
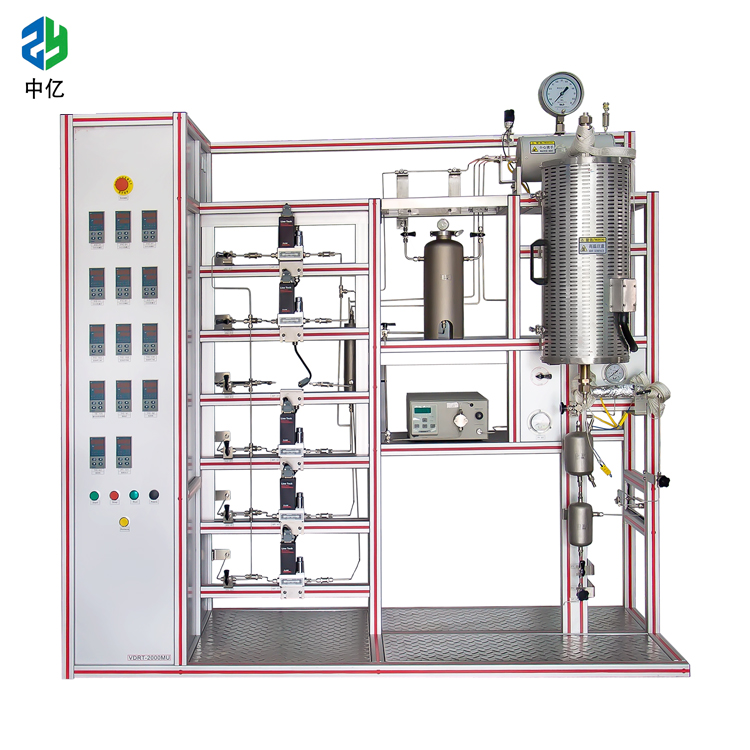
(a) The pilot fixed bed reactor; (b) reactor model. Download Scientific Diagram
The three regimes have different advantages and disadvantages, which we have outlined in Table 1. Mixed/hybrid bed reactors have a combination of advantages and disadvantages of both the packed.

Fixed Bed Multitube Reactor Kelompok 3 Kelas A2 Instrumentasi Proses YouTube
A multitube fixed bed reactor and the use of such a reactor for carrying out catalytic gas-phase reactions, in particular for carrying out exothermic and endothermic catalytic gas-phase reactions such as the preparation of phthalic anhydride (PA), acrylic acid, methacrylic acid (MAA), acrolein, maleic anhydride (MA), glyoxal, phosgene, hydrocyanic acid or vinyl formamide (VFA).

A schematic diagram of the fi xedbed multitubular FTS reactor (a)... Download Scientific Diagram
The goal of obtaining a better insight into fixed bed reactor behavior is being advanced by new simulation techniques (Dixon et al., 2006) and modern non-invasive experimental approaches (Gladden, 2003, Geske et al., 2013, Wehinger et al., 2016, Dong et al., 2017, Karthik et al., 2020). In particular, there is increasing use of 3-D particle.

Schematic diagram of a fixed bed reactor Download Scientific Diagram
tubular fixed-bed reactor, in which the catalyst is arranged in the tubes, and the heat carrier circu lates externally around the tubes (Fig. 1.1 B). Fixed-bed reactors with an integrated heat sup ply or removal are discussed in Chapter 4. Fixed-bed reactors for industrial syntheses are generally operated in a stationary mode (i.e.,

