
Tuberculous Meningitis in Patients Infected with the Human Immunodeficiency Virus NEJM
Assuming the case detection ratio (CDR) for TBM was the same as all TB, we estimated that in 2019, 164,000 (95% UI; 129,000-199,000) adults developed TBM globally; 23% were among people living with HIV. Almost 60% of incident TBM occurred in males and 20% were in adults 25-34 years old. 70% of global TBM incidence occurred in Southeast Asia.
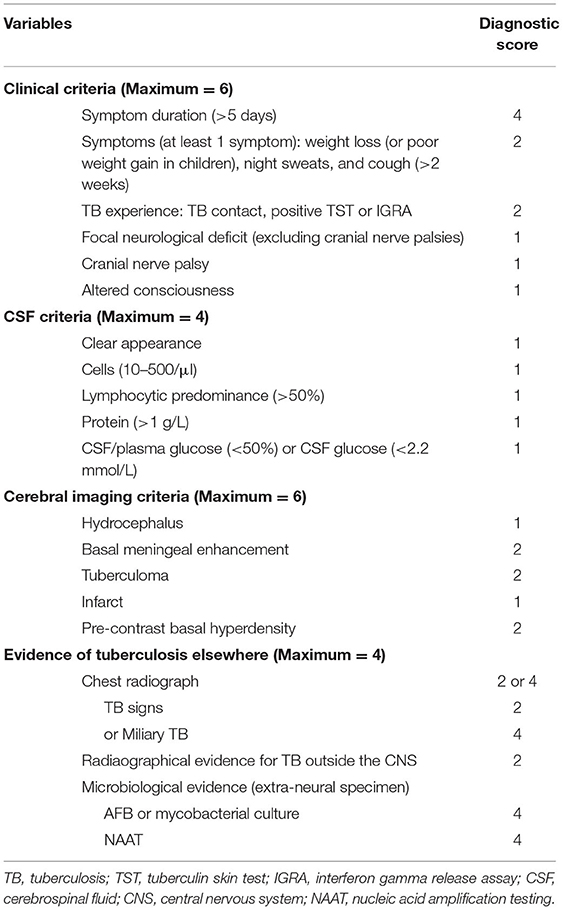
Frontiers The Sensitivity of Diagnostic Criteria of Marais S, et al. in Confirmed Childhood
Tuberculous meningitis. A17.0 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2024 edition of ICD-10-CM A17.0 became effective on October 1, 2023. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of A17.0 - other international versions of ICD-10 A17.0 may differ.

Tuberculous meningitis a uniform case definition for use in clinical research The Lancet
Tuberculous meningitis, also known as TB meningitis or tubercular meningitis, is a specific type of bacterial meningitis caused by the Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection of the meninges—the system of membranes which envelop the central nervous system. Signs and symptoms Fever and.
Tuberculous Meningitis Manual of Diagnosis and Therapy by Chin (English) Paperb 9780128188255
Introduction. Central nervous system (CNS) tuberculosis is one of the more serious manifestation of extra pulmonary TB constituting 6% of all TB cases. 1 Among CNS tuberculosis, tuberculous meningitis (TBM) remains the most common presentation. In spite of advances in diagnostic technology and effective therapeutic options, it continues to pose significant management challenges.
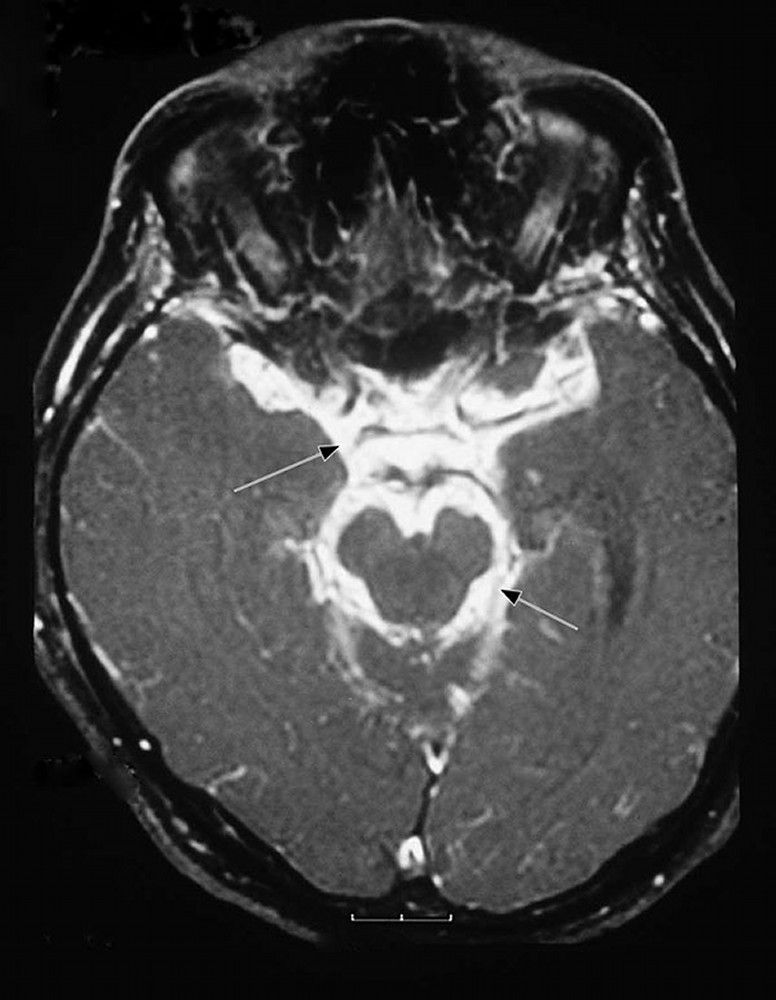
Image Tuberculous Meningitis MSD Manual Professional Edition
Methods: This is a retrospective cohort of adult patients with a central nervous system (CNS) TB International Classification of Diseases, Ninth/Tenth Revision (ICD-9/10) diagnosis code (013*, A17*) identified in the Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project, State Inpatient and State Emergency Department (ED) Databases from 8 states. Missed.
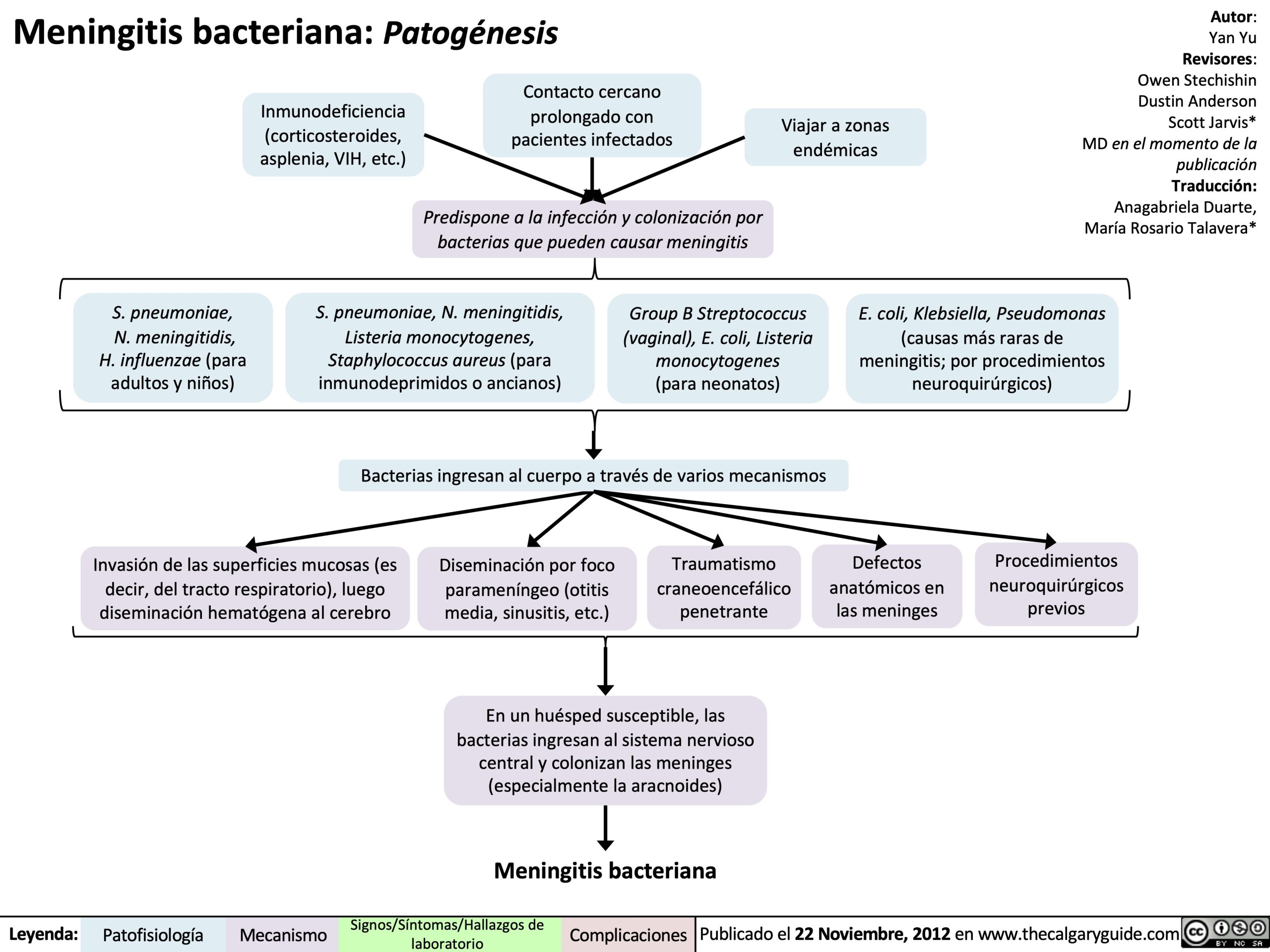
meningitisbacterianapatogenesis Calgary Guide
Introduction. Tuberculous meningitis (TBM) is the most devastating form of tuberculosis (TB) in children, with high mortality and morbidity (1, 2).The neurological disability due to TBM has significant long-term consequences for children, their families and healthcare systems (); prevention and early diagnosis are therefore critical.For programmes to effectively respond to this public health.
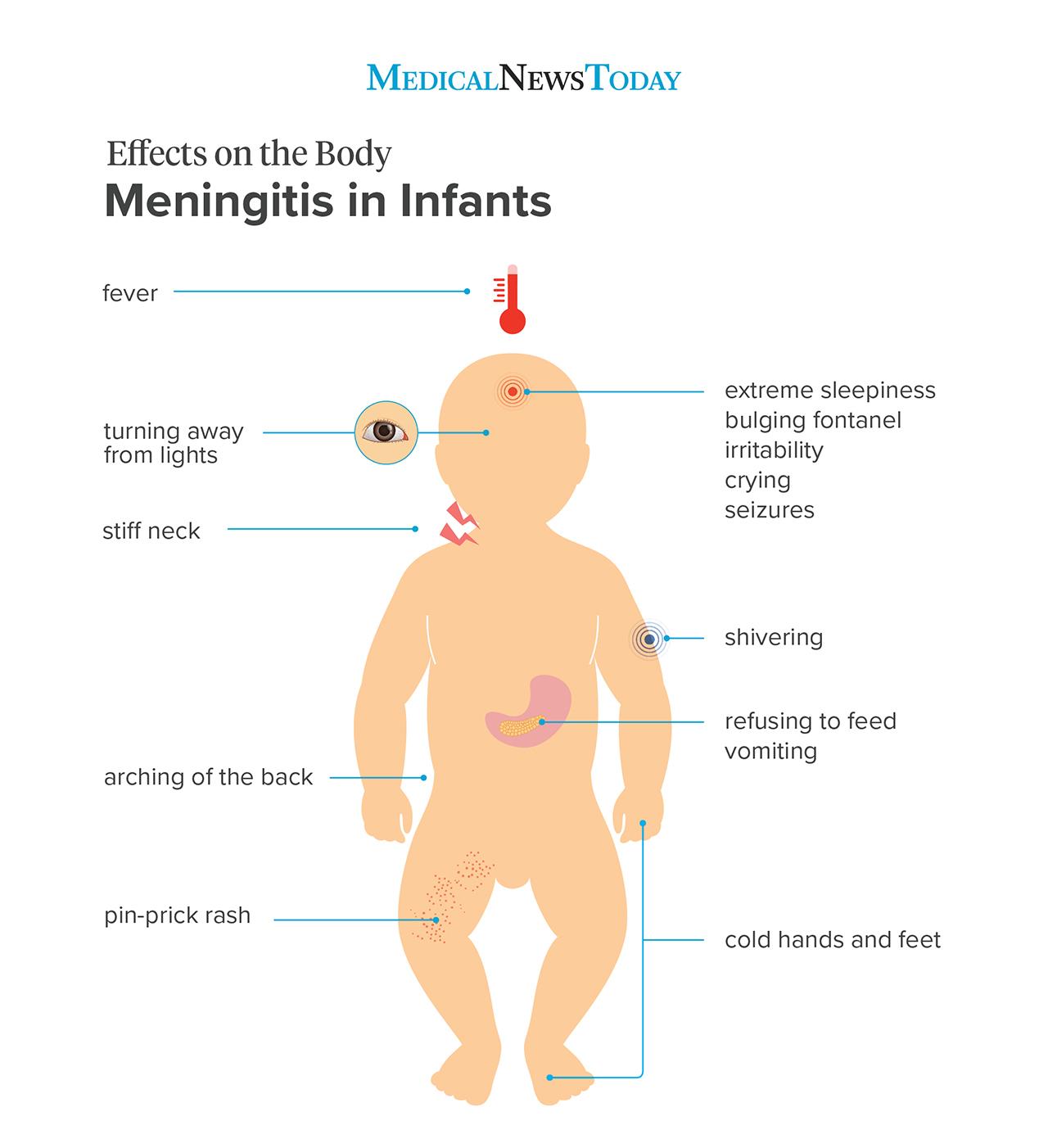
Meningitis rash Pictures, symptoms, and similar rashes
Forms of central nervous system (CNS) infection due to Mycobacterium tuberculosis include meningitis, tuberculoma, and spinal arachnoiditis. An overview of CNS tuberculosis (TB) is presented separately. (See "Central nervous system tuberculosis: An overview" .) Issues related to clinical manifestations and diagnosis of tuberculous meningitis.

Tuberculous meningitis progress and remaining questions The Lancet Neurology
New ICD-10-CM Codes: Z11.7: "Encounter for testing for latent tuberculosis infection". Z86.15: "Personal history of latent tuberculosis infection". Z22.7: "Carrier of latent tuberculosis," which includes a previous positive test for TB infection without evidence of disease, but excludes: "nonspecific reaction to cell-mediated.

Tuberculous meningitis more questions, still too few answers The Lancet Neurology
The overall MRR was 1.79 (95%CI: 1.09-2.95) for TBM patients compared to the population control cohort. TBM patients in the age group 31-60 years at time of diagnosis had the highest relative risk of death (MRR 2.68; 95%CI 1.34-5.34). The TBM patients had a higher risk of death due to infectious disease, but not from other causes of death.

Cerebrovascular complications in tuberculous meningitis—A resonance imaging study in 90
A00-B99 - Certain infectious and parasitic diseases. A15-A19 - Tuberculosis. A17 - Tuberculosis of nervous system. A17.0 - Tuberculous meningitis. A17.1 - Meningeal tuberculoma. A17.8 - Other tuberculosis of nervous system. A17.9 - Tuberculosis of nervous system, unspecified. Code. Includes.

Tuberculous Meningitis in Patients Infected with the Human Immunodeficiency Virus NEJM
Tuberculosis (TB) is one of the most important infectious diseases and one of ten most common causes of death globally,1 with almost 10 million new cases per year and 1.5 million deaths (WHO report 2011).2 It is estimated that a third of the world's population is infected with TB of whom approximately 10% will develop clinically apparent disease. TB is also in the top 15 of causes of disease.

Tuberculous Meningitis in Patients Infected with the Human Immunodeficiency Virus NEJM
The 2024 edition of ICD-10-CM G03.8 became effective on October 1, 2023. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of G03.8 - other international versions of ICD-10 G03.8 may differ. meningoencephalitis ( G04.-) meningomyelitis ( G04.-) 097 Non-bacterial infection of nervous system except viral meningitis with mcc.
