
Causes Of Gastritis And How To Deal With It
Diseases of esophagus, stomach and duodenum. ( K20-K31) Gastritis and duodenitis. ( K29) K29.70 is a billable diagnosis code used to specify a medical diagnosis of gastritis, unspecified, without bleeding. The code is valid during the current fiscal year for the submission of HIPAA-covered transactions from October 01, 2023 through September 30.

Icd 10 Code For Mild Inactive Chronic Gastritis
Radiographic features. While it may not often be needed for routine workup, gastritis may be seen as thickening of the gastric folds and wall. In severe cases, the gastric wall will demonstrate low attenuation compatible with submucosal edema and inflammation. The mucosa may also enhance due to hyperemia and at times may give a layered.
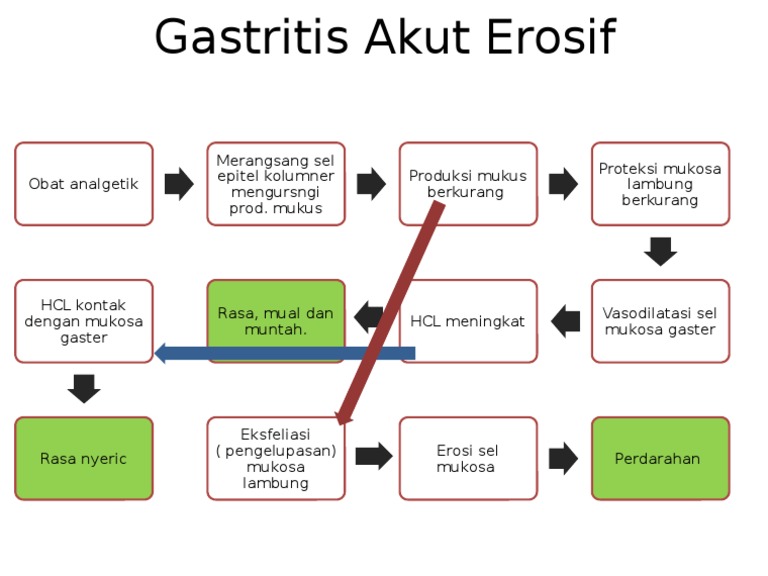
