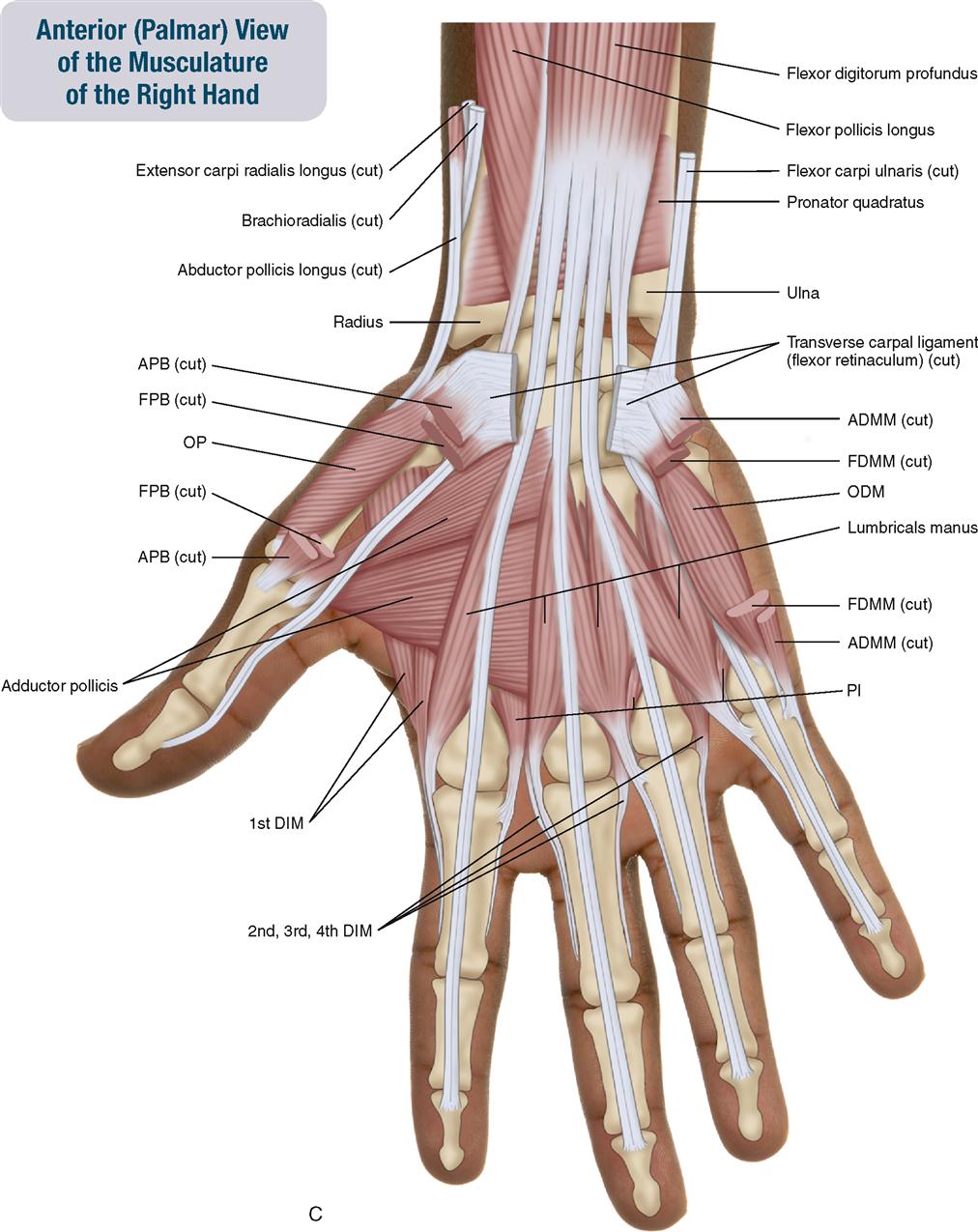
7. Muscles of the Forearm and Hand Musculoskeletal Key
The manus (Latin for hand, plural manus) is the zoological term for the distal portion of the fore limb of an animal. In tetrapods, it is the part of the pentadactyl limb that includes the metacarpals and digits (phalanges). During evolution, it has taken many forms and served a variety of functions. It can be represented by the hand of primates, the lower front limb of hoofed animals or the.
