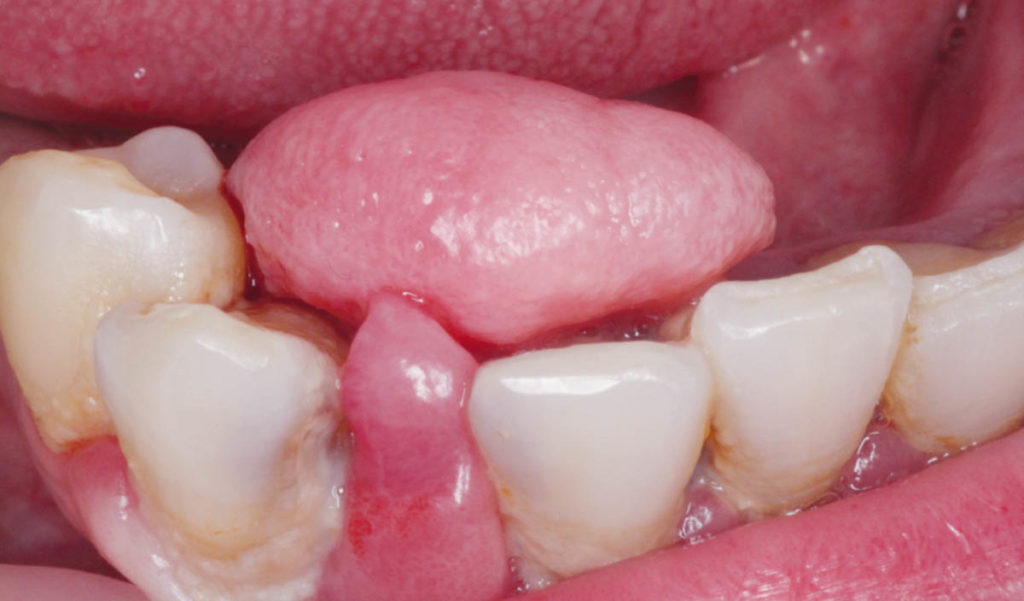
Fibroma bucal ