
Varicella zoster virus vasculopathies diverse clinical manifestations, laboratory features
The varicella-zoster virus (VZV) is a highly contagious virus of the herpes family. Chickenpox (or primary VZV infection) is a common childhood disease. With universal childhood varicella vaccination, which was introduced in 1995, most adults in the United States (US) and Europe are immune.[1] It is estimated that >90% of the antenatal population is seropositive for VZV IgG antibody and.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/chickenpox-symptoms1-5ae1f76a30371300367d3032.png)
Chickenpox Signs, Symptoms, and Complications
A contagious childhood disorder caused by the varicella zoster virus. It is transmitted via respiratory secretions and contact with chickenpox blister contents. It presents with a vesicular skin rush, usually associated with fever, headache, and myalgias. The pruritic fluid-filled vesicles occur 10-21 days after exposure and last for 3-4 days.

Decoding the architecture of the varicellazoster virus transcriptome
Varicella is a highly contagious disease caused by the varicella-zoster virus (VZV). It usually presents as a generalized pruritic maculopapulovesicular rash. The incubation period is typically 14-16 days after exposure to the virus (range 10-21 days). Patients are contagious 1-2 days before rash onset until all lesions have crusted or.
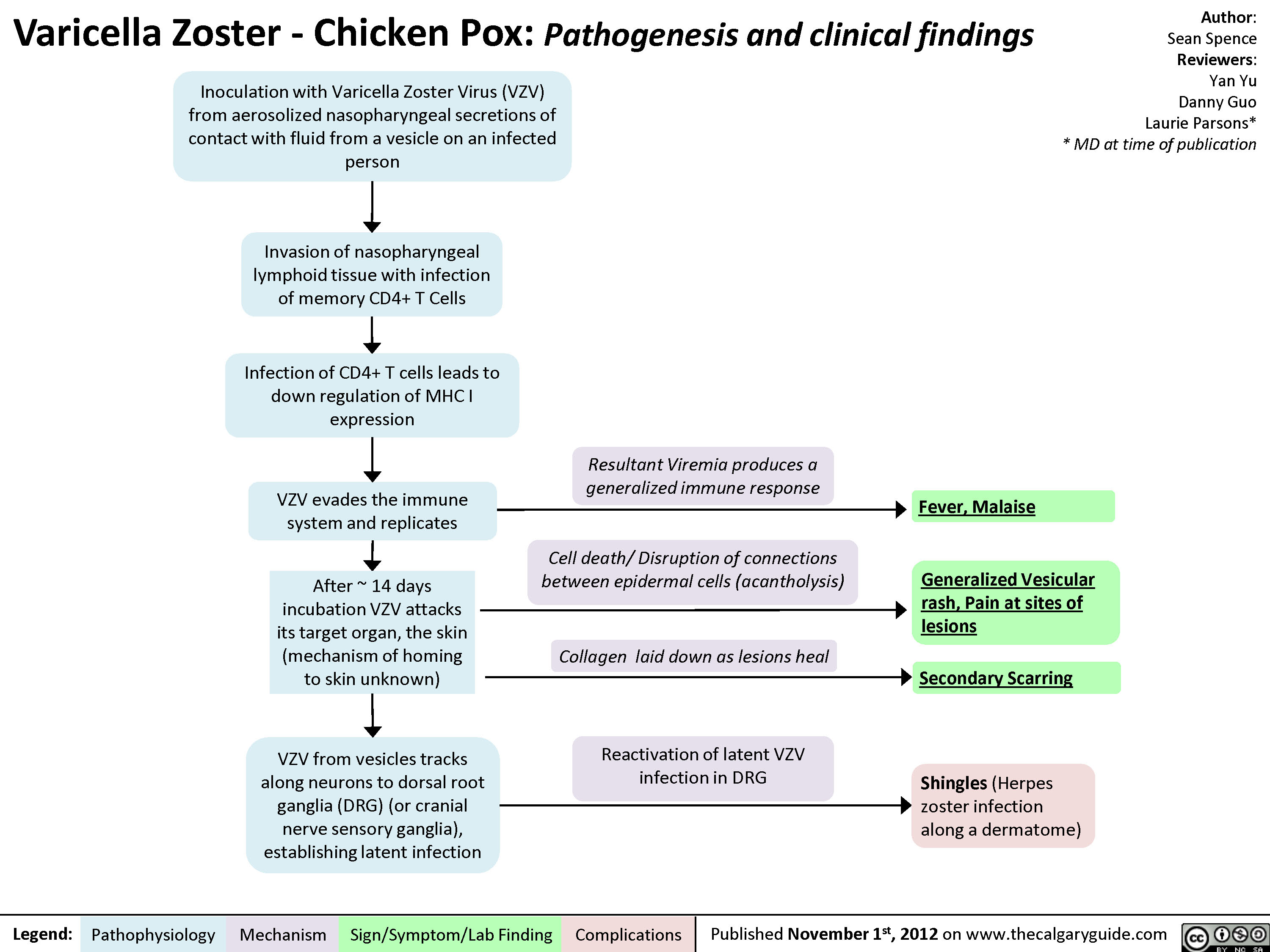
Varicella Zoster (Chicken Pox) Calgary Guide
Varicella (chickenpox) is an acute infectious disease. It is caused by varicella-zoster virus (VZV), which is a DNA virus that is a member of the herpesvirus group. After the primary infection, VZV stays in the body (in the sensory nerve ganglia) as a latent infection. Primary infection with VZV causes varicella.
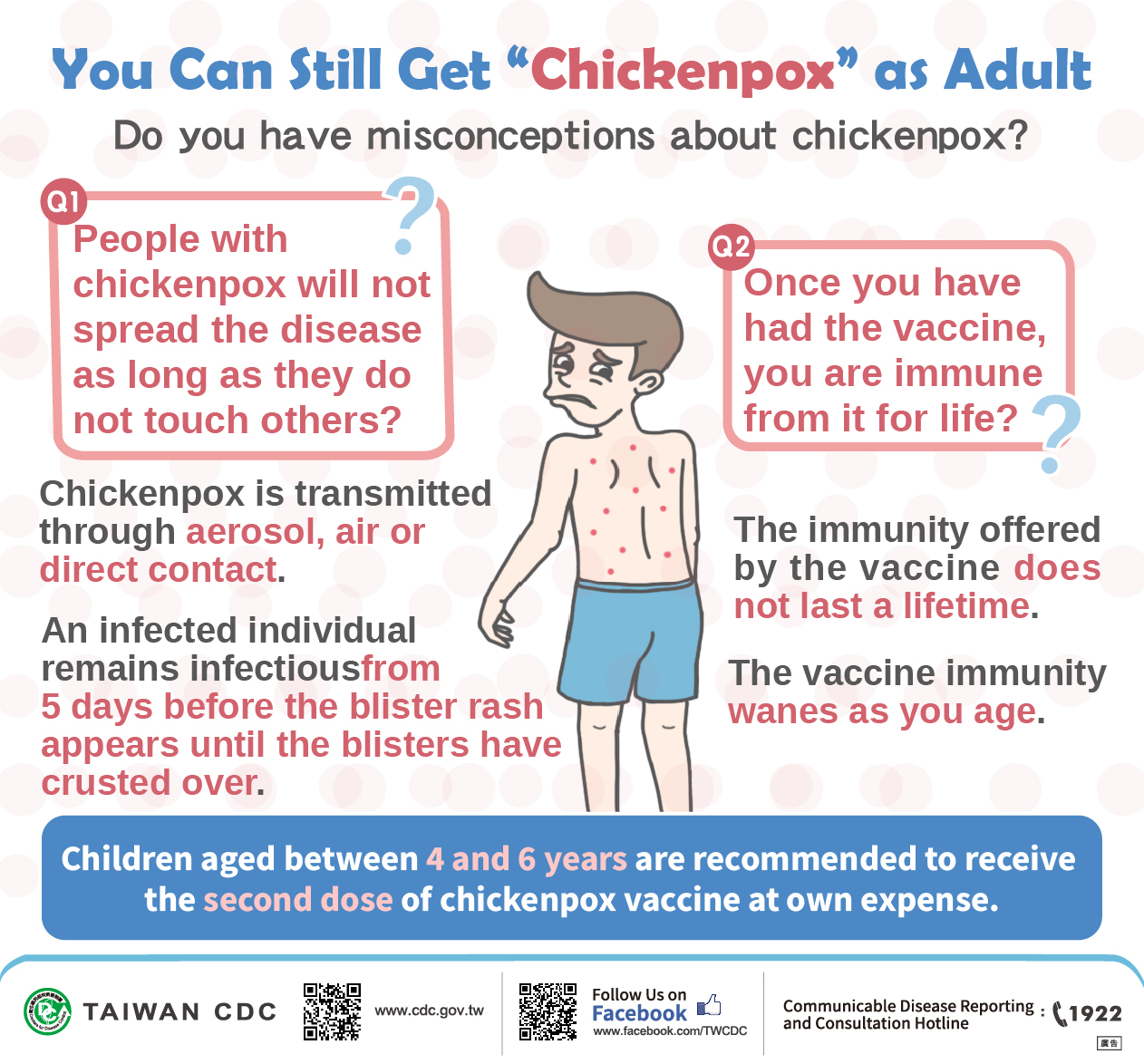
Complicated Varicella Taiwan Centers for Disease Control
Diagnosis varicella atau cacar air (chickenpox) umumnya ditegakkan secara klinis berdasarkan karakteristik lesi kulit. Akan tetapi, pemeriksaan penunjang seperti tes Tzanck, pemeriksaan serologis, dan isolasi virus dengan polymerase chain reaction atau kultur dapat dilakukan jika perlu, terutama pada kasus-kasus yang atipikal. [3] Anamnesis.