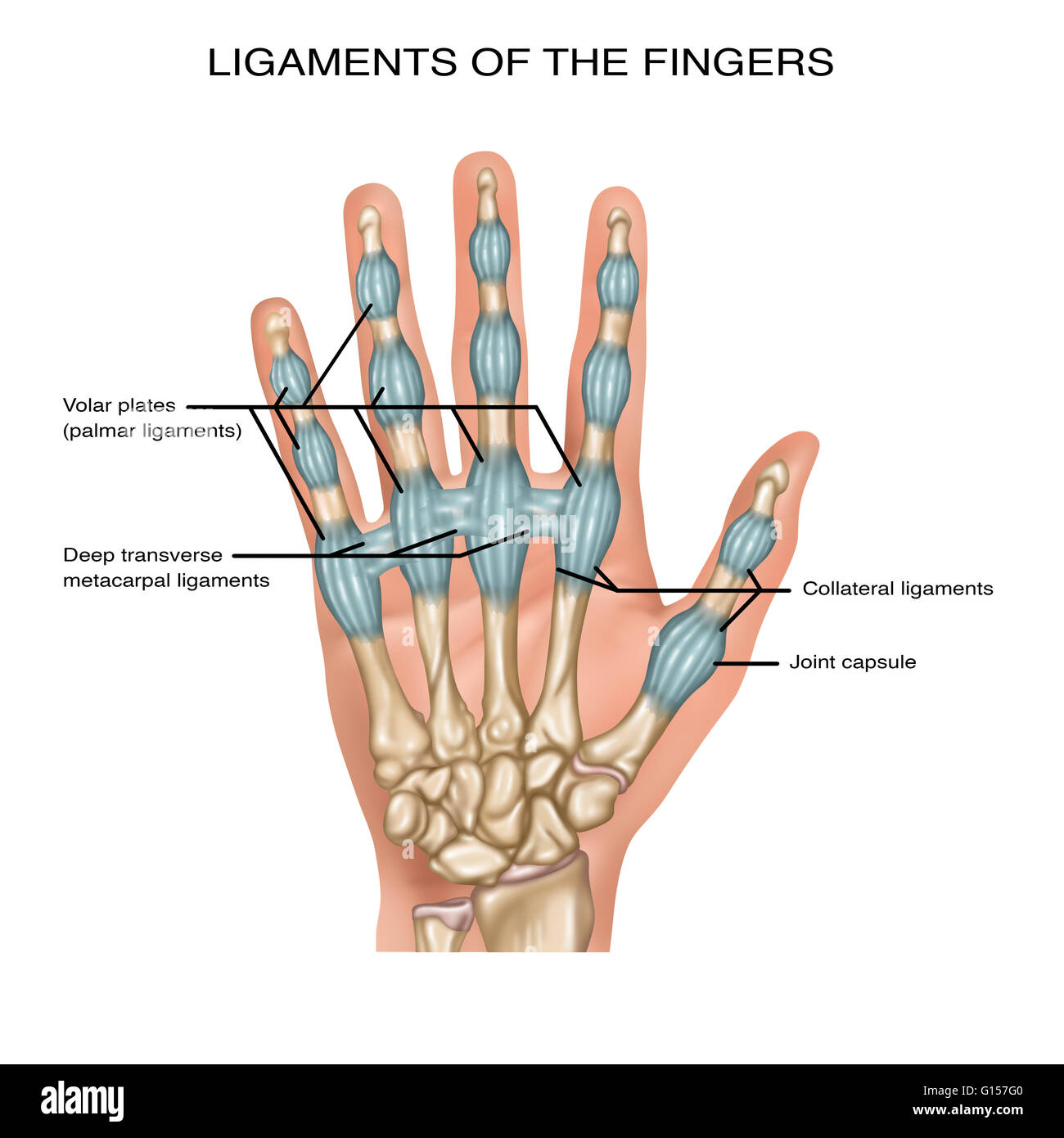
Illustration showing ligaments of the fingers. Noted are the volar plates (palmar ligaments
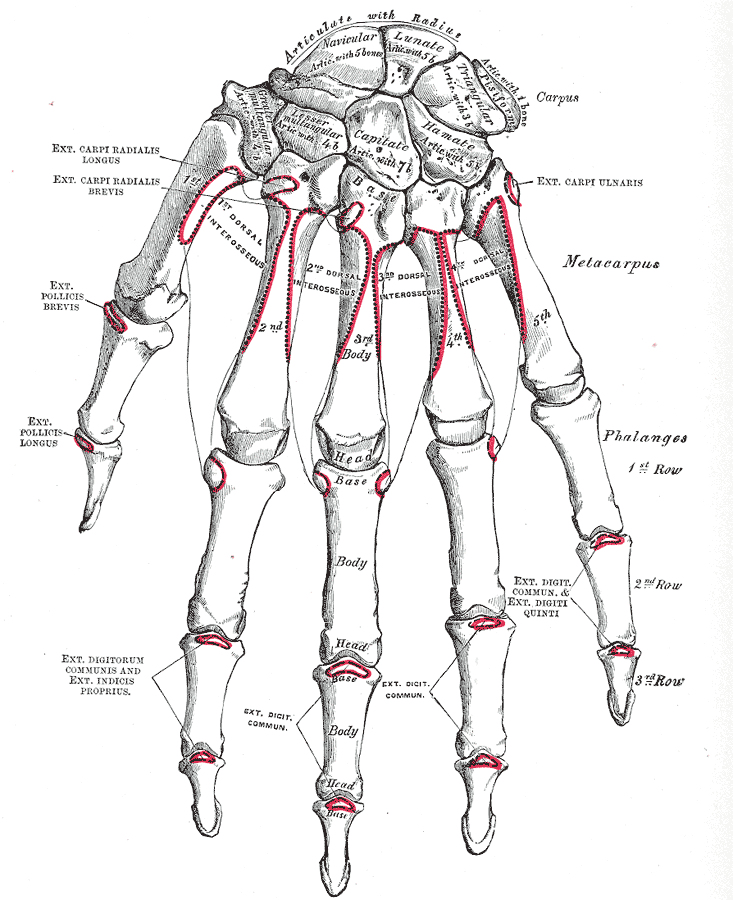
The Bones of the Wrist (Ossa Carpalia) At the base of the wrist, we have eight carpal bones anatomically arranged in two rows. The proximal row includes scaphoid, lunate, triquetrum, and pisiform bones, but the distal row - the hamate, capitate, trapezium, and trapezoid bones. The arrangement of carpal bones in two rows poorly correlates with.
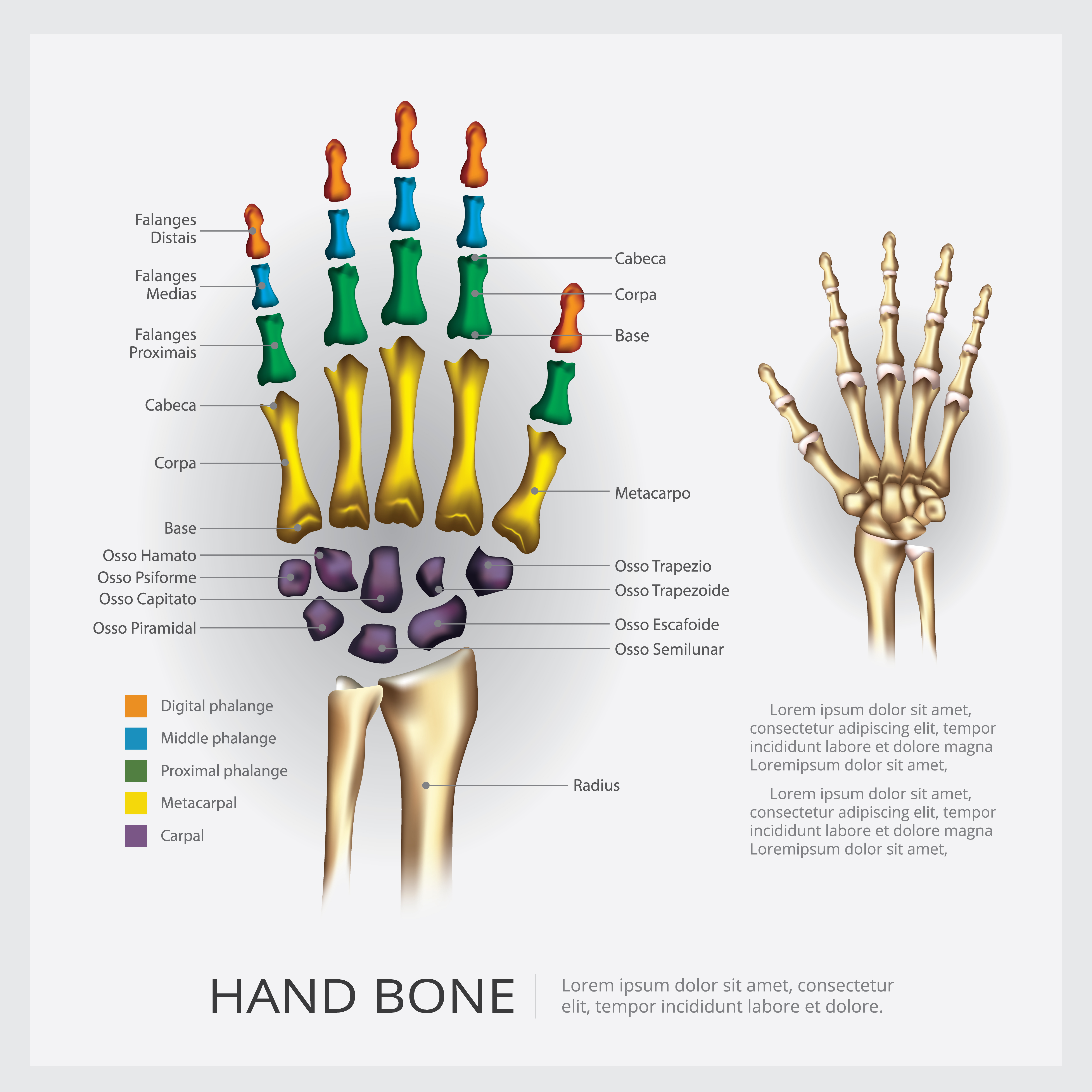
