
Figure 8 from The periosteum. Part 1 Anatomy, histology and molecular biology. Semantic Scholar
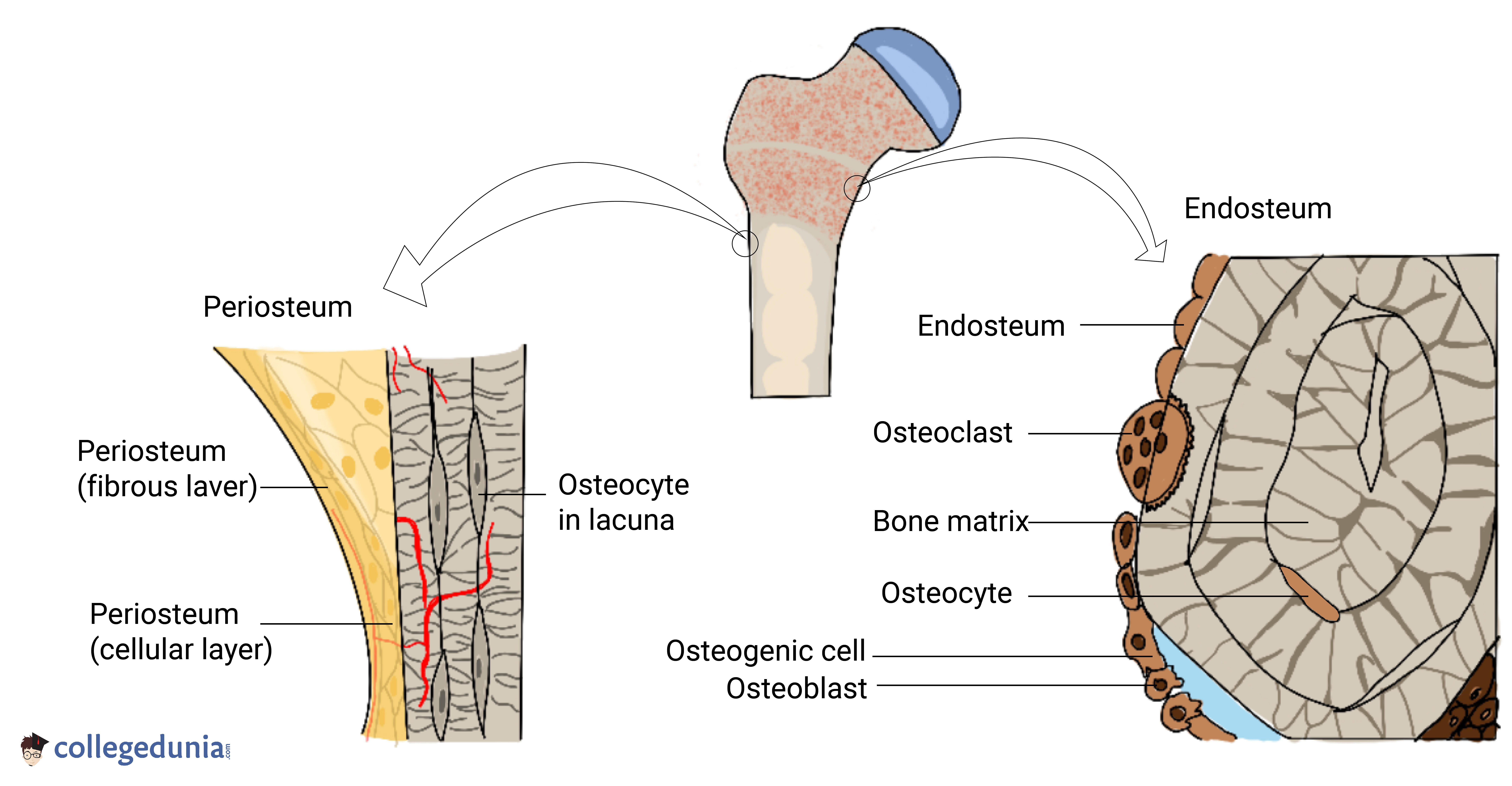
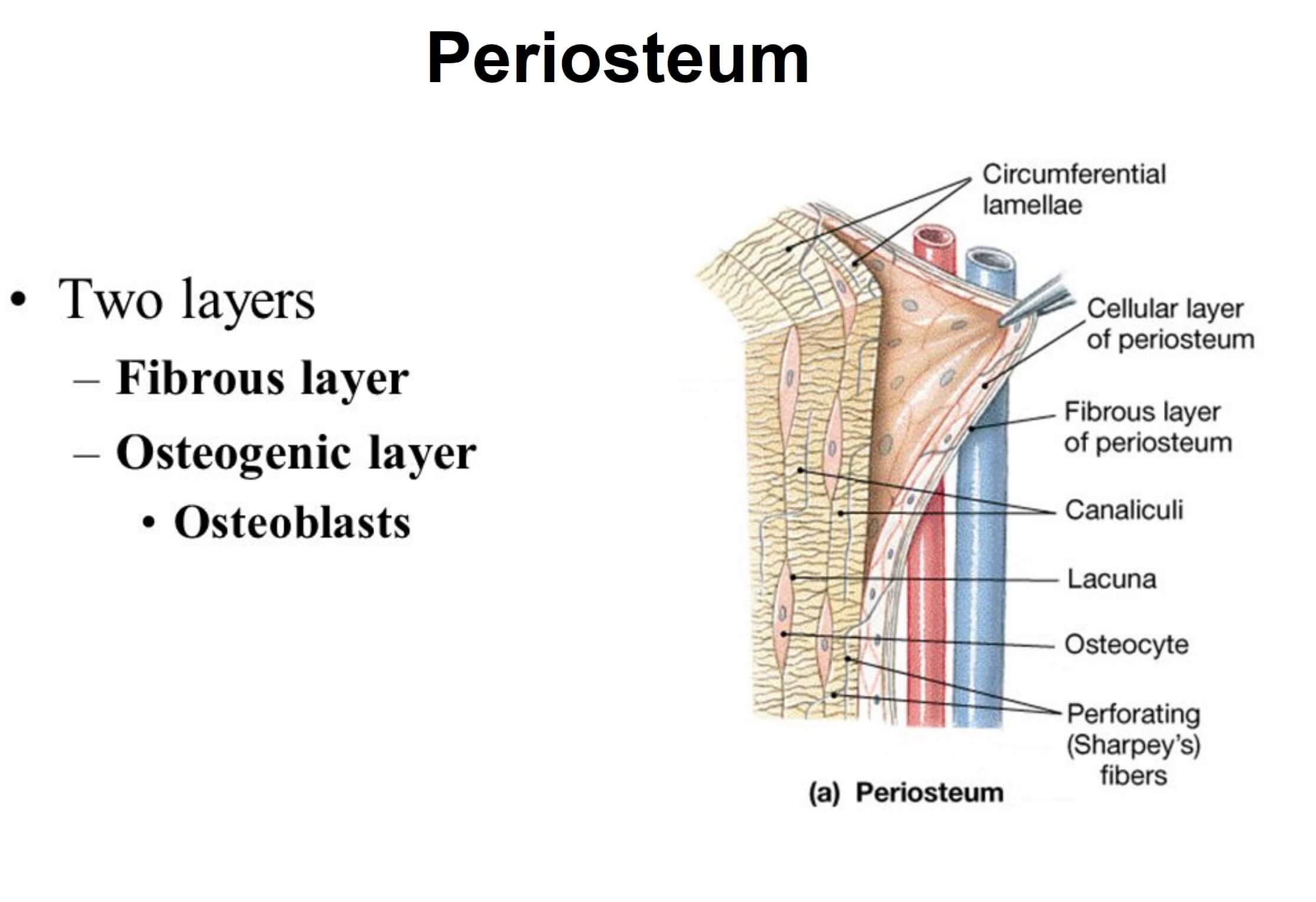
The periosteum is composed of two layers and is found on most surfaces of bones. The inner layer, or osteogenic layer, helps with bone model and remodel. The outer layer, or fibrous layer, is a.
