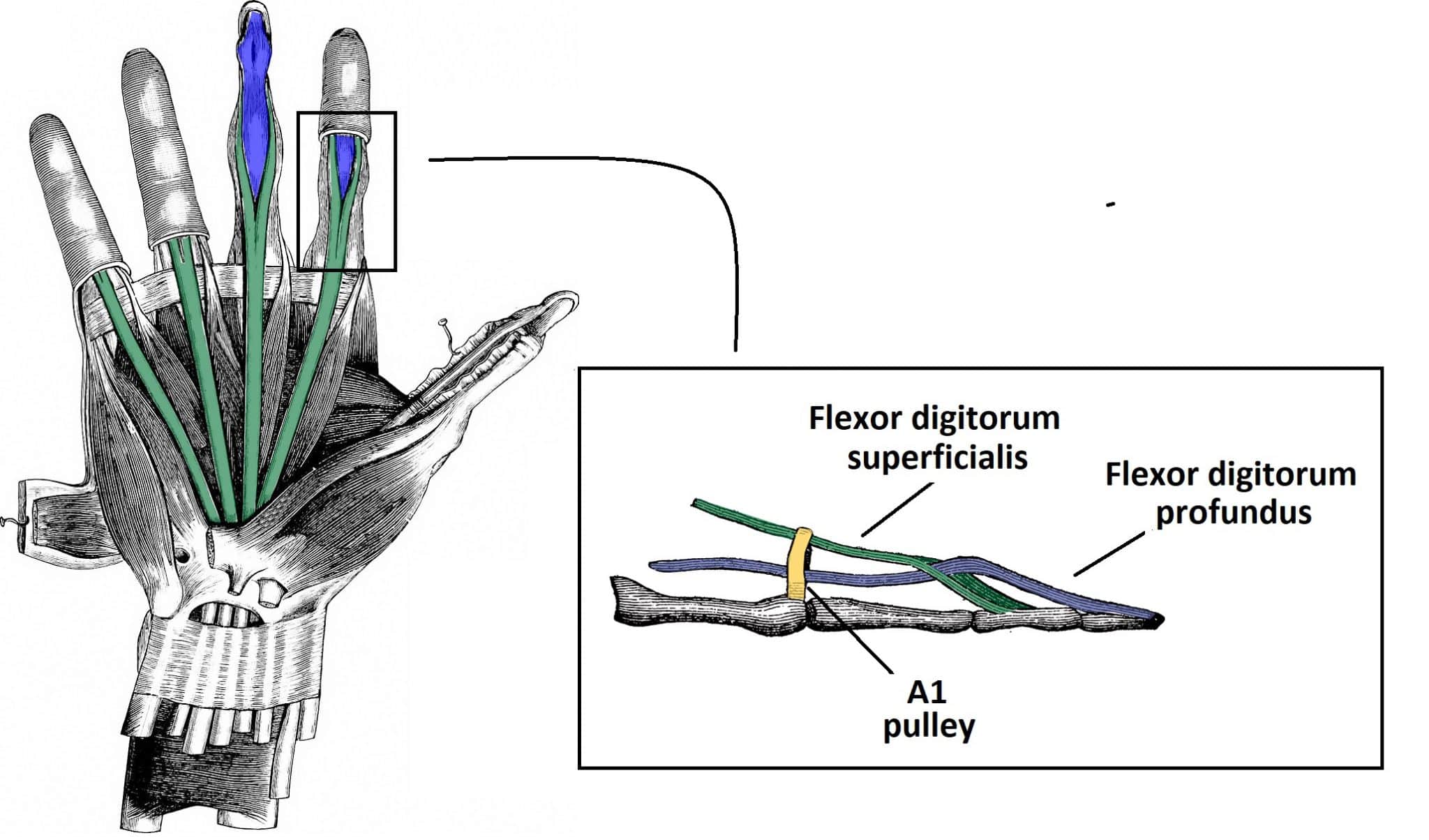
The Flexor Pulley System of the Hand Annular Cruciate Oblique TeachMeAnatomy
The flexor pulley system of the hand is a complex structure that co-ordinates flexion of the digits. It consists of: Long flexor tendons - and their associated synovial sheaths.; Annular pulleys - 5 associated with each finger, 2 associated with the thumb.; Cruciate pulleys - 3 associated with each finger.; Oblique pulley - 1 associated with the thumb.

