24.2 Isomers of Organic Compounds Chemwiki
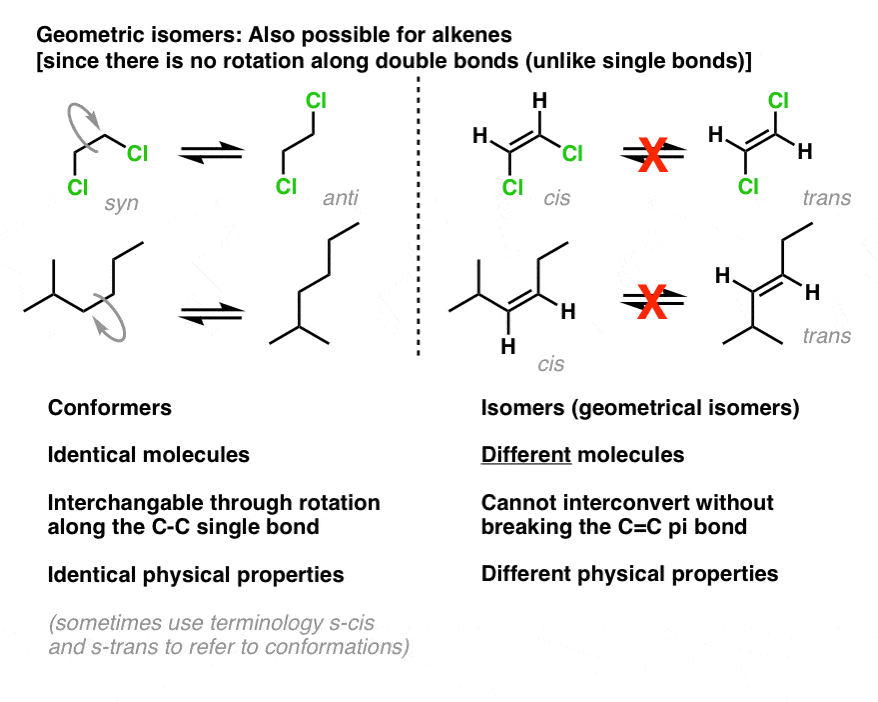
Geometric (cis / trans) isomerism. These isomers occur where you have restricted rotation somewhere in a molecule. At an introductory level in organic chemistry, examples usually just involve the carbon-carbon double bond - and that's what this page will concentrate on. Think about what happens in molecules where there is un restricted rotation.

Isomer Definition, Types, Example and Quiz Biology Dictionary
Geometric isomerism, also known as cis-trans isomerism, is a form of stereoisomerism. Like all stereoisomers, geometric isomers are compounds that are made up of the same constituent atoms and are connected in the same sequence but differ in the orientation of those atoms in space. All geometric isomers require restricted rotation within the.
isomere geometrique definition
Geometric isomers are chemical species with the same type and quantity of atoms as one another, yet having different geometric structures. In geometric isomers, atoms or groups exhibit different spatial arrangements on either side of a chemical bond or ring structure. Geometric isomerism is also called configurational isomerism or cis-trans.
World of Biochemistry (blog about biochemistry) Geometric isomers
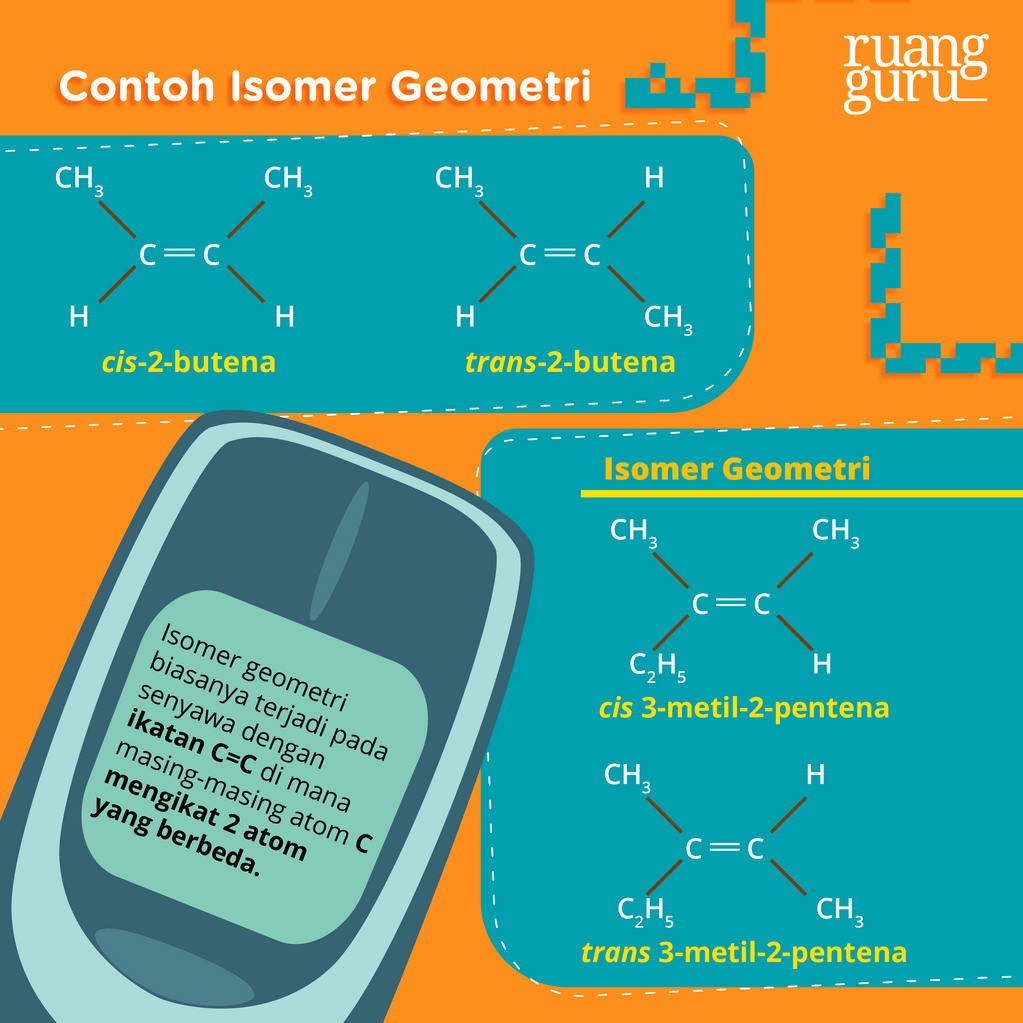
Kedua atom metil di cis-2 butena terkait karbon. Lalu tetap berada pada satu sisi ruang geometris. Sedangkan pada trans-2 butena pada sisi berbeda dan bersebrangan. Penamaannya juga berbeda. Contoh Isomer Geometri Senyawa Misalnya isomer geometri senyawanya alkena pentana C5H10 pada 2-pentana. Isomer tersebut dari 2 pentana rumus kimianya C5H10.
PPT Exp 10A Geometric Isomers PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID4494363
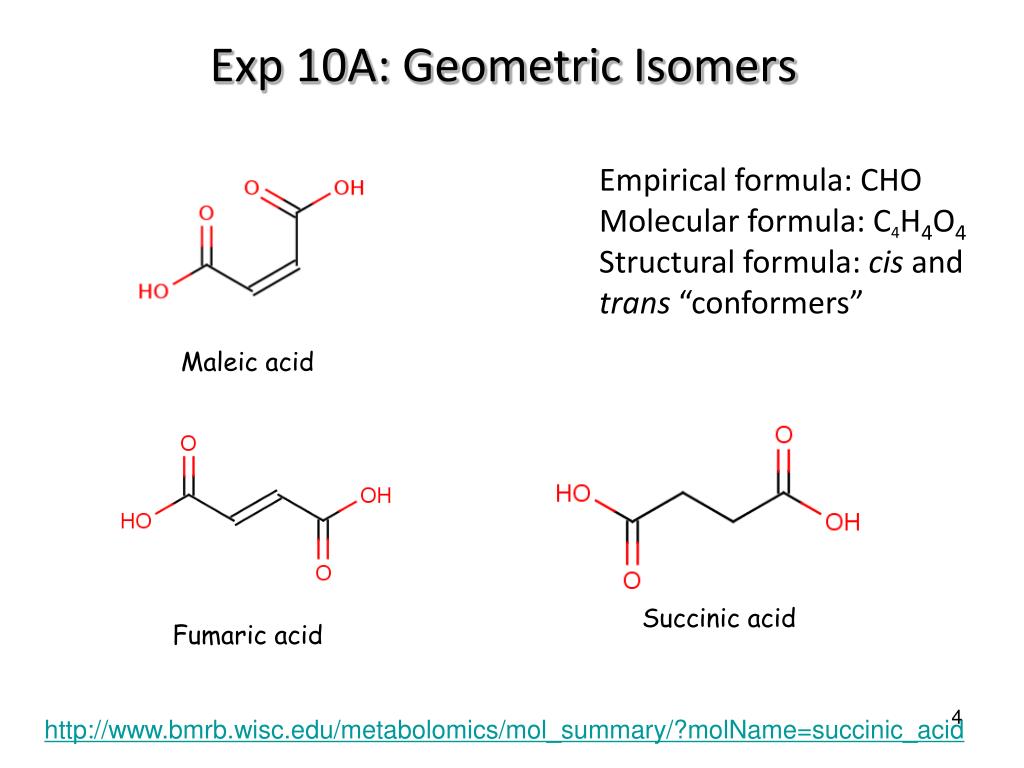
Geometric isomers are two or more compounds with the same number and types of atoms, and bonds, but which have different geometries for the atoms. For instance, fumaric acid and maleic acid have the same molecular formula and weight, yet they are not the same molecule. As early as the 1920's researchers sought to understand why fumaric acid killed bacteria, but was not harmful to humans.

Optimized geometric structure of the Y(L)3 (a) Isomer 1 (more stable),... Download Scientific
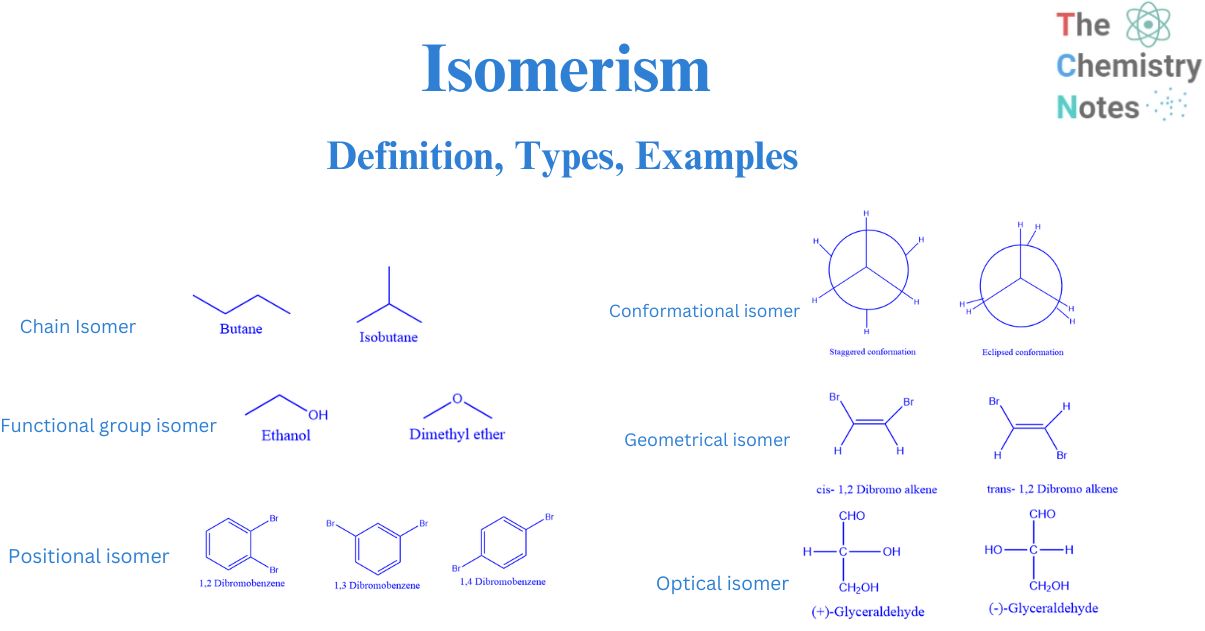
Isomer. In chemistry, isomers are molecules or polyatomic ions with identical molecular formula - that is, same number of atoms of each element - but distinct arrangements of atoms in space. [1] Diamond and graphite are a familiar example; they are isomers of carbon. Isomerism refers to the existence or possibility of isomers.

Organic Molecules and Isomers Biology 201 The Chemistry of Life
Geometric isomer: One molecule in a set of stereoisomers which differ in the E / Z or cis/trans arrangement of substituents or functional groups. E and Z Geometric Isomers. E-2-Butene Z-2-Butene: Cis and trans Geometric Isomers. Cis-1,2-Dimethyl cyclobutane.
Kimia Kelas 11 Pengertian Isomer, Jenisjenisnya, Serta Contohnya Belajar Gratis di Rumah
Geometric isomers differ in the spatial arrangement of substituents on a double bond or non-aromatic ring system. Especially in the case of 1,2-disubstituted alkenes, one usually speaks of a cis-/trans- isomerism.In the case of longer chains and/or higher substituted compounds, naming according to the (Z)-, (E)- notation using the CIP rules is necessary to clearly indicate the configuration.

Geometric Isomers (9/11) Organic Chemistry NCEA Level 2 Chemistry StudyTime NZ YouTube
Cis-trans (geometric) isomerism exists when there is restricted rotation in a molecule and there are two nonidentical groups on each doubly bonded carbon atom. The IUPAC naming is the same as alkene except for the addition of the cis or trans prefix. 2.2: Geometric Isomers is shared under a CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 license and was authored, remixed, and.
Isomerism Definition, Types, Examples
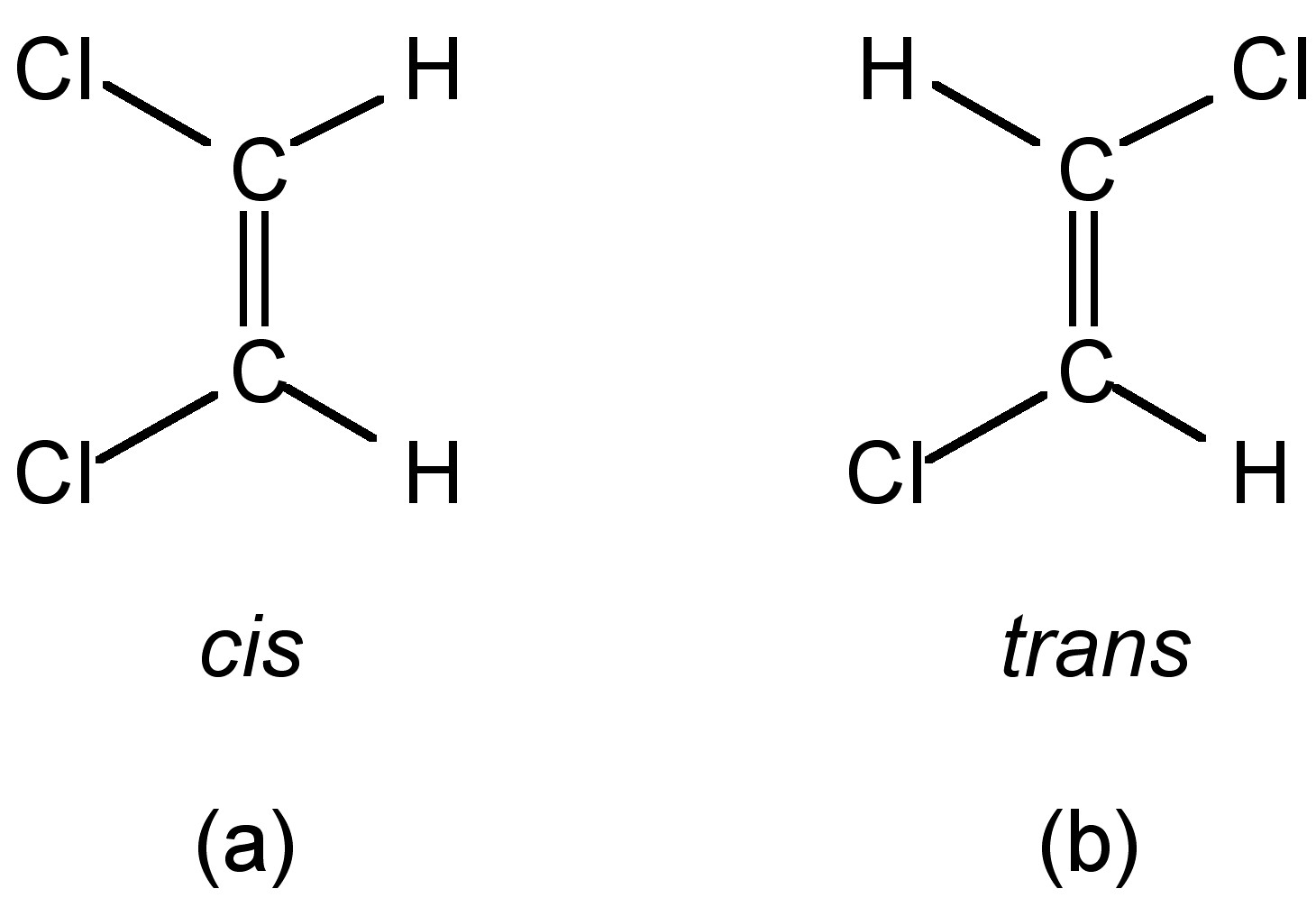
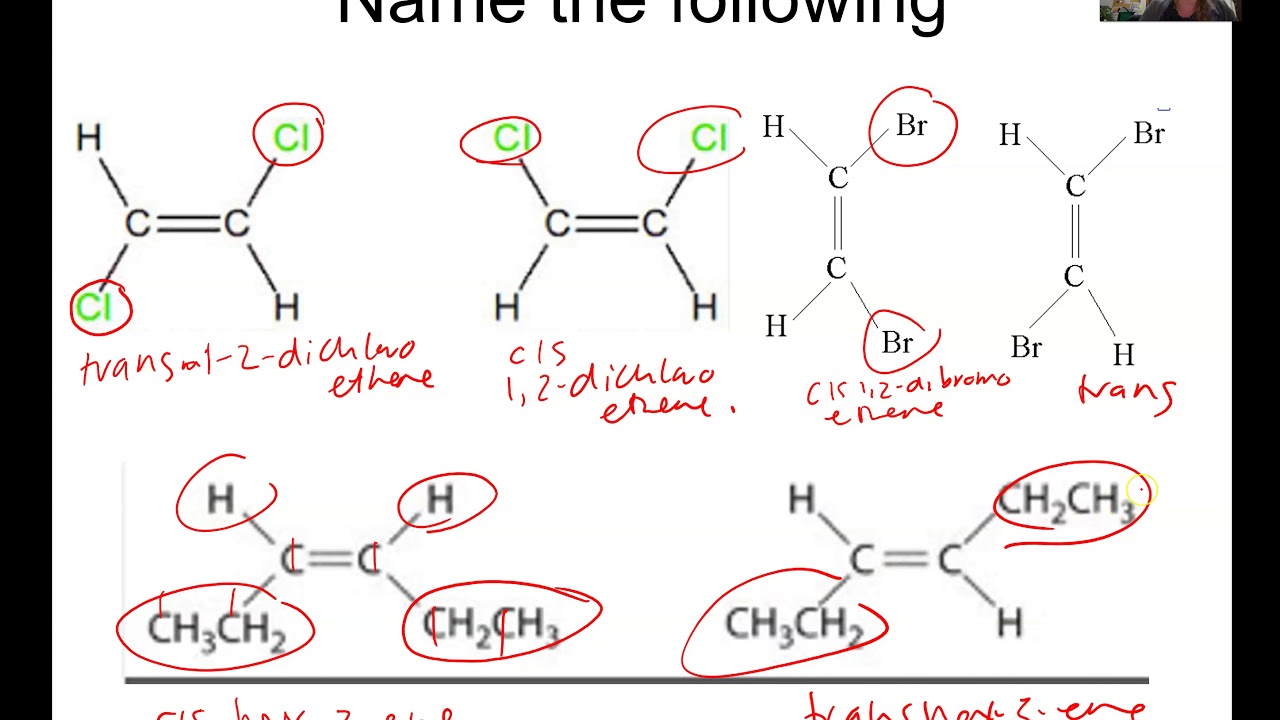
The isomer with the two Cl atoms on opposite sides of the molecule is the trans isomer (Latin trans, meaning "across") and is named trans-1,2-dichloroethene. These two compounds are cis-trans isomers (or geometric isomers), compounds that have different configurations (groups permanently in different places in space) because of the presence.
Six types of isomer structure Adobe Stock
Conformational Isomers. The C-C single bonds in ethane, propane, and other alkanes are formed by the overlap of an sp 3 hybrid orbital on one carbon atom with an sp 3 hybrid orbital on another carbon atom, forming a σ bond. Each sp 3 hybrid orbital is cylindrically symmetrical (all cross-sections are circles), resulting in a carbon-carbon single bond that is also cylindrically symmetrical.
2 5 Lesson 6 Geometric Isomers PART B YouTube
Tutorial illustrating geometric isomers in polymer repeat units. Illustrated with 3D model.Video lecture for Introduction to Materials Science & Engineering.

Geometric Isomer Easy Science Easy science, Geometric, Understanding
Geometric Isomers Definition. Geometric isomerism is a kind of stereoisomerism. It is also known as cis-trans isomerism or E-Z isomerism. Geometric isomerism occurs due to the restricted rotation about carbon-carbon double bonds or carbon-carbon single bonds in cyclic compounds. Geometric isomers are the stereoisomers which differ from each.
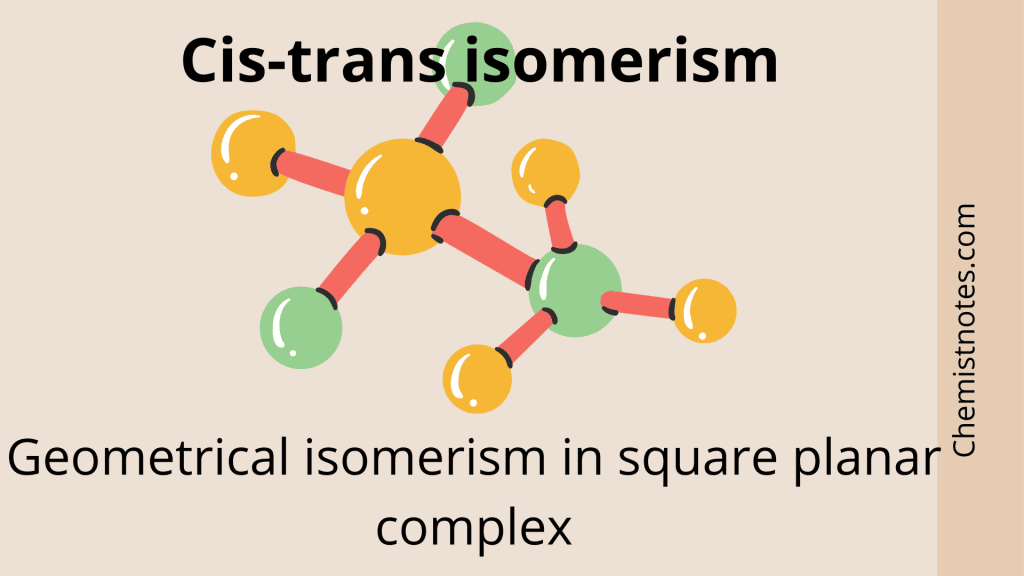
Geometrical Isomerism Cistrans isomerism Chemistry Notes
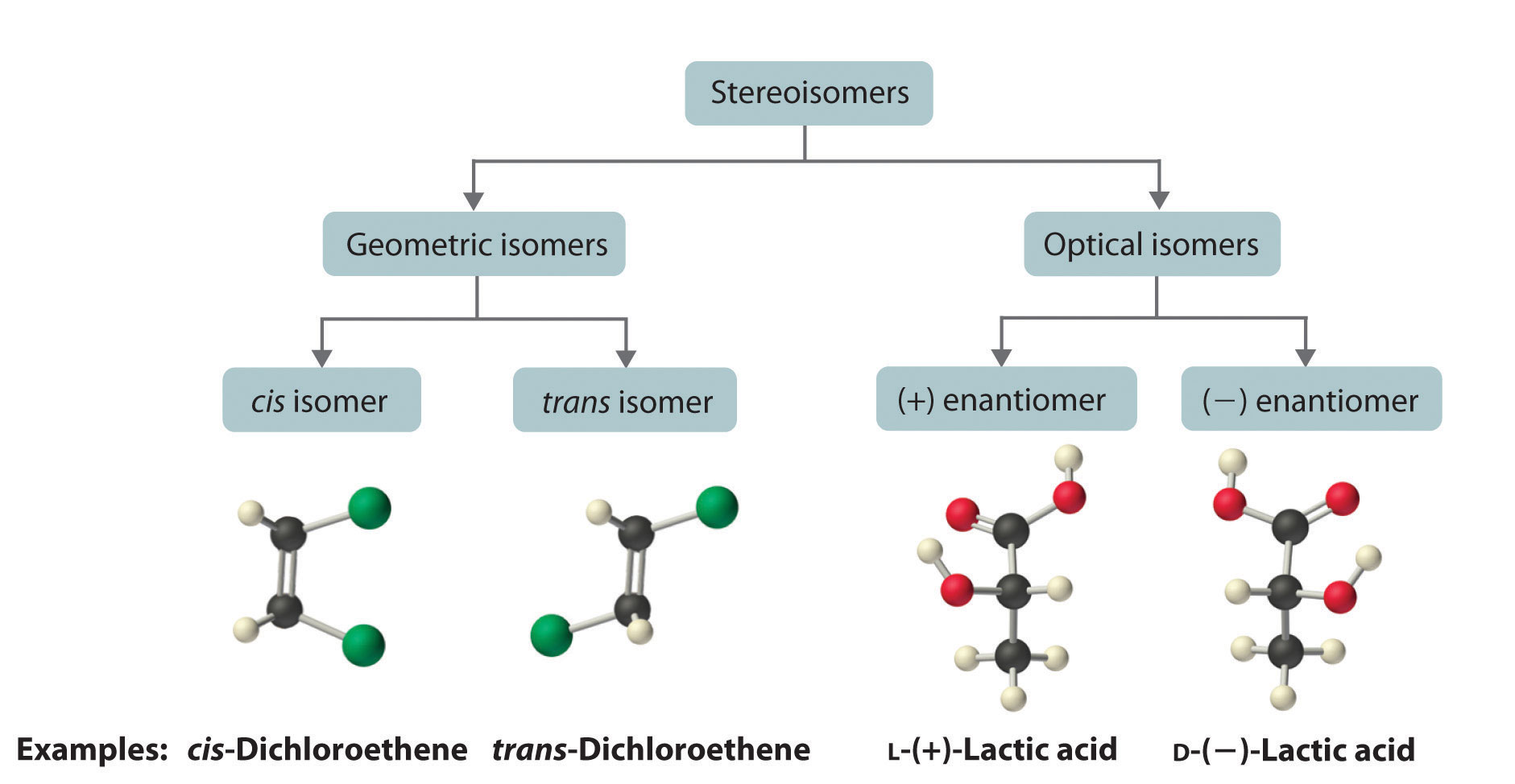
Although geometric isomers have completely different physical and chemical properties (for example, cis-and trans-2-butene have different boiling points and densities), optical isomers (also called enantiomers) differ in only one characteristic--their interaction with plane polarized light.When a beam of light is passed through a certain type of filter, all of the waves except those in one.