Patofisiologi Gastritis Akut Erosif
Erosive osteoarthritis; Erosive osteoarthrosis ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code K29.20 [convert to ICD-9-CM] Alcoholic gastritis without bleeding Alcoholic gastritis; Gastritis, alcoholic ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code K29.01 [convert to ICD-9-CM] Acute gastritis with bleeding
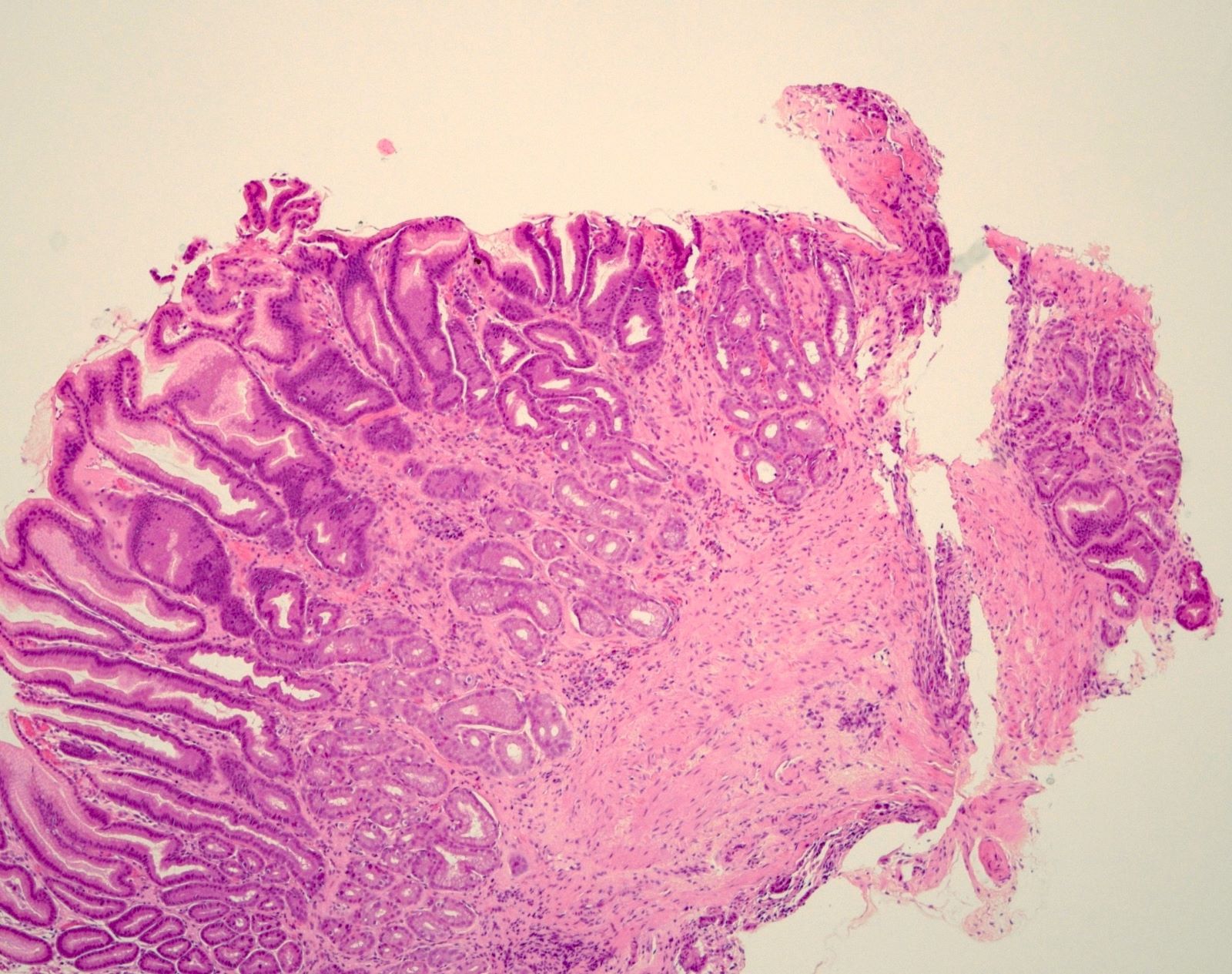
Pathology Outlines Erosive gastritis
ICD-10: К29.60 - other gastritis without bleeding Epidemiology. Both genders, at any age, can be affected when exposed to the causative agents of erosive gastritis Sites.. H. pylori gastritis will show active chronic gastritis with organisms which can be seen on H&E, special stain or immunostain. Low grade dysplasia will show hyperchromatic.