Flexor Tendon Injuries
Flexor pollicis brevis is the most medial of the thenar muscles. It lies medial to the abductor pollicis brevis and opponens pollicis muscles, while it is lateral to adductor pollicis muscle.. Along its course, the superficial head of the muscle passes along the radial side of the tendon of flexor pollicis longus, whereas the deep head passes deep to the same tendon.

Flexor Digiti Minimi Pedis Learn Muscles
summary. Flexor Tendon Injuries are traumatic injuries to the flexor digitorum superficialis and flexor digitorum profundus tendons that can be caused by laceration or trauma. Diagnosis is made clinically by observing the resting posture of the hand to assess the digital cascade and the absence of the tenodesis effect.
Flexor Digitorum Profundus Origin And Insertion
DISCUSSION. Flexor sheath infections, also known as infected tenosynovitis, are a relatively common infection of the hand with a prevalence ranging from 2.5% to 9.4% of hand infections. 3 If misdiagnosed, flexor sheath infections can lead to serious, life-threatening consequences. Digital flexor sheaths are a closed continuous synovial system that invest the flexor digitorum profundus and.

Flexor Tendon Injuries
Flexor carpi radialis is a fusiform muscle located in the anterior forearm. It belongs to the superficial layer of the anterior forearm compartment, along with the pronator teres, flexor carpi ulnaris, palmaris longus and flexor digitorum superficialis muscles. All these muscles share the function of flexing the hand on the wrist, which is why.

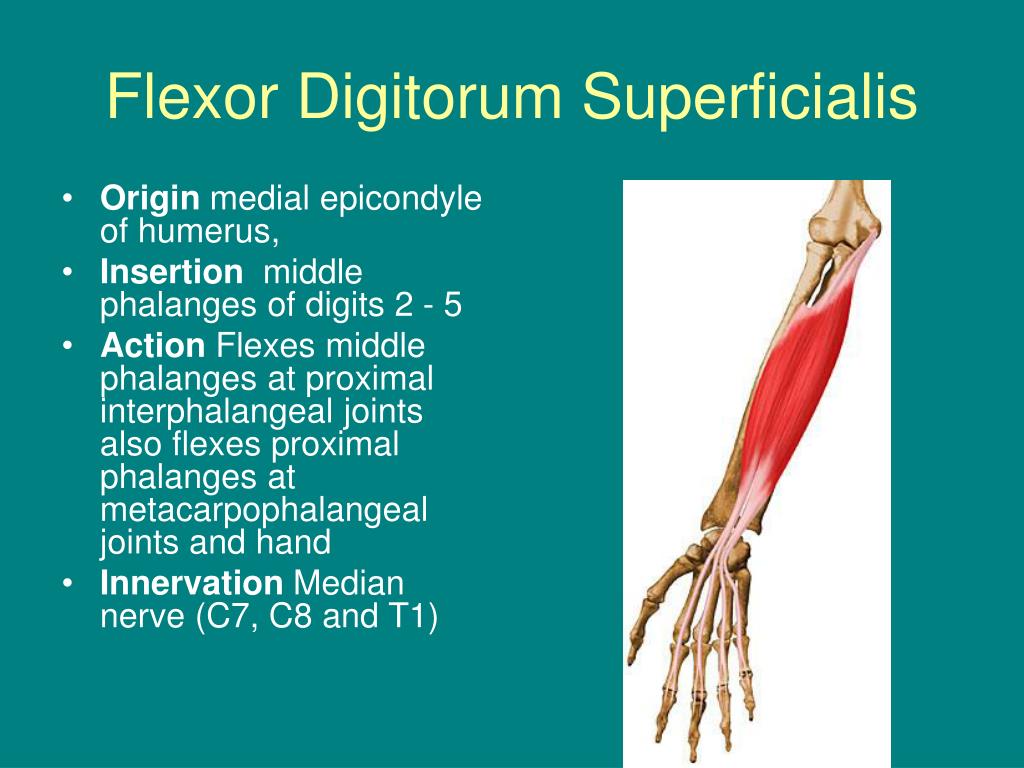
Anatomy of Flexor Digitorum Superficialis —
Tenosynovitis is usually painful. It can affect tendons connected to any muscle that helps one of your limbs push, pull or extend (your flexor and extensor muscles). You might also have trouble moving the affected part of your body like you usually can. The most common places tenosynovitis affects include your: Hands. Wrists. Feet.
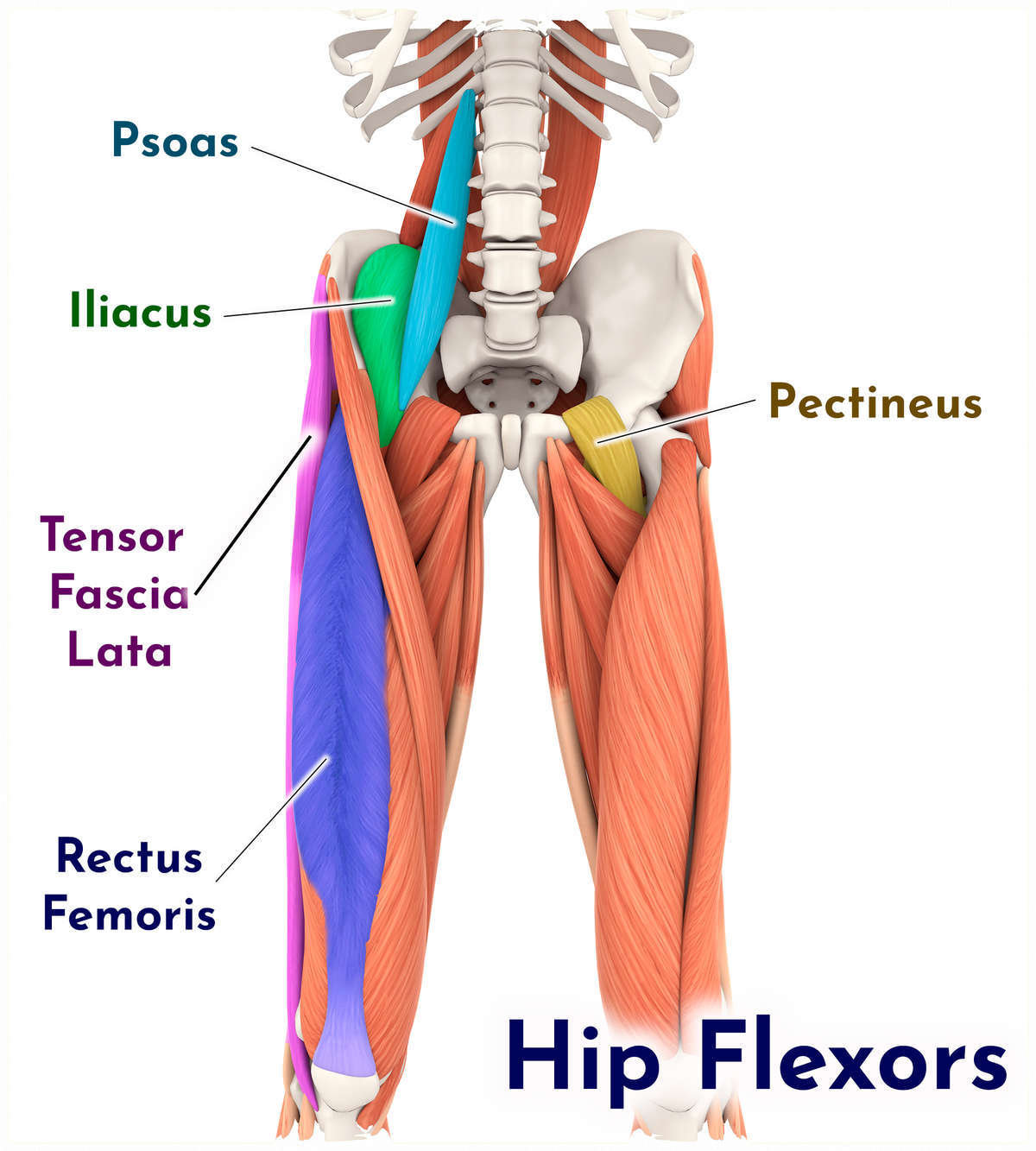
Hip Flexors Combo — ElasticSteel
The withdrawal response (reflex), also known as the nociceptive flexion reflex, is an automatic response of the spinal cord that is critical in protecting the body from harmful stimuli. The first known definition of a reflex dates back to 1649 when René Descartes noted that specific bodily movements occurred instantaneously and independent of the process of thought. Modern definitions state.