Human Anatomy Hand Bone Vector Illustration 536870 Vector Art at Vecteezy
The interphalangeal joints of the hand are synovial hinge joints that span between the proximal, middle, and distal phalanges of the hand. In digits 2-5 these joints can be further classified based on which bones are involved. The proximal interphalangeal joint (PIPJ or PIJ) is located between the proximal and middle phalanges, while the distal.
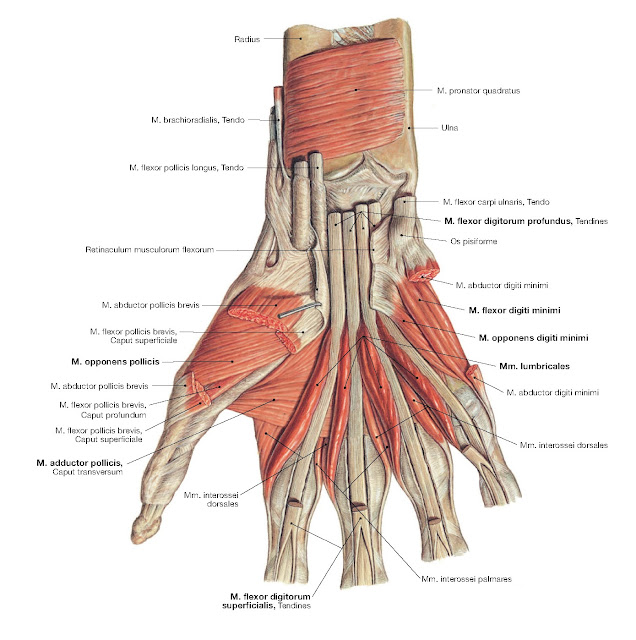
MUSCLES OF THE HAND ANATOMY wikitomy
A. ANATOMI TANGAN (MANUS) Anatomi tangan atau manus sangat kompleks. Articulatio radio carpea dan manus terdiri dari 27 tulang. Ke-27 tulang ini diklasifikasikan sebagai carpal, metacarpal, atau phalanges. Setiap tangan memiliki lima tulang metacarpal yang memiliki dasar, batang, leher, dan kepala. Tangan memiliki

Dorsal Interossei Manus Learn Muscles
Manus and pes of opossum (Didelphis virginiana) and human (Homo sapiens): human manus (A), human pes (C), opossum manus (B), and opossum pes (D). Illustrations from Jollie 1962 under CC0 public domain. Rodents are diverse in terms of their locomotion, and this is reflected in their autopods. Rodents have seven carpals, but the scaphoid and.