Medical Massage Courses & Certification Science of Massage Institute » PERIOSTAL MASSAGE. PART
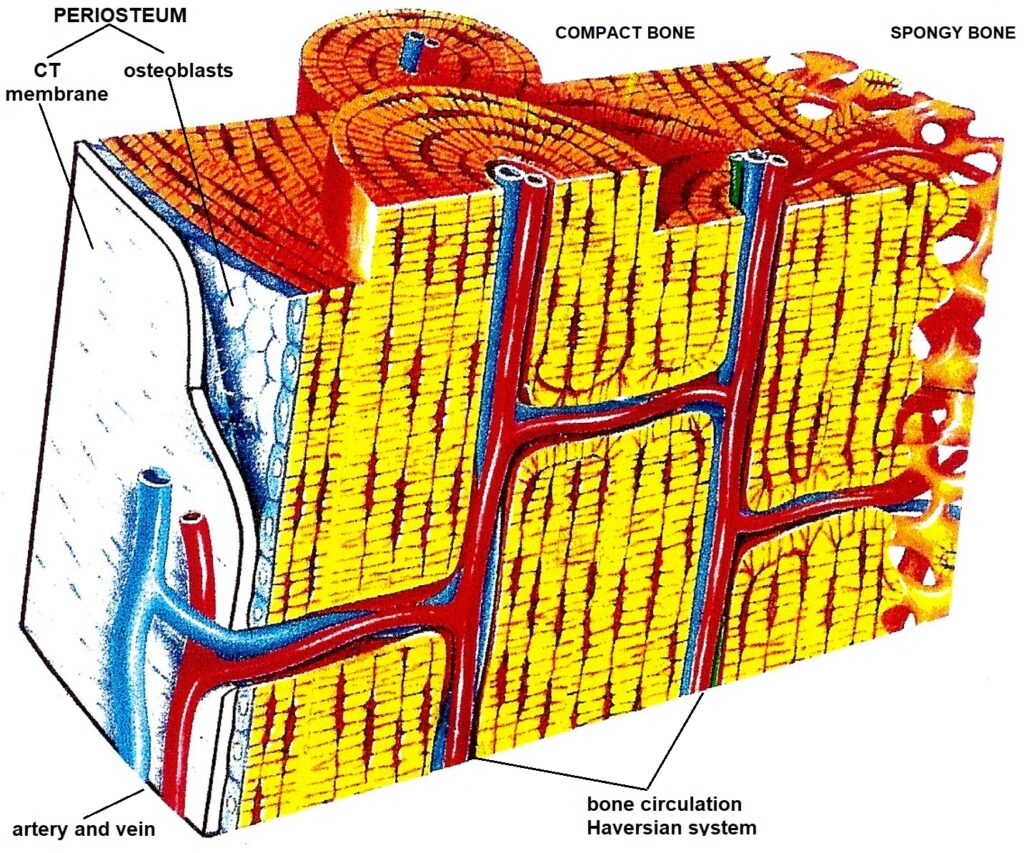
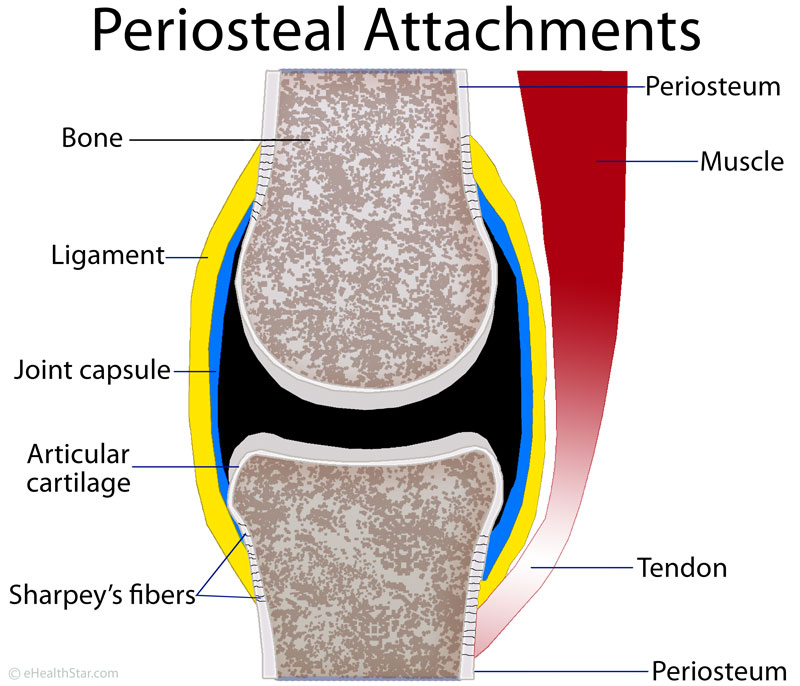
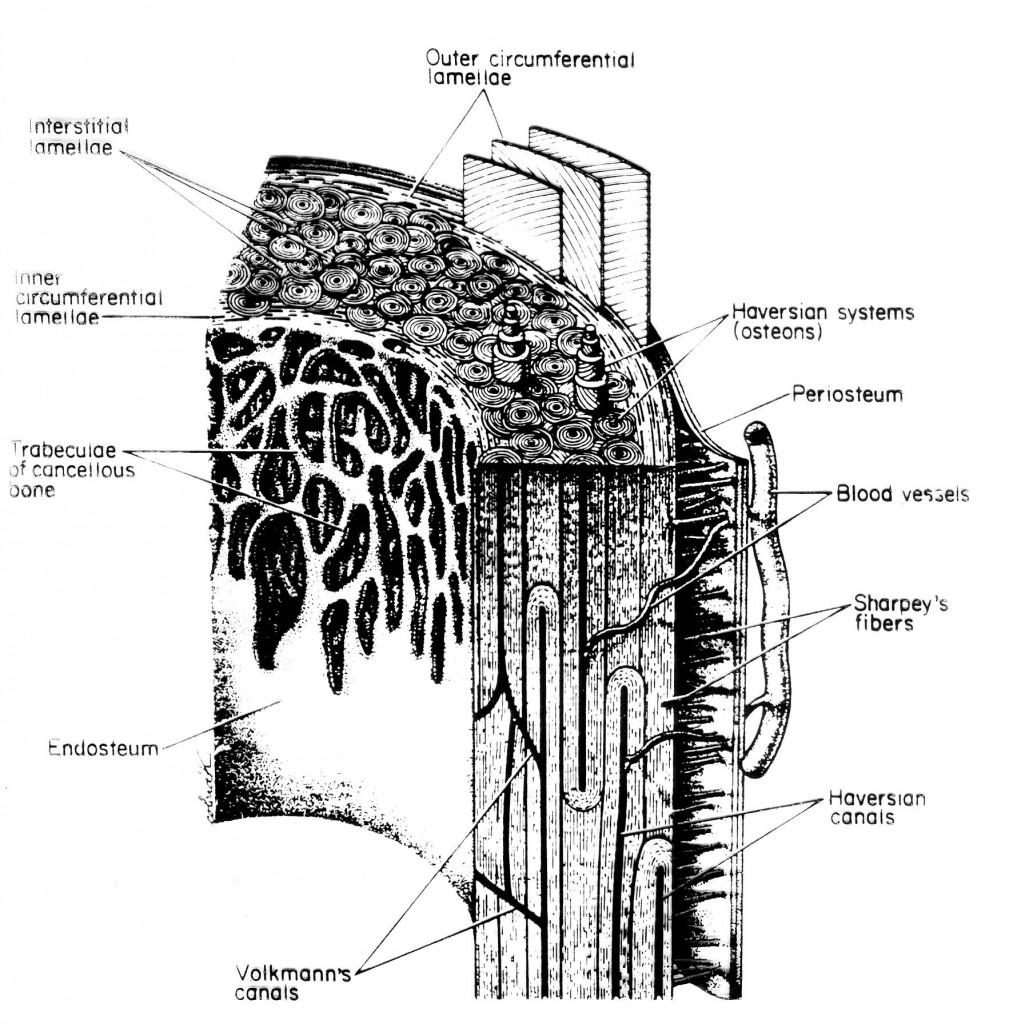