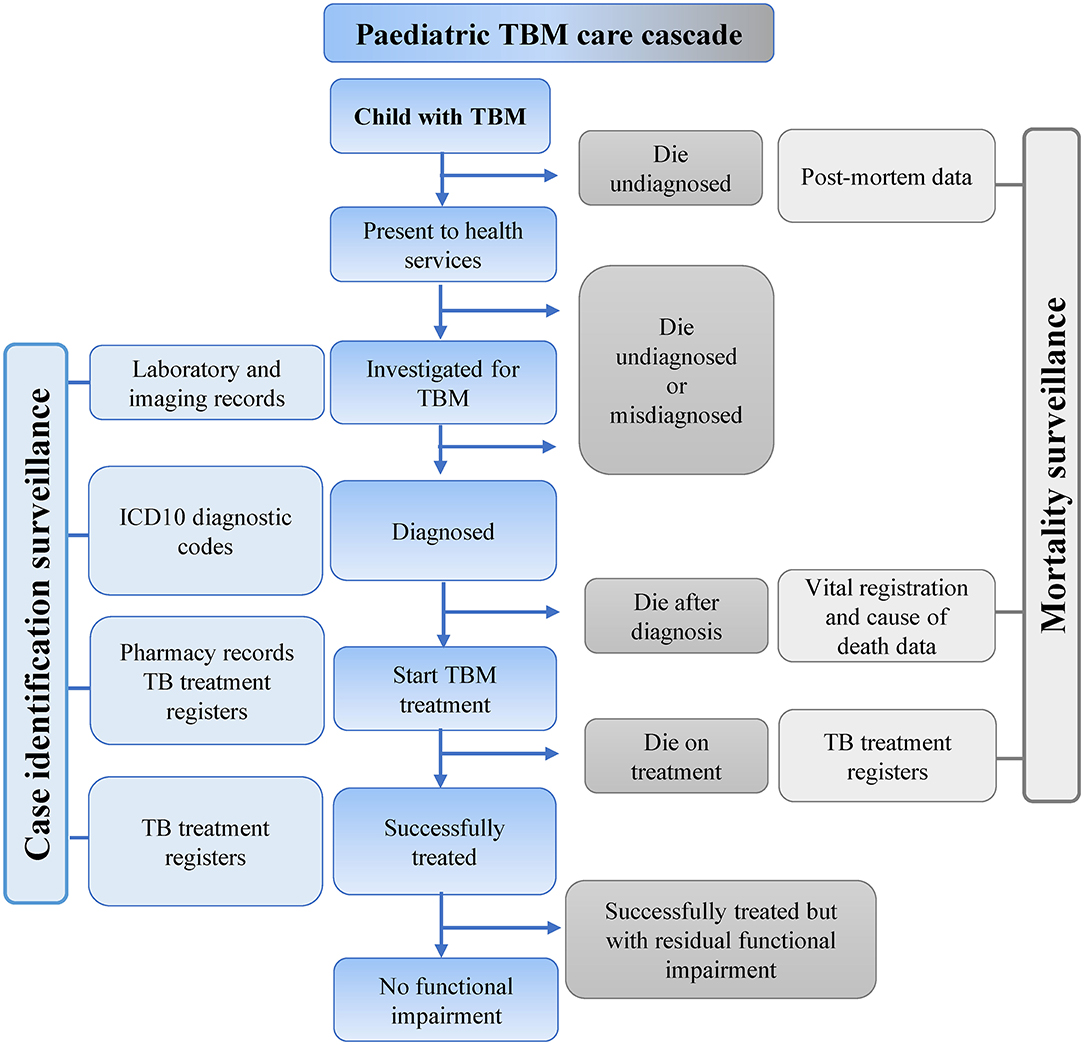
Frontiers Tuberculous Meningitis in Children A Public Health Emergency
TB ICD-10 Codes Cheat Sheet Tennessee TB Elimination Program 2 11/5/15 A15: Respiratory Tuberculosis. A17: TB of the Nervous System A17.0 TB meningitis A17.1 Tuberculoma of meninges A17.81 Tuberculoma of brain and spinal cord A17.82 Tuberculous myelitis A17.83 Tuberculous mononeuropathy A17.89 Other TB of nervous system TB of Other Organs.

Tuberculous Meningitis
Meningitis in bacterial diseases classified elsewhere G01-. ICD-10-CM has a coding convention that requires the underlying condition be sequenced first followed by the manifestation. Wherever such a combination exists there is a "use additional code" note at the etiology code,.