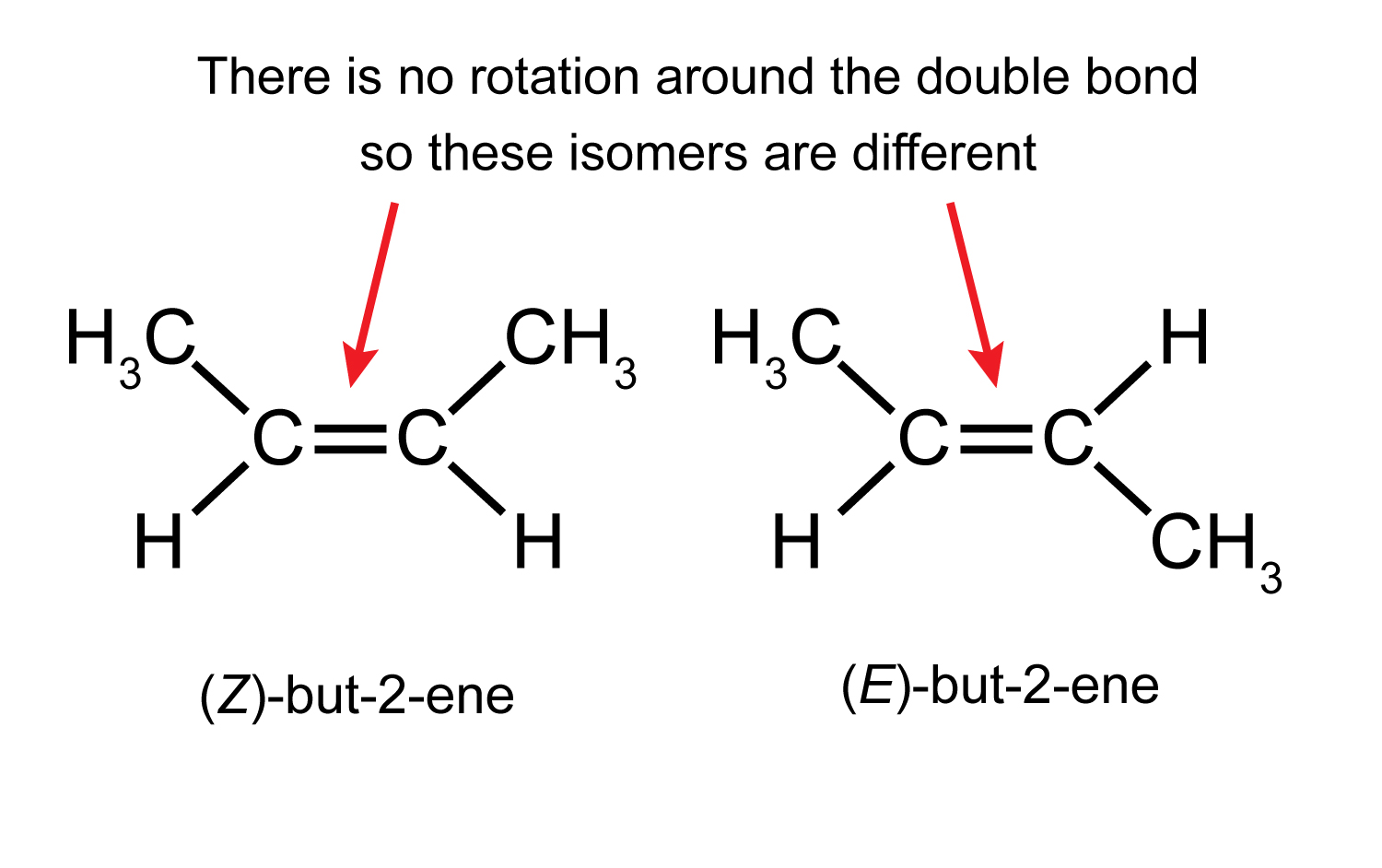
Maths skills Geometry Exploring Understanding Isomers
Geometric isomerism (also known as cis-trans isomerism or E-Z isomerism) is a form of stereoisomerism. This page explains what stereoisomers are and how you recognise the possibility of geometric isomers in a molecule. Further down the page, you will find a link to a second page which describes the E-Z notation for naming geometric isomers.