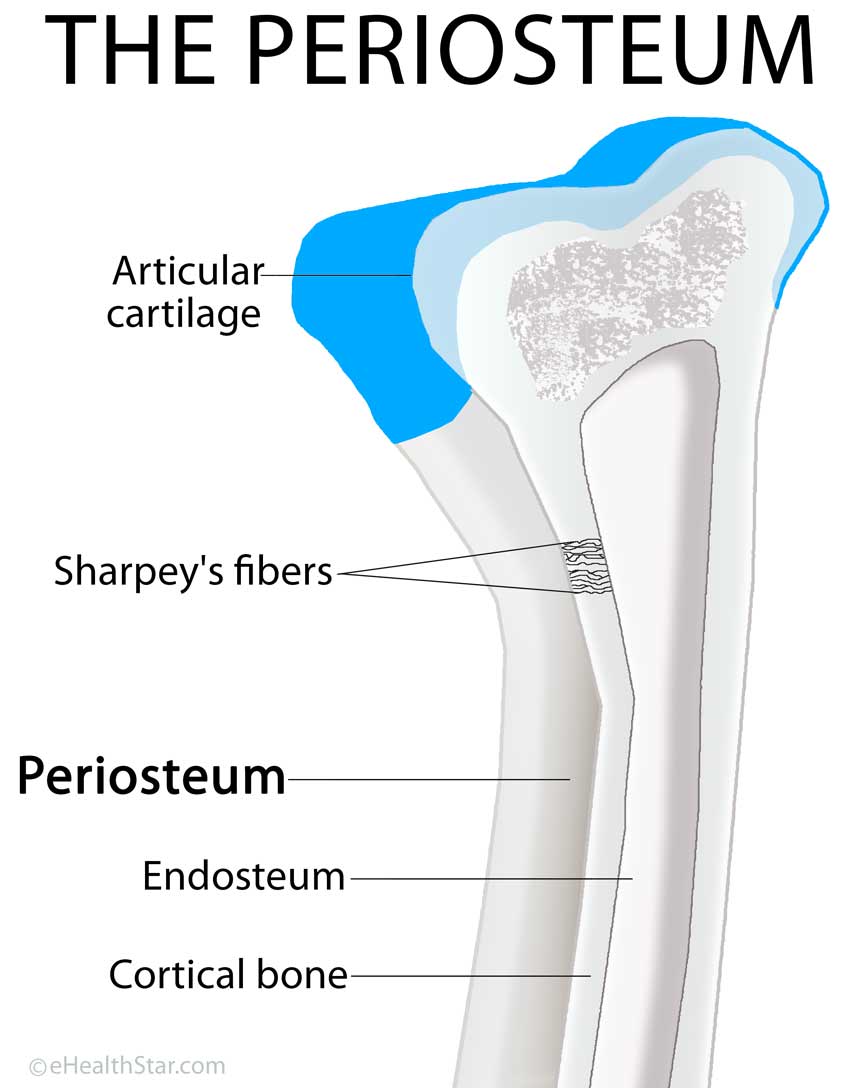
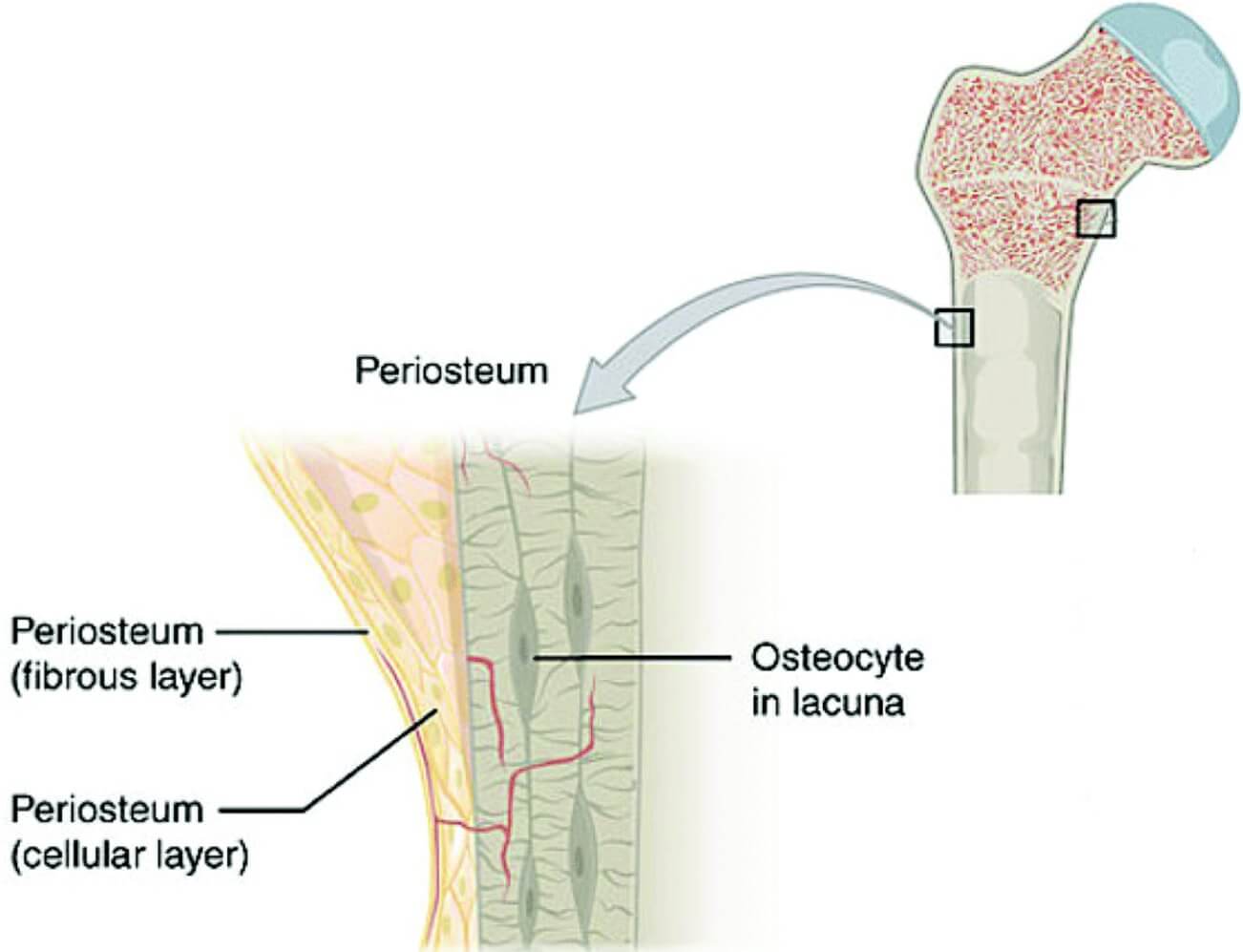
The periosteum is a thin membrane covering all bone surfaces except for articular, tendon insertions and sesamoid bone surfaces [].The periosteum is firmly anchored to the underlying bone via Sharpey's fibers [].The simple appearance of the periosteum belies its complexity as a composite structure that provides physical protection for the bone, a mechano-sensor for sensing mechanical loading.