VaricellaZoster Virus/Chickenpox Concise Medical Knowledge
Clinical Focus: This value set contains concepts that represent varicella zoster (i.e., chickenpox and shingles) infections. Data Element Scope: This value set may use the Quality Data Model (QDM) category related to Diagnosis. Inclusion Criteria: Includes only relevant concepts associated with all varicella zoster infections. This is a grouping of ICD-10-CM and SNOMED CT codes.

Diagnosis Varicella Alomedika
In the differential diagnosis, providers should consider possible varicella-related complications when biologically plausible, even when varicella vaccine was received. It is also possible to distinguish vaccine-type VZV from wild type by examination of the viral deoxyribonucleic acid through specialized PCR testing [ 29 , 31 ].

Varicella (chickenpox) Immunisation Advisory Centre
The diagnosis of VZV infection is usually a clinical diagnosis based on the characteristic vesicular lesions, which are seen widespread in chickenpox (varicella) or in a restricted dermatomal pattern with associated neuritis in shingles (herpes zoster). However, additional diagnostic information may be useful in the following situations:

Varicella Chickenpox Nursing Diagnosis and Nursing Care Plan
Varicella, also known as chickenpox, is a self-limited viral infection caused by varicella-zoster virus (VZV), a member of the Herpesviridae family. Prior to the clinical implementation of the varicella vaccine, more than 99% of adults aged 40 and older had evidence of previous infection. Transmission occurs via airborne respiratory droplets or.