Gastritis Erosif PDF
ICD-10. ICD-10-CM Codes. Diseases of the digestive system. Diseases of esophagus, stomach and duodenum. Gastritis and duodenitis (K29) K28.9. K29.

What is Gastroenteritis? ICD10 Codes for Gastroenteritis YouTube
Introduction Gastritis refers to the inflammation of the gastric mucosa and is often used to describe the abnormal appearance of abnormal gastric mucosa on endoscopy or radiology. Gastritis encompasses infectious or immunological inflammation of the gastric mucosa and the host's response. [1]

P15 Sugano ICD10 Classification of Gastritis International Statistical Classification Of
Erosive gastritis is gastric mucosal erosion caused by damage to mucosal defenses. It is typically acute, manifesting with bleeding, but may be subacute or chronic with few or no symptoms. Diagnosis is by endoscopy. Treatment is supportive, with removal of the inciting cause and initiation of acid-suppressant therapy.

Icd 10 Code For Hx Of Gastritis
In the ICD-10, all the digestive diseases are classified under K code with different two-digit numbers. 6 However, H. pylori was not integrated into gastritis classification in the gastritis section (K29) of ICD-10, even though H. pylori gastritis is the predominant type of gastritis and clinically by far the most relevant because of its.

Gastritis Erosif Penyebab, Gejala, dan Cara Mengobati
K29.50 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2024 edition of ICD-10-CM K29.50 became effective on October 1, 2023. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of K29.50 - other international versions of ICD-10 K29.50 may differ.
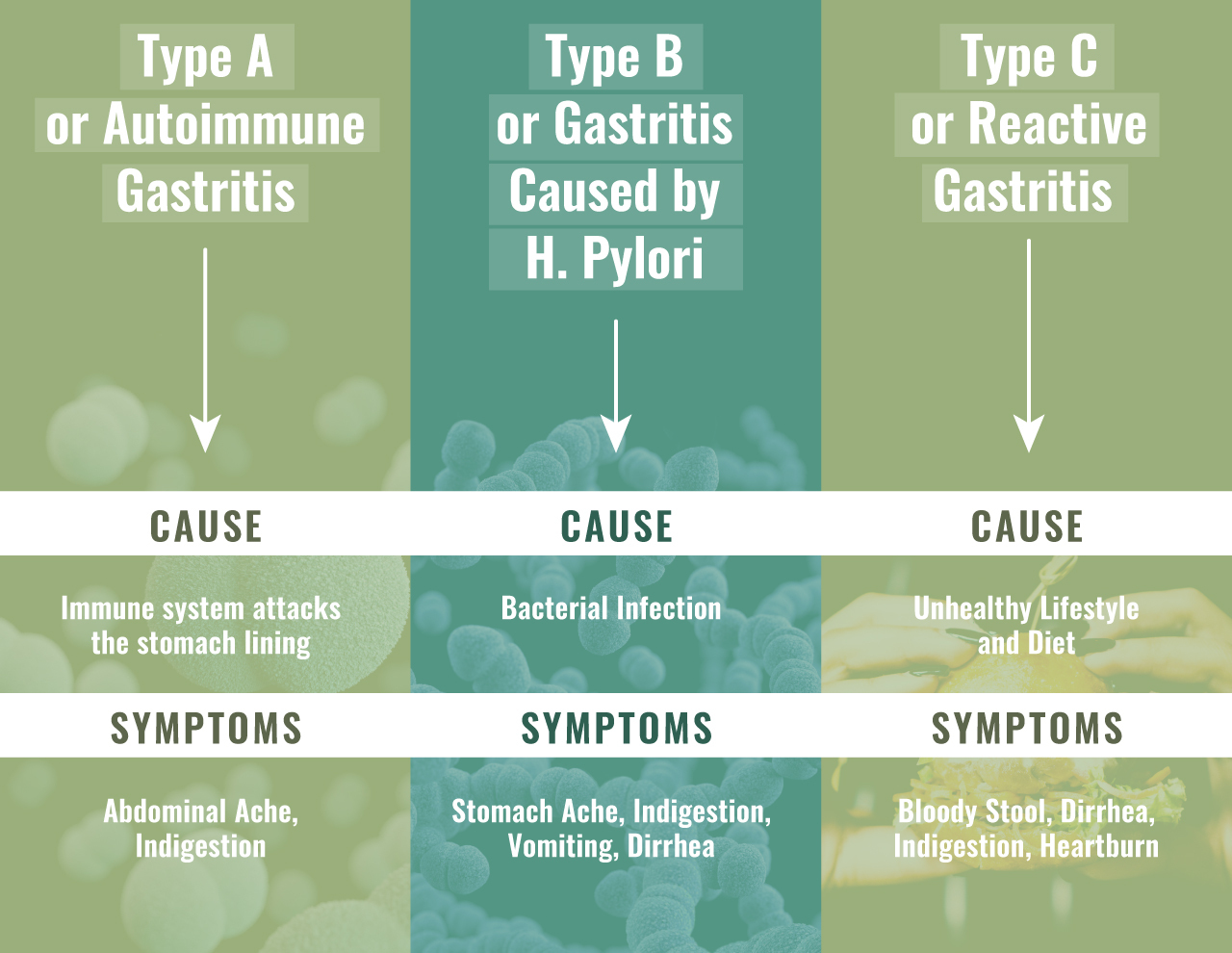
Chronic Gastritis What Is It, Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, And More
Gastritis is an inflammation of the stomach lining. The stomach lining is a mucus-lined barrier that protects the stomach wall. Weaknesses or injury to the barrier allows digestive juices to damage and inflame the stomach lining. Several diseases and conditions can increase the risk of gastritis. These include inflammatory conditions, such as.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/what-is-gastritis-symptoms-and-treatment-1741803-color-V1-3794a3dbece24d789ac724ed3bff5b4c.png)
Gastritis Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment
A type 1 excludes note is a pure excludes. It means "not coded here". A type 1 excludes note indicates that the code excluded should never be used at the same time as K29.A type 1 excludes note is for used for when two conditions cannot occur together, such as a congenital form versus an acquired form of the same condition.