Periosteum Physiopedia
Perimysium. This type of tissue is found in skeletal muscles and is responsible for the voluntary movements of bones. The perimysium also called interfascicular connective tissue, is a connective tissue sheath that surrounds individual muscle fascicles (bundles of muscle fibers), and separates them from other fascicles within the skeletal muscle.

Periosteum Function, Structure, Protection Britannica
The periosteum is a membranous tissue that covers the surfaces of bones. It is an intricate structure composed of an outer fibrous layer that gives structural integrity and an inner cambium layer that possesses osteogenic potential. During growth and development it aides in bone elongation and modelling, and when a bone is fractured.
Periosteum Anatomy, Functions, and Damage
1/3. Synonyms: none. Osteoblasts are bone-forming cells derived from osteoprogenitor stem cells which arise from mesenchymal tissue. They are mostly located in the periosteum and the endosteum but may also occur within compact bone, in regions of remodeling. Histologically, active osteoblasts, which are engaged in bone matrix synthesis, appear.
Periosteum Definition, Location, Anatomy, Histology and Function eHealthStar
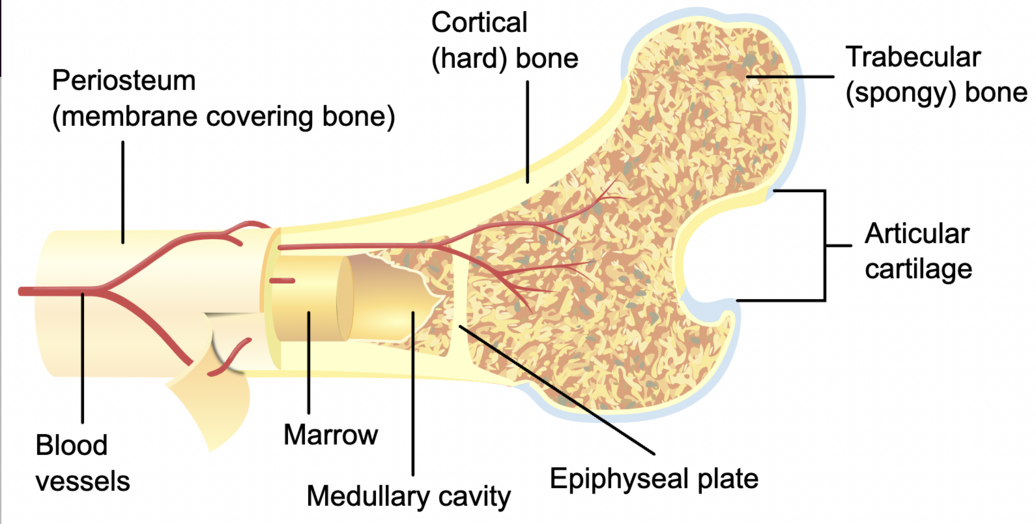
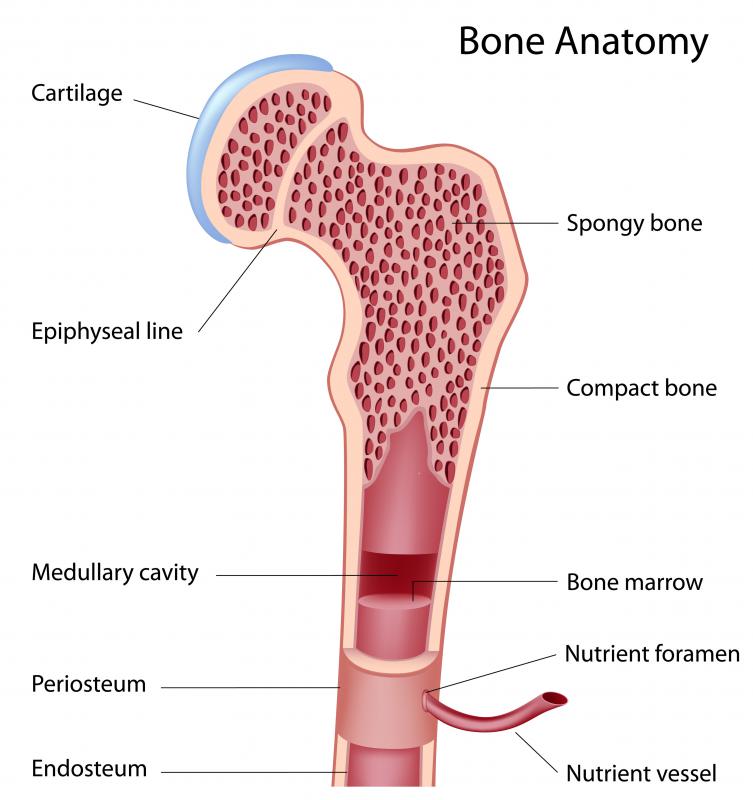
The periosteum is a fibrous sheath that covers bones. It contains the blood vessels and nerves that provide nourishment and sensation to the bone. The periosteum tends to be thicker in younger people. The thickness decreases when the bones are mature. The periosteum also allows bone to grow and heal after fracture.