Schematic view of the singletube fixedbed reactor Download Scientific Diagram
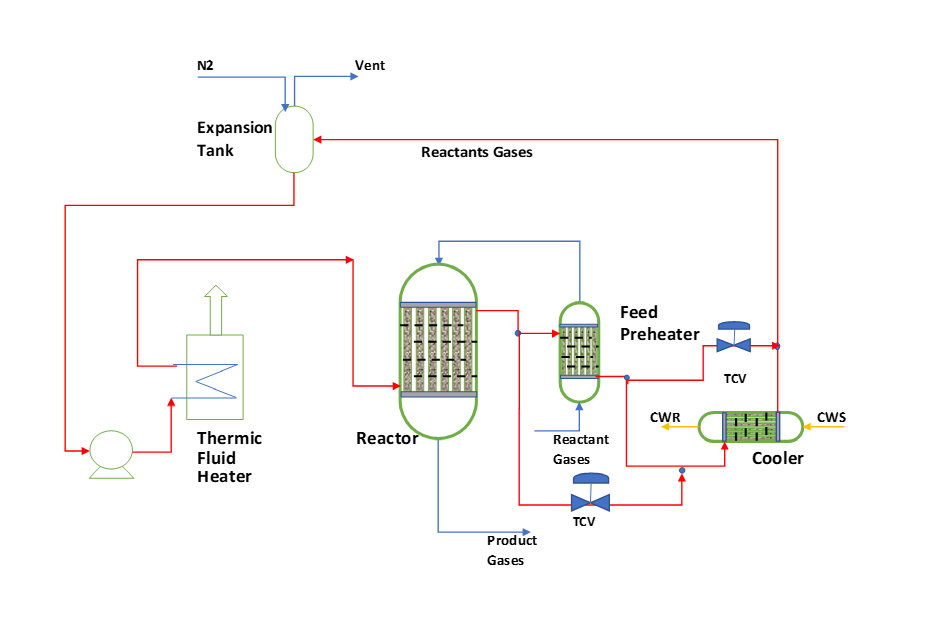
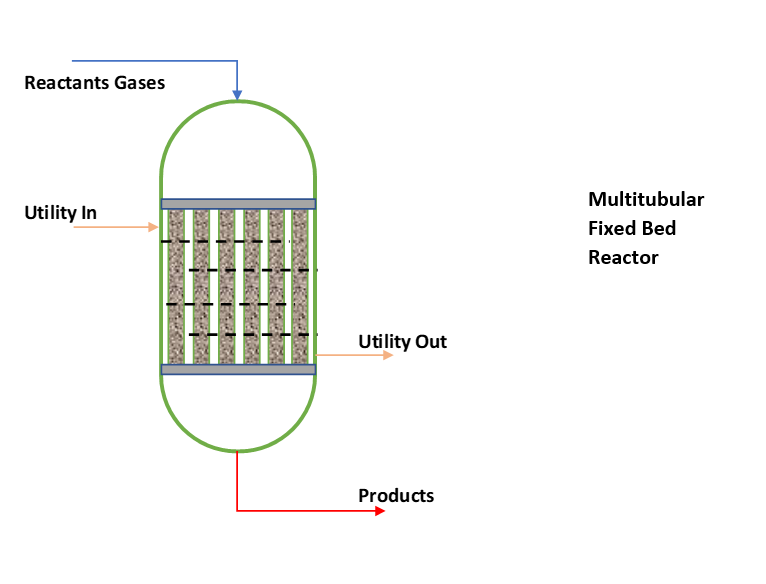
Fixed bed reactors. A fixed bed reactor is a cylindrical tube filled with catalyst pellets with reactants flowing through the bed and being converted into products. The catalyst may have multiple configuration including: one large bed, several horizontal beds, several parallel packed tubes, multiple beds in their own shells. The various.

Tubular Reactor The Ultimate FAQ Guide Filson Filter
reactors with a commercial multi-tubular packed-bed reactor for methanol synthesis. They concluded that the packed-bed reactor had a better performance than structured systems due to the e ective convective heat transfer mechanism in the catalyst bed, which is shown as lower hot-spot temperatures and higher radial heat transfer rates.
Fixed Bed Reactor ChemEnggHelp
Starting from the review of current industrial designs, the present paper analyzes thermal interaction between reactants and coolant in multitubular fixed-bed reactors. The interaction can be described quantitatively in terms of parameters characterizing transport processes both on the tube side and in the intertubular space.