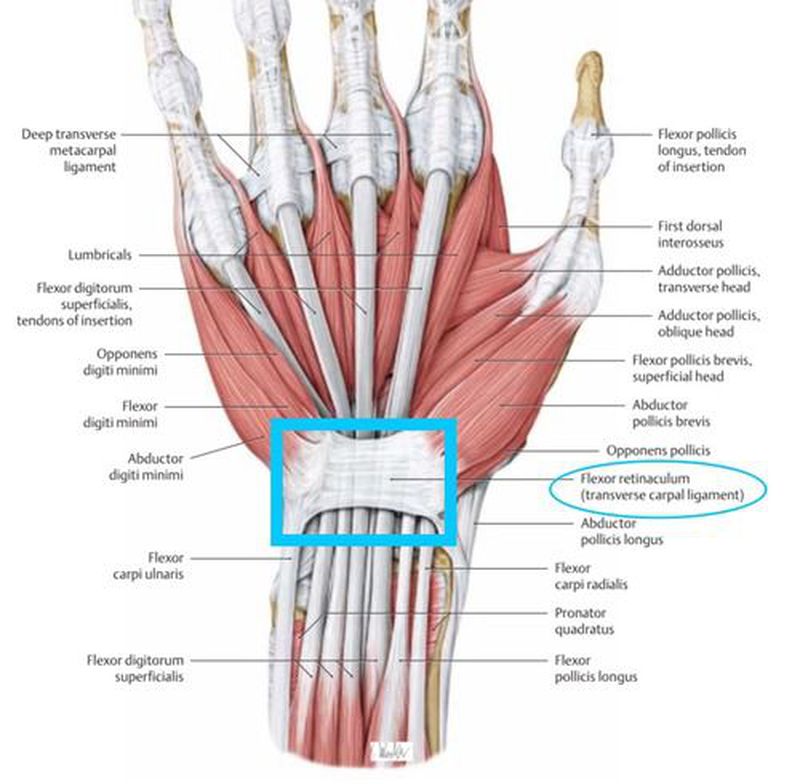
Flexor Retinaculum MEDizzy
Withdrawal reflex. The withdrawal reflex ( nociceptive flexion reflex or flexor withdrawal reflex) is a spinal reflex intended to protect the body from damaging stimuli. [1] The reflex rapidly coordinates the contractions of all the flexor muscles and the relaxations of the extensors in that limb causing sudden withdrawal from the potentially.

Repin to revise the muscle facts about the flexor digitorum superficialis muscle with Kenhub
Finger Flexors Flexor digitorum profundus (FDP) tendons. FDP tendons help bend the index, middle, ring, and small fingers at the fingertip joint. The muscle that moves these tendons is a common muscle belly shared by all the fingers. The muscle belly divides into 4 tendons. They run down the forearm and within the carpal tunnel.

Anatomy Of The Flexor Digitorum Profundus Muscle Everything You Need To Know Dr. Nabil
Tenosynovitis is a broad term describing the inflammation of the fluid-filled synovium within the tendon sheath. It commonly manifests as pain, swelling, and contractures, depending on the etiology. The condition can affect any tendon in the body surrounded by a sheath but has a predilection for the hand, wrist, and foot. A basic understanding of the tendon anatomy allows the clinician to.
What is a Hip Flexor? Plano Orthopedic & Sports Medicine Center
Structure. The flexor hallucis longus is situated on the fibular side of the leg. It arises from the inferior two-thirds of the posterior surface of the body of the fibula, with the exception of 2.5 cm. at its lowest part; from the lower part of the interosseous membrane; from an intermuscular septum between it and the peroneus muscles, laterally, and from the fascia covering the tibialis.