Periosteum Definition, Function, Location and Pictures
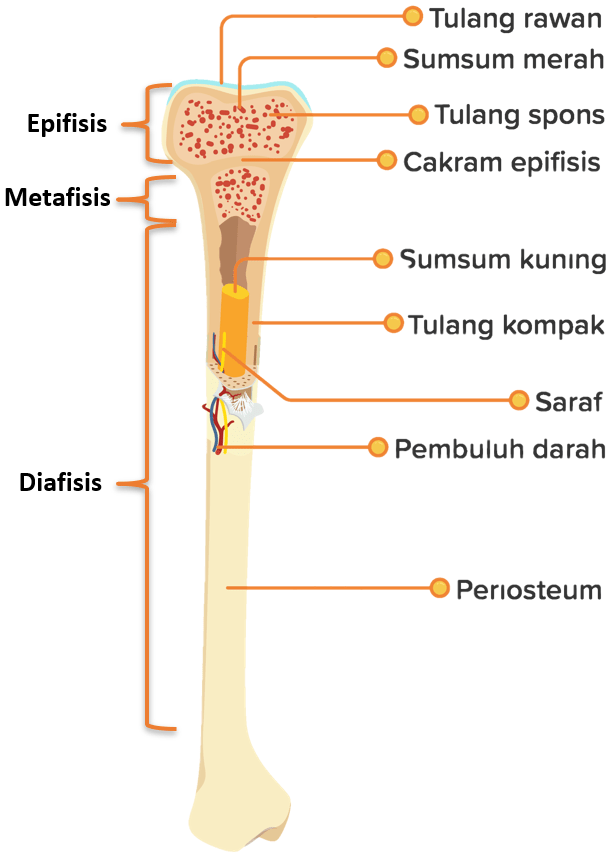
Fungsi Periosteum. Pada dasarnya Periosteum membantu dalam melayani fungsi yang diantaranya ialah sebagai penahan atas tendon dan juga ligamen, Dimana ia akan membantu mencret darah agar dapat masuk dan keluar dengan baik dari tulang dan juga membantu dalam masa perkembangan tulang.. Selain itu periosteum ialah merupakan salah satu bagian yang sangat penting atas sistem kerangka dan kerap.
What Is the Function of Periosteum? (with pictures)
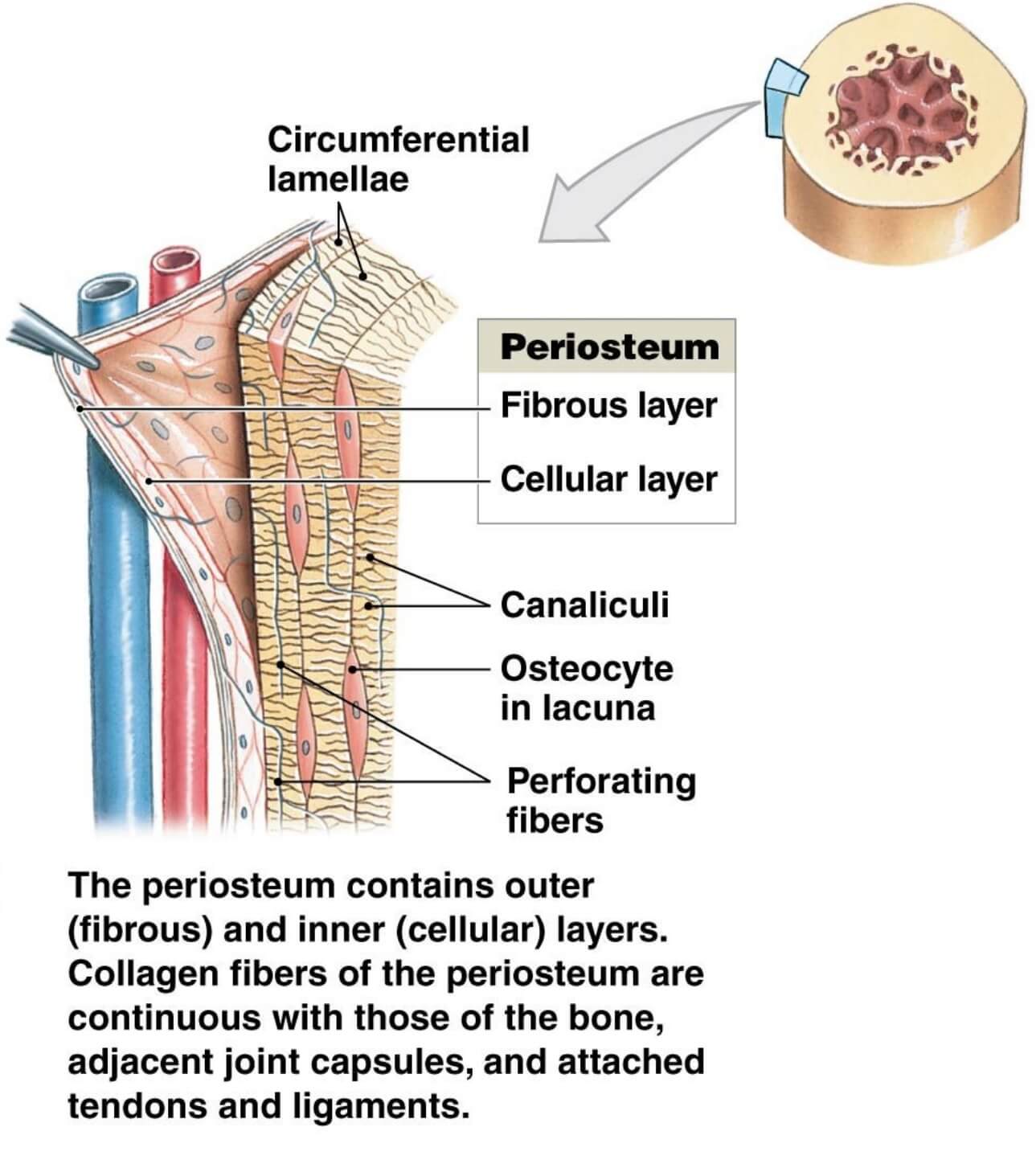
periosteum, dense fibrous membrane covering the surfaces of bones, consisting of an outer fibrous layer and an inner cellular layer (cambium).The outer layer is composed mostly of collagen and contains nerve fibres that cause pain when the tissue is damaged. It also contains many blood vessels, branches of which penetrate the bone to supply the osteocytes, or bone cells.
Pada tulang paha, bagian yang berfungsi untuk memf...
The periosteum is a membranous tissue that covers the surfaces of your bones. The only areas it doesn't cover are those surrounded by cartilage and where tendons and ligaments attach to bone.

periosteum diagram Diagram Quizlet
Periosteum. Sebagai permukaan terluar dari tulang, bagian ini berisi pembuluh darah dan saraf yang membantu memberikan nutrisi ke tulang.. Salah satu fungsi utama tulang datar adalah melindungi organ vital dari cedera. Misalnya, tulang tengkorak melindungi otak, tulang rusuk dan sternum melindungi jantung dan paru-paru, serta tulang panggul.
Periosteum Definition, Location, Anatomy, Histology and Function eHealthStar
The Anatomy of the Periosteum. In 1925, Blaisdell published a classic paper in which he describes the periosteum as a structure comprised of 2 layers, with osteoblast-like cells in the inner layer (Blaisdell, 1925).We now know in more detail that the outer "fibrous" layer consists of fibroblasts, collagen, and elastin along with a nerve and microvascular network (Allen et al., 2004).