Patent US7226567 Multitube fixedbed reactor, especially for catalytic gas phase reactions
For integral fixed bed reactors, isothermality is typically the most difficult performance criterion to satisfy. Mears provides a useful criterion, defining isothermality to be achieved when the average reaction rate at the cross-section of the hot spot in an integral reactor is within 5% of the rate at the wall temperature [32]. This criterion.

fixed bed reactor /catalyst testing reactor/ FCC/RFCC
In this design, the reactor models, denoted R1 to R4, only differed in the tube diameter. In our previous study, a bench-scale tubular fixed bed reactor model was validated by comparing the experimental reaction results and the 2D temperature distribution in the catalyst bed against the results from experiments (Shen et al., 2021). Only the.
Fixed Bed Reactor ChemEnggHelp
Fundamentally, you can see a multitube fixed bed reactor is like a shell & tube type exchanger. Where reactant gases enter tube side through bed of solid catalyst. And reaction takes place to convert the reactants into products. The temperature of reactor is controlled by heat transfer media circulation in shell side.

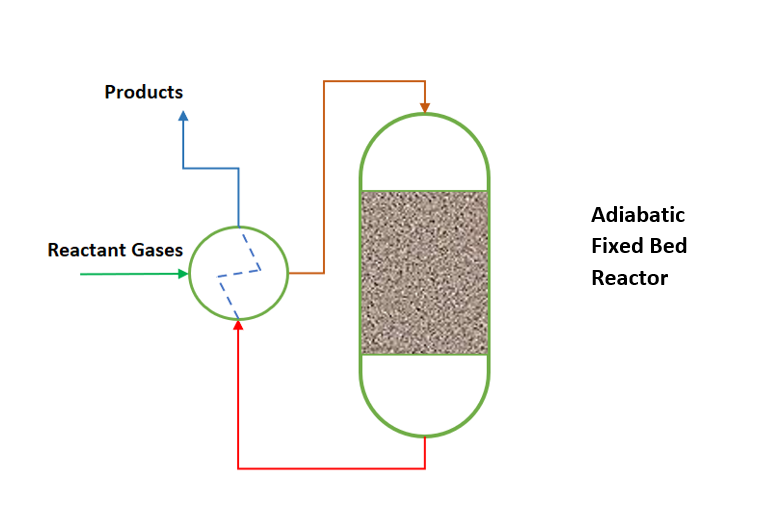
Adiabatic fixedbed reactors Big Chemical Encyclopedia
For the single-bed reactor the optimized length of 11.96m including 0.5m of inert section at the entrance region and for the double-bed reactor design the optimized lengths of 5.72m for the first.

Schematic of the fixed bed reactor system Download Scientific Diagram
Using the Phases to Guide in the Choice of Reactor Configuration. How the Type of Reaction Affects the Size of the Reactor. Burner. PFTR: Pipe/Tube, Empty Pipe for Fluid Systems. PFTR: Static Mixer in Tube. PFTR: Empty Pipe/Tube for Fluids and Solids. PFTR: Empty Multitube, Nonadiabatic. PFTR: Fixed Bed Catalyst in Tube or Vessel: Adiabatic

FTS fixedbed reactor. a Real photograph, b schematic view Download Scientific Diagram
Today 51 (1999) 319. ethane ODH over Mo-V-Nb in a fixed-bed reactor, a 30% increase [3] T. Blasco, J.M. Lopez-Nieto, Oxidative dyhydrogenation of short chain alkanes in the ethylene selectivity was observed when oxygen was dis- on supported vanadium oxide catalysts, Appl. Catal. A. 157 (1997) 117..
Fixed Bed Reactor ChemEnggHelp
A fixed-bed multitubular reactor, comprising a plurality of reaction tubes ( 3 ) filled with a catalyst and catalyst temperature measurers ( 4 ) measuring the temperatures of the reaction tubes near the radical center parts thereof. The catalyst temperature measurer ( 4 ) is installed in each of a part of the plurality of reaction tubes ( 3 ), and the measurement positions thereof are.
Fixed bed Tubular reactors
Fixed Bed Reactor is a topic that covers the principles, design, and applications of reactors with solid catalysts or adsorbents. Learn from the latest research articles and case studies on topics such as pilot-scale testing, autothermal operation, load-flexible optimization, and direct air capture using fixed bed reactor systems.

Patent US7588739 Fixed bed multitube reactor Google Patents
Practical guidelines are required for the design and operation of complicated catalytic packed-bed reactors. Primary among design considerations is the avoidance of operating regions of high parametric sensitivity, in which small changes in operating conditions can lead to thermal runaway in the reactor. Existing criteria for predicting these.