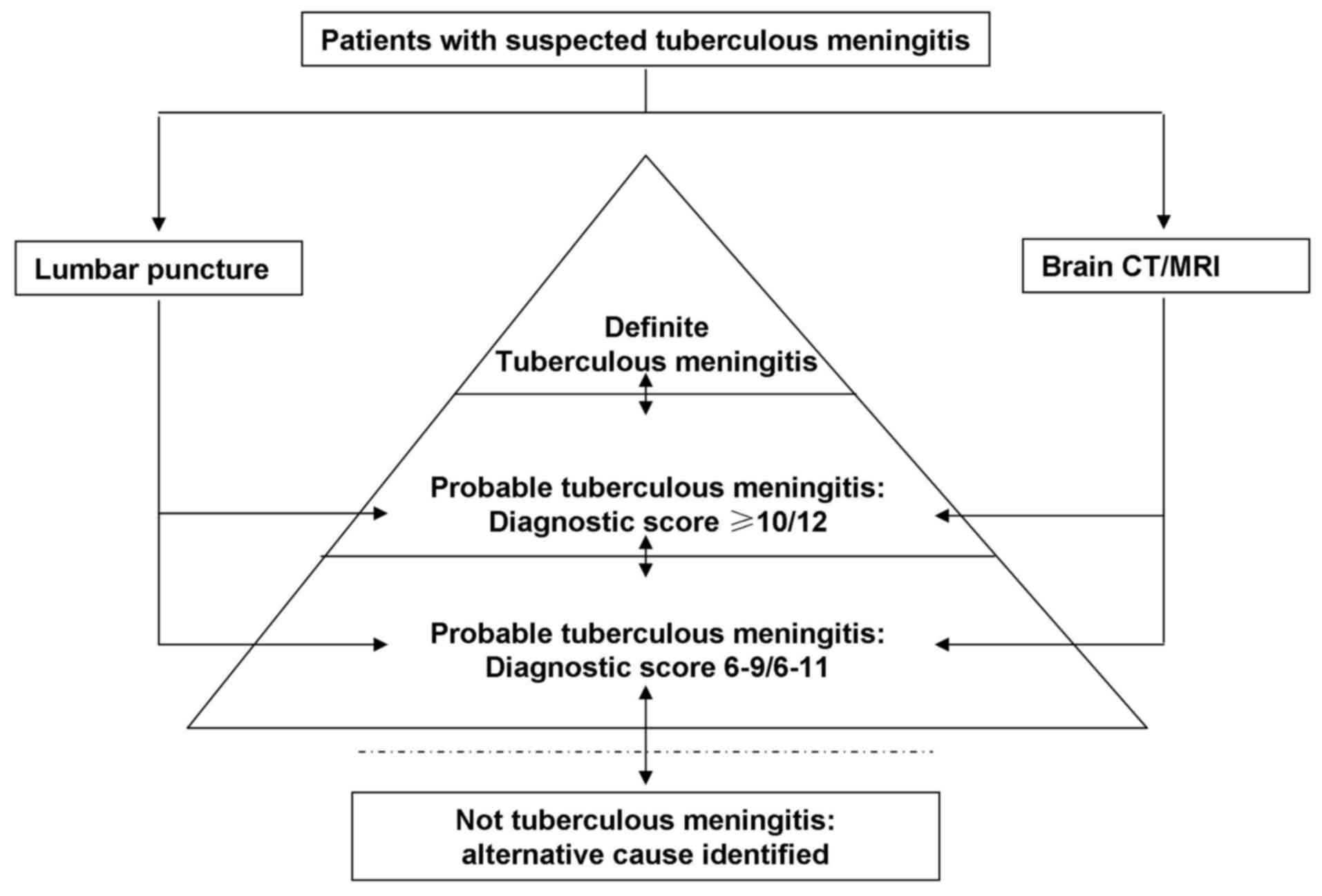
Tuberculous meningitis diagnosis and treatment in adults A series of 189 suspected cases
View ICD-10 Tree Chapter 1 - Certain infectious and parasitic diseases (A00-B99) » Tuberculosis (A15-A19) » Tuberculous meningitis (A17.0) Related MeSH Terms. A form of bacterial meningitis caused by MYCOBACTERIUM TUBERCULOSIS or rarely MYCOBACTERIUM BOVIS. The organism seeds the meninges and forms microtuberculomas which subsequently rupture.