What is Periosteum? News Dentagama
Fungsi. Periosteum melayani beberapa fungsi termasuk penahan tendon dan ligamen, membantu mencret darah masuk dan keluar dari tulang dan membantu pertumbuhan tulang. Periosteum merupakan bagian penting dari sistem kerangka dan ditemukan sebagai membran di sepanjang bagian luar tulang. Membran ini terdiri dari jaringan ikat padat tidak teratur.

Periosteum of Bone Definition & Function Video & Lesson Transcript
The periosteum is a thin membrane on the outside of your bones. It serves to protect your bones but also has the ability to help them heal. It can even help your body grow new bone when damage occurs.
What is Periosteum? News Dentagama
The periosteum is the medical definition for the membrane of blood vessels and nerves that wraps around most of your bones. Periosteum is pronounced peRRY-OSS-tee-um. It's what delivers bones their blood supply and gives them their sense of feeling. Special cells in the periosteum help your bones grow and develop and repairs them after a bone.
What is Periosteum? News Dentagama
Conclusion. The periosteum is a complex structure composed of an outer fibrous layer that lends structural integrity and an inner cambium layer that possesses osteogenic potential. During growth and development it contributes to bone elongation and modeling, and when the bone is injured, participates in its recovery.

Two main types of periosteum osteogenesis intramembranous ossification... Download Scientific
Quick Facts. The periosteum is a specialized connective tissue covering all bones of the body; in adults, it consists of two layers that are not sharply defined, the external layer being a network of dense connective tissue containing blood vessels, and the internal layer composed of more loosely arranged collagenous bundles with spindle-shaped connective tissue cells, osteogenic precursor.