
The best immediate treatment for patients with a primary cerebral condition is stabilization of the airway, breathing, and circulation. In particular, when the patient is only pain responsive or unresponsive, airway patency must be ensured, by placing the patient in the recovery position, and summoning personnel qualified to secure the airway.

ACLS Primary Survey (ABCDE) ACLS Training Materials
In almost all medical and surgical emergencies, consider hypovolaemia to be the primary cause of shock, until proven otherwise. Unless there are obvious signs of a cardiac cause, give intravenous fluid to any patient with cool peripheries and a fast heart rate. In surgical patients, rapidly exclude haemorrhage (overt or hidden).

What is ABCDE and why is it important?
Results. Test validation showed a Cronbach's alpha of 0.71 and an expert-novice comparison of 91.9% (standard deviation (SD) 9.1) and 72.4% (15.2) respectively (p < 0.001).Of 954 eligible participants, 240 filled out the questionnaire.
Why you should use an ABCDE approach to patient assessment Medcast
Open the airway by placing one hand on the forehead to tilt the head back and use two fingers from the other hand to lift the chin. If they are unresponsive, you need to move on to breathing as quickly as possible. Breathing. You now need to check if the casualty is breathing normally. Place your ear above their mouth, looking down their body.

The ABCDE approach with important assessment points and examples of... Download Table
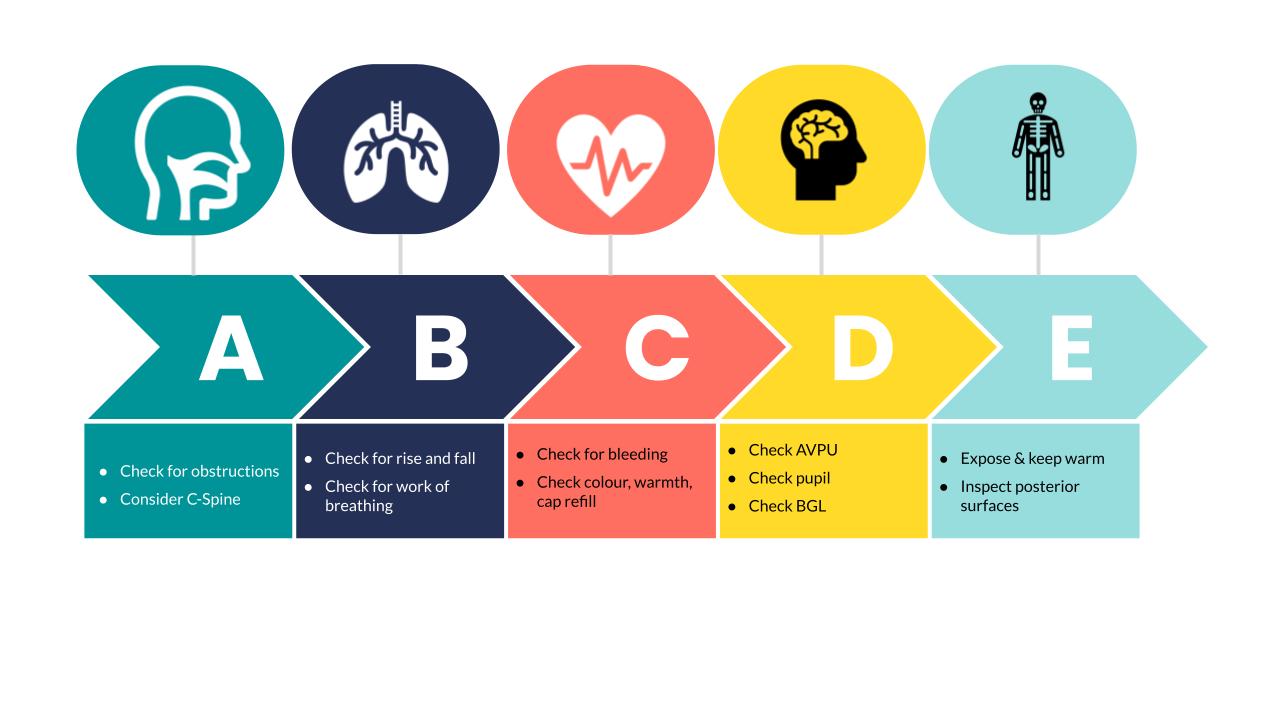
Removal of the patient' clothes is encouraged so that they can be fully assessed. Oxygen should be applied to achieve saturation of 94-98%. The primary survey of a trauma patient involves: A irway - with cervical spine control. B reathing. C irculation including control of exsanguinating external haemorrhage. D isability.

Table 5 from The ABCDE primary assessment in the emergency department in medically ill patients
The primary survey was made to assess patients and address life-threatening injuries rapidly. While not perfect, it addresses the most common and immediate causes of death within 5 areas. These causes include: Airway obstruction. Pneumothorax. Massive hemorrhage, both internal and external. Flail chest.

PPT The approach to the critically ill patient PowerPoint Presentation ID5330424
Initial steps Introduction. Introduce yourself to the team, including your name and role.. In practice, there is usually a team leader who is separate from the doctor carrying out the primary survey. In an OSCE scenario, you may be fulfilling both roles. If feasible, it is sensible to have a team brief before the arrival of a trauma patient, where everyone introduces themselves, makes an.

Pediatric Trauma Primary Survey CABCDE C Catastrophic GrepMed
The goal of this work is to develop a comprehensive process model for the primary survey in trauma that can support ABSM. Methods: A process model for the primary survey of patients with blunt traumatic injuries was developed using Advanced Trauma Life Support guidelines and peer-reviewed publications. This model was then validated using video.

ABCDE ATLS PDF
Circulation (C) If no pulse call cardiac arrest team Look: for pallor, cyanosis, distended neck veins; Feel: for a central pulse (carotid/femoral) rate and rhythm; check for capillary refill time

ABCDE trauma Assessment Primary Survey in emergency setting Emergency Medicine YouTube
Performed after the primary survey Primary Survey Thoracic Trauma in Children and initial stabilization are completed; Examine patient from head to toe, including all orifices (ears, nose Nose The nose is the human body's primary organ of smell and functions as part of the upper respiratory system. The nose may be best known for inhaling.

ABCs of Emergency Response Understanding the Primary Survey Process YouTube
Re-assess the patient after any intervention. Assess the patient's airway. Head-tilt & chin-lift (1/2) Head-tilt & chin-lift (2/2) Jaw thrust step 1: Place two fingers under the angle of the mandible (on both sides) and anchor your thumbs on the patient's cheek. Jaw thrust step 2: Lift the mandible forwards.

How To Assess a Deteriorating Patient (ABCDE Assessment)
Visit the post for more. 10 The primary survey Principles of rapid initial assessment. The primary survey forms the rapid initial assessment of the acutely unwell patient in any context, and in the case of major trauma is directed exclusively at identifying and treating immediately life-threatening injuries.