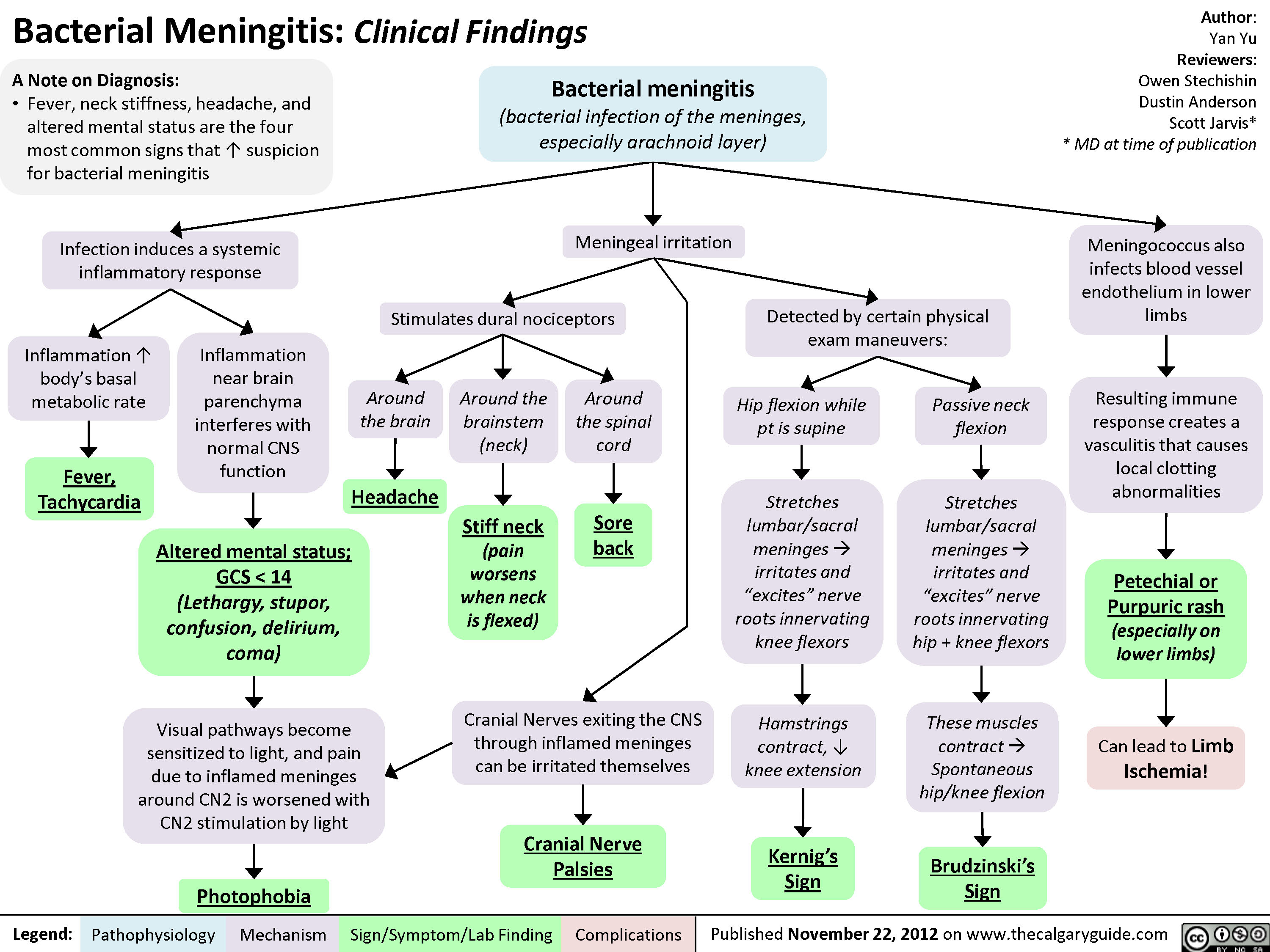
Bacterial Meningitis Clinical Findings Calgary Guide
A fever, stiff neck, and vomiting may follow. More severe symptoms can make you feel confused or drowsy, leading to a coma. Without treatment, this disease can threaten your life. Treatment involves taking antibiotics, often with corticosteroids. The best results occur when treatment begins early.