What Is The Correct Icd 10 Code For Gastritis
Gastritis characterized by hypertrophy of the gastric mucosa with creation of giant gastric folds. It is associated with hypoalbuminemia due to albumin loss from the stomach. Signs and symptoms include nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, edema, and weight loss. Gastritis with hypertrophy of the gastric mucosa.

Icd 10 Code For Mild Inactive Chronic Gastritis
Erosive Gastritis is a type of gastritis that gradually eats away at our stomach lining. This is caused by acid, alcohol, bile, or certain recreational drugs. Its most common cause is using non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (or NSAIDs for short). By eating away at our stomach linings, Erosive Gastritis will give rise to ulcers.

Acute erosive gastritis ROQED
The purpose of this Clinical Practice Update Expert Review is to provide clinicians with guidance on the diagnosis and management of atrophic gastritis, a common preneoplastic condition of the stomach, with a primary focus on atrophic gastritis due to chronic Helicobacter pylori infection—the most common etiology—or due to autoimmunity. To date, clinical guidance for best practices related.
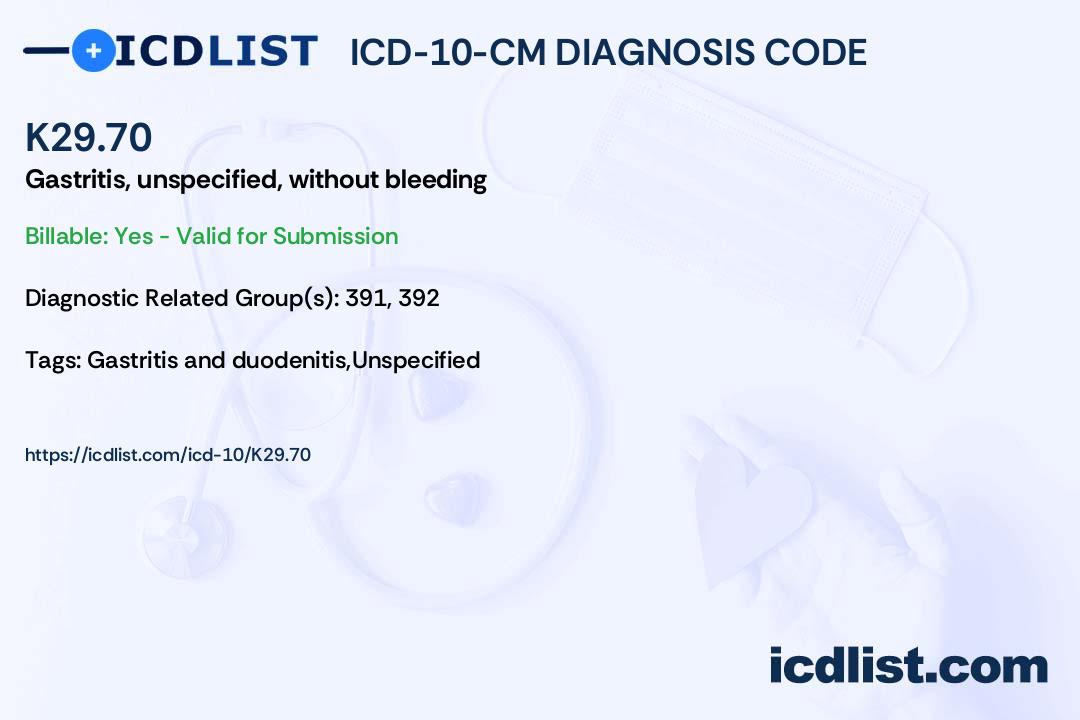
ICD10CM Diagnosis Code K29.70 Gastritis, unspecified, without bleeding
Pyloritis Suppurative gastritis ICD-10-CM K29.60 is grouped within Diagnostic Related Group (s) (MS-DRG v41.0): 391 Esophagitis, gastroenteritis and miscellaneous digestive disorders with mcc 392 Esophagitis, gastroenteritis and miscellaneous digestive disorders without mcc

Icd 10 Cm Code For Acute Hemorrhagic Gastritis
eosinophilic gastritis or gastroenteritis ( K52.81) Zollinger-Ellison syndrome ( E16.4) The following code (s) above K29 contain annotation back-references that may be applicable to K29 : K00-K95 Diseases of the digestive system K20-K31 Diseases of esophagus, stomach and duodenum Code History