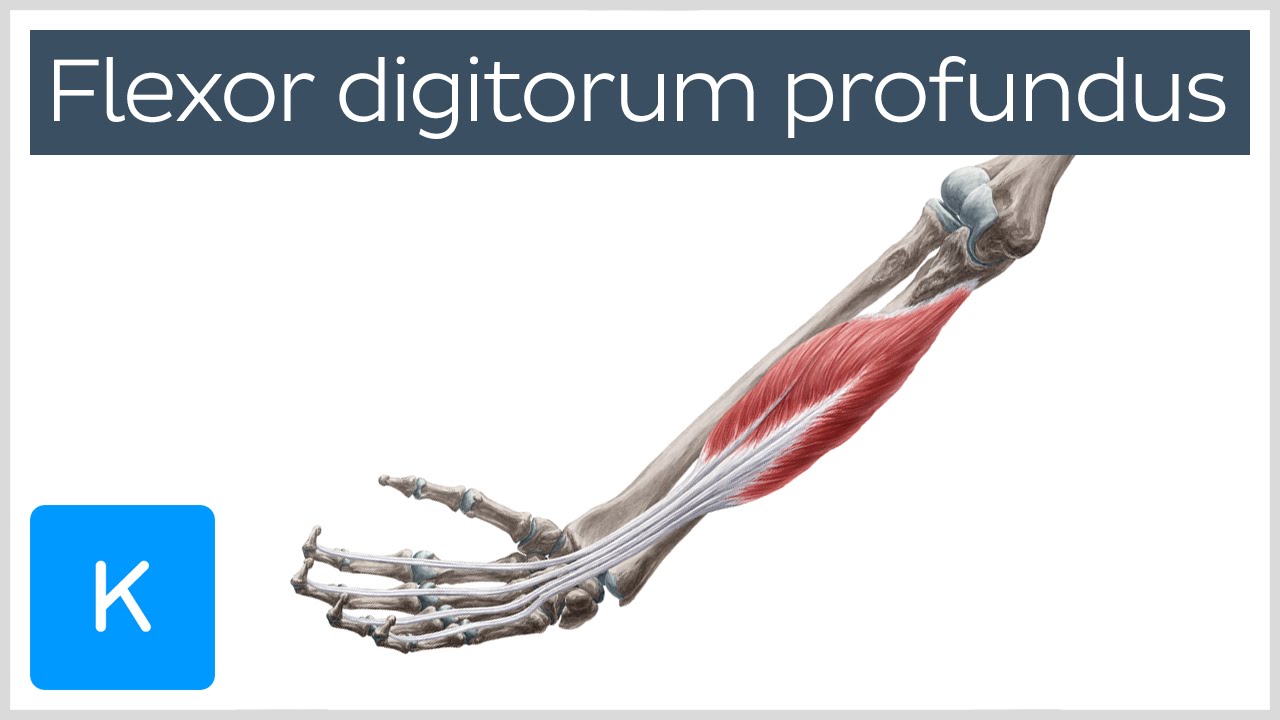
Flexor digitorum profundus muscle Origin, Insertion, Innervation & Function Anatomy Kenhub
Pronator Teres Syndrome (PTS) is a compression neuropathy of the median nerve at the elbow. It is not as common as compression at the wrist which is Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS). PTS and CTS present similarly, however PTS can be distinguished by a lack of sensation in the distribution of the palmar cutaneous branch of the median nerve (PCBMN.
Hip Flexor Anatomy Diagram Sexiz Pix
Superficial view. (Flexor digitorum brevis visible at center.) The flexor digitorum brevis is a muscle which lies in the middle of the sole of the foot, immediately above the central part of the plantar aponeurosis, with which it is firmly united. Its deep surface is separated from the lateral plantar vessels and nerves by a thin layer of fascia .

Flexor Digitorum Superficialis Flexor Digitorum Superficialis to Anterior Interosseous
Otot fleksor dan ekstensor adalah bagian dari sistem gerak tubuh atau yang disebut dengan sistem muskuloskeletal. Pada sistem ini, baik sendi, tulang, dan otot rangka tubuh akan bekerja sama untuk secara serempak menciptakan gerakan. Advertisement. Tubuh manusia terdiri dari ratusan otot yang diklasifikasikan menjadi tiga jenis, yaitu otot.