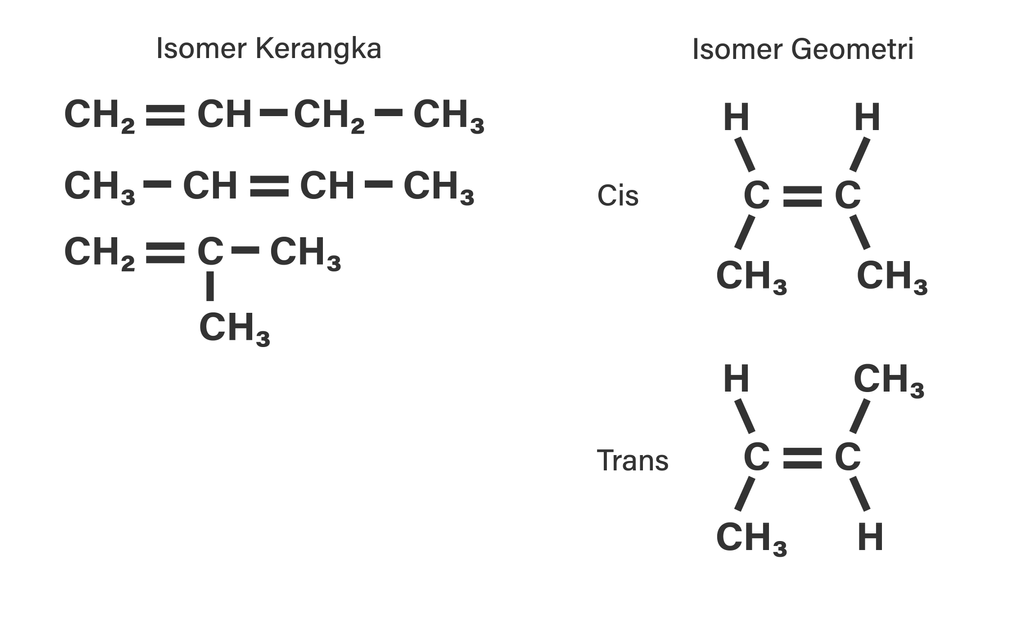
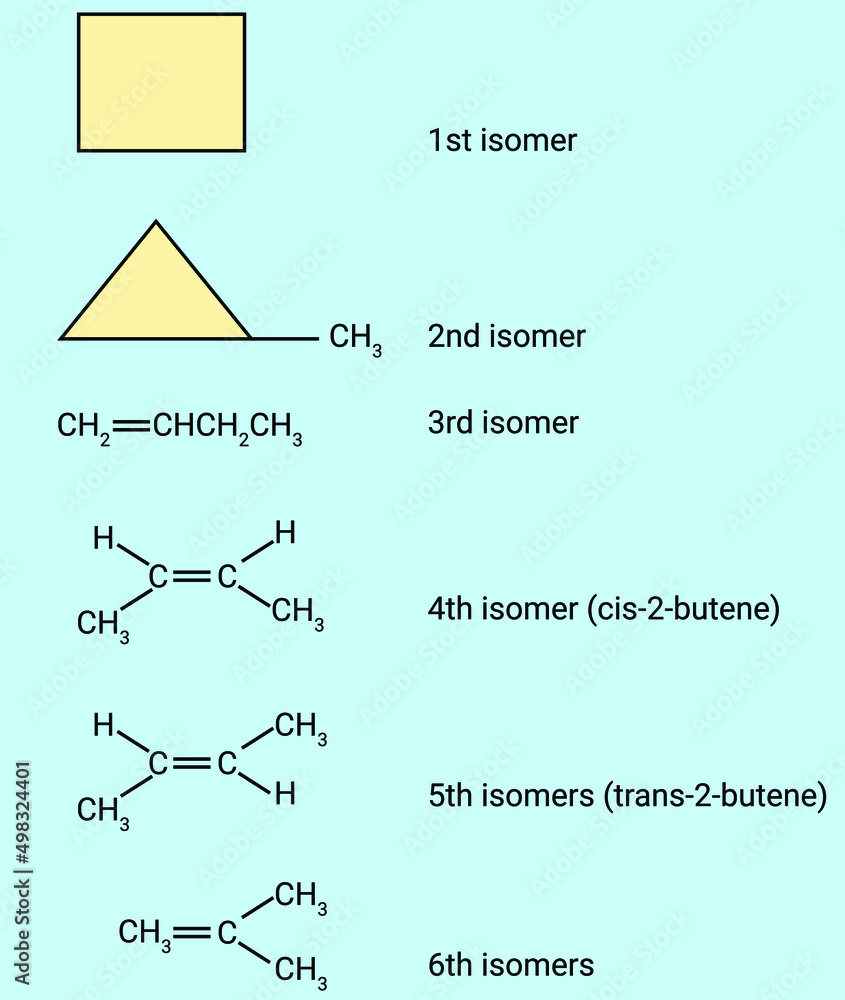
Tentukan isomerisomer dari C4H8 dengan menggambar...
cis-but-2-ene trans-but-2-ene. Cis-trans isomerism, also known as geometric isomerism, describes certain arrangements of atoms within molecules.The prefixes "cis" and "trans" are from Latin: "this side of" and "the other side of", respectively.In the context of chemistry, cis indicates that the functional groups (substituents) are on the same side of some plane, while trans conveys that they.