Manus human anatomy organs
Gross anatomy. The EDBM muscle lies along the ulnar side of the extensor tendon of the 2 nd digit (usually fourth wrist compartment 5 ). It commonly arises at the distal end of the radius and posterior radiocarpal ligament to insert most commonly on the 2 nd digit. However, insertion can also be seen on the 3 rd, 4 th, or 5 th digits, as well.
anatomy of left hand and wrist
The manus (Latin for hand, plural manus) is the zoological term for the distal portion of the fore limb of an animal. In tetrapods, it is the part of the pentadactyl limb that includes the metacarpals and digits (phalanges).During evolution, it has taken many forms and served a variety of functions.It can be represented by the hand of primates, the lower front limb of hoofed animals or the.
Hand Anatomy Labeled
Anatomi tubuh manusia. 1. Sistem rangka. Tubuh manusia didukung oleh sistem rangka, yang terdiri dari 206 tulang yang dihubungkan oleh tendon, ligamen, dan tulang rawan. Tulang ini disusun oleh kerangka aksial dan kerangka apendikular. Kerangka aksial terdiri dari 80 tulang yang terletak di sepanjang sumbu tubuh manusia.

Bones of the Hand Carpal Bones Metacarpal bones Geeky Medics
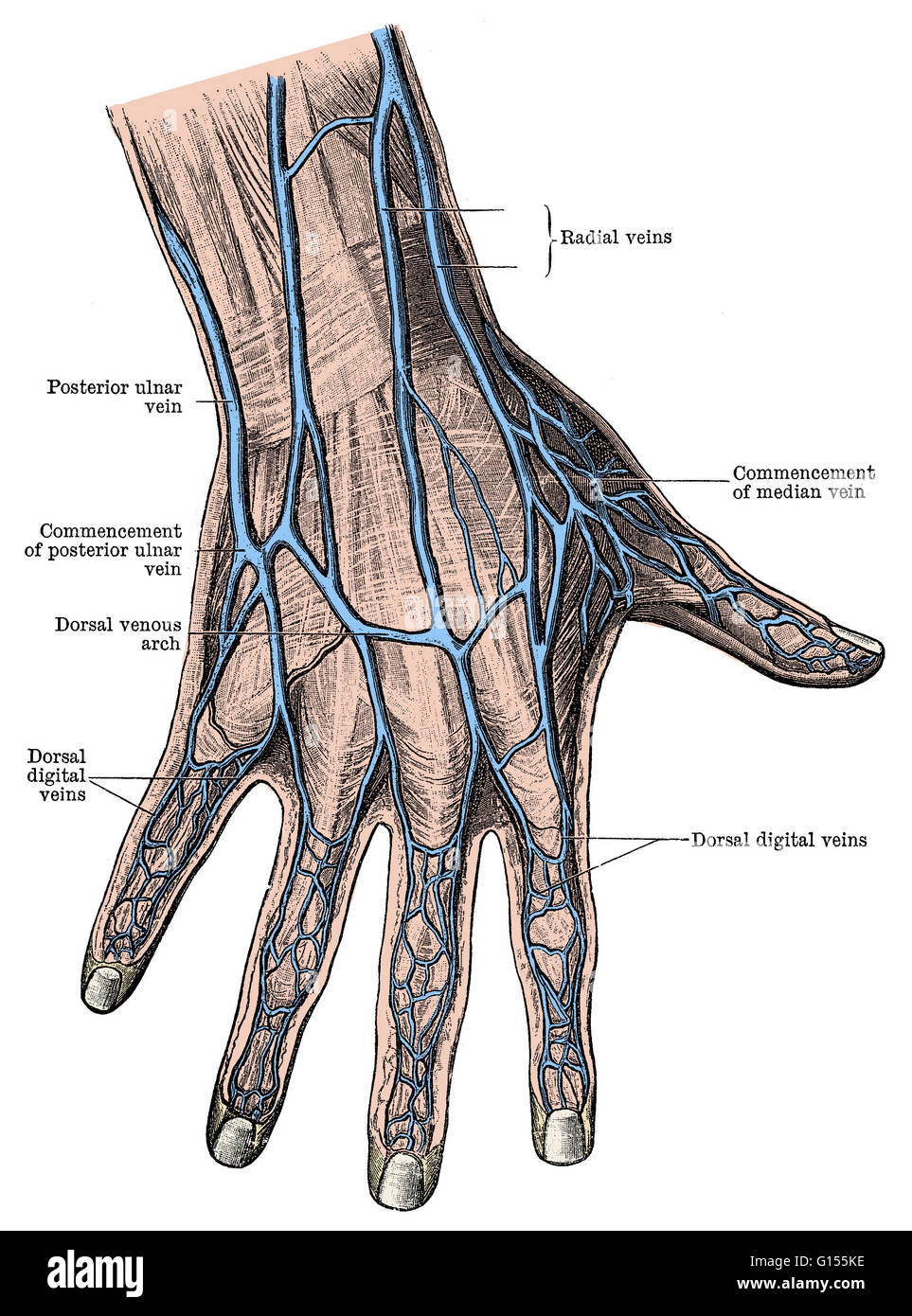
Dorsum manus. Latin synonym: Regio dorsalis manus Synonym: Dorsal region of hand Definition The dorsum of hand (opisthenar area, dorsal area) is the corresponding area on the posterior part of the hand. I agree herein to the cession of rights to my contribution in accordance with the Terms.

Muscles of the Posterior Hand Superficial View Learn Muscles
Ossa manus. Definition. The skeleton of the hand is subdivided into three segments: the carpus or wrist bones; the metacarpus or bones of the palm; and the phalanges or bones of the digits. This definition incorporates text from a public domain edition of Gray's Anatomy (20th U.S. edition of Gray's Anatomy of the Human Body, published in 1918.

Anatomy Of Hand Ligaments ANATOMY