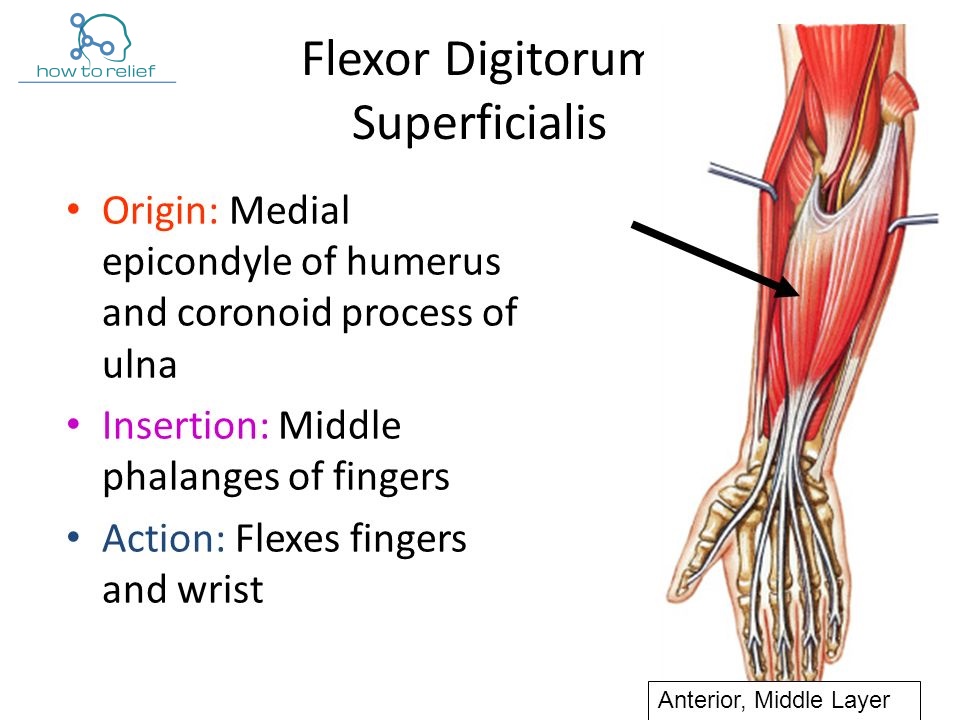
Flexor Digitorum Superficialis Origin, Insertion, Nerve Supply & Action » How To Relief
Flexor synergy patterns of the upper extremity after stroke commonly involve these main movements: External rotation and abduction of the shoulder. Flexion of the elbow. Supination or pronation of the forearm. Flexion of the wrist and fingers. In other words, whenever you try to move your affected arm, your shoulder will raise, your elbow will.
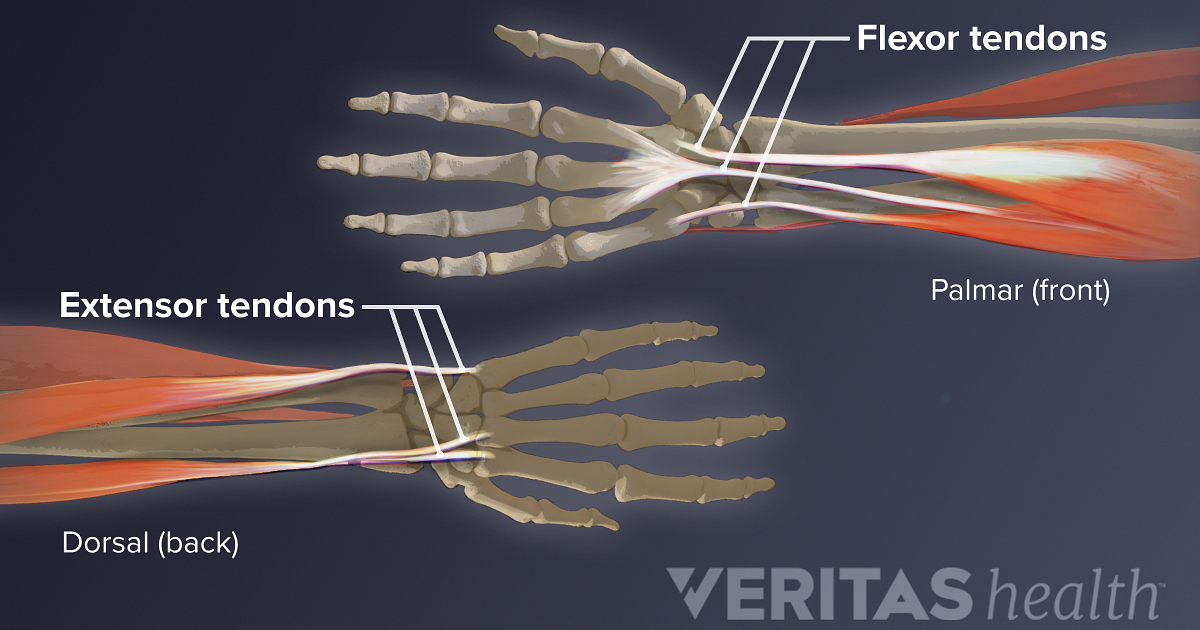
Wrist Flexor Anatomy
Figure 28.13. While walking, there must be coordinated, reciprocal activation of the extensor and flexor muscles of each leg; as an extensor is contracted (gray bar) the flexor must relax. Additionally, the muscle activation of one leg must be the opposite of the other leg, so the right extensor and the left flexor are activated at the same time.