Disseminated varicella zoster virus encephalitis The Lancet
Varicella [chickenpox] B01 Varicella [chickenpox] B01-Clinical Information. A contagious childhood disorder caused by the varicella zoster virus. It is transmitted via respiratory secretions and contact with chickenpox blister contents. It presents with a vesicular skin rush, usually associated with fever, headache, and myalgias.
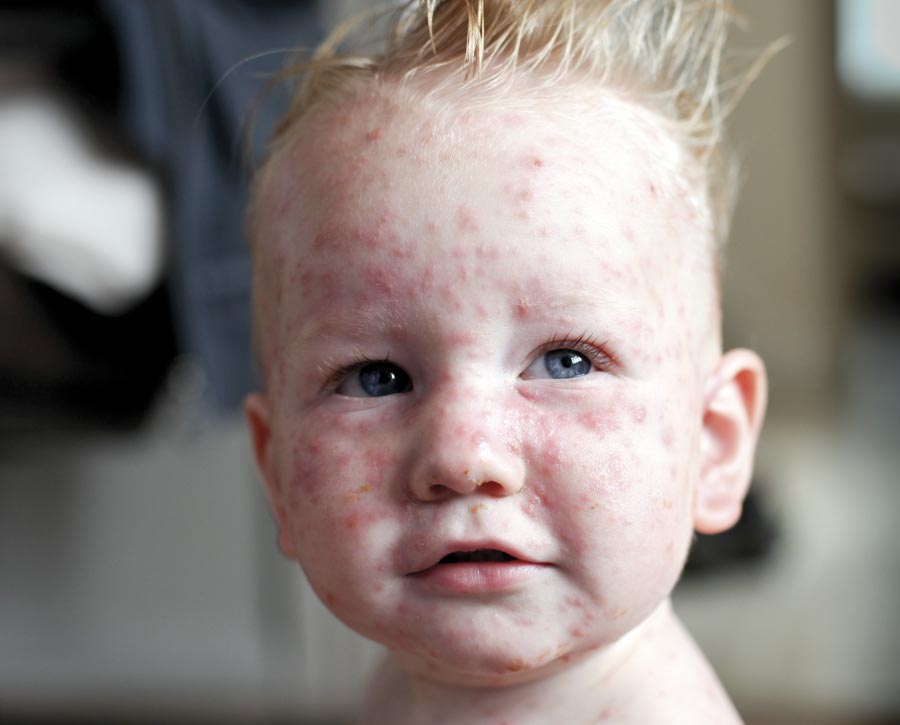
Chickenpox No Adults Allowed Medical Forum
Varicella without complication. B01.9 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2024 edition of ICD-10-CM B01.9 became effective on October 1, 2023. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of B01.9 - other international versions of ICD-10 B01.9 may differ.

Varicella sintomi, cause e cure Ohga!
Laboratory Testing. Laboratory testing is recommended to: Confirm suspected cases of varicella. Confirm varicella as the cause of outbreaks. Confirm varicella in severe cases (hospitalizations or deaths) or unusual cases. Determine susceptibility to varicella. Determine if suspected vaccine-related adverse events were caused by vaccine-strain VZV.

Varicella Pneumonia in an Adult NEJM
Varicella-zoster virus (VZV) is a highly contagious member of the Herpesviridae family also known as human herpesvirus 3. Humans are the only host for VZV, and the virus is passed by direct contact, spread of respiratory secretions, or aerosolized infectious material from open skin lesions. Primary varicella is highly infectious, with secondary attack rates of nearly 100% among susceptible.

Chickenpox (varicella zoster) Clinical Review
For more information on varicella-zoster virus specimen collection, storage, and handling, please contact: National VZV Laboratory. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 1600 Clifton Road, NE. Atlanta, GA 30333. Tel: 404-639-2178 or 404-754-0114. Email: [email protected].

Disseminated Varicella Infection NEJM
View ICD-10 Tree. Chapter 1 - Certain infectious and parasitic diseases (A00-B99) » Viral infections characterized by skin and mucous membrane lesions (B00-B09) » Varicella [chickenpox] (B01) ICD-10 Subcodes (5) B01.0 - Varicella meningitis. B01.1 - Varicella encephalitis, myelitis and encephalomyelitis. B01.2 - Varicella pneumonia.

Disseminated Verrucous Varicella Zoster With Exclusive Follicular Involvement Dermatology
Varicella (chickenpox) is an acute, highly contagious disease caused by varicella-zoster virus (VZV), a member of the herpesvirus family. Only one serotype of VZV is known, and humans are the only reservoir. Following infection, the virus remains latent in neural ganglia and in about 10-20% of cases it is reactivated it is reactivated to cause herpes zoster, or shingles, generally in persons.