Lumbrical muscles of hand (Musculi lumbricales manus) The lumbrical muscles, which get their name due to their worm-like appearance (lumbricidae - Latin = earthworm), are four short intrinsic muscles of the hand located between the metacarpal bones, deep to the palmar fascia.Along with the dorsal interossei and the palmar interossei, the lumbrical muscles belong to the short muscles of the hand.
:watermark(/images/watermark_5000_10percent.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/overview_image/711/phoEAD7Bc2XtFoahwQHYKw_phalanges-of-the-hand_english.jpg)
Phalanges of the hand Anatomy and function Kenhub
Manus (anatomy) The manus ( Latin for hand, plural manus) is the zoological term for the distal portion of the forelimb of an animal. In tetrapods, it is the part of the pentadactyl limb that includes the metacarpals and digits ( phalanges ). During evolution, it has taken many forms and served a variety of functions.

anatomy 02 musculi manus 1 by baila on DeviantArt
AMBOSS
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/13851/Dorsal_interossei_muscles_of_hand.png)
Dorsal interossei of hand Anatomy and function Kenhub
Nurullah YÜCEL (MD, PhD)Sağlık Bilimleri Üniversitesi Hamidiye Uluslararası Tıp FakültesiAnatomi Anabilim Dalı Öğretim ÜyesiHerkesin erişimine açık olan bu.

Understanding the Anatomy of the Hand Health Life Media
Tıp, Diş Hekimliği, FTR, Sağlık Bilimleri Fakülteleri, Ebelik, Hemşirelik vb. bölümler için anatomi maketleri ve kemikler üzerinden ossa manus (el kemikleri).

Skeletal Anatomy of the Hand Hand Clinics
The phalanges are fourteen in number, three for each finger, and two for the thumb. Each consists of a body and two extremities. The body tapers from above downward, is convex posteriorly, concave in front from above downward, flat from side to side; its sides are marked by rough which give attachment to the fibrous sheaths of the Flexor tendons. The proximal extremities of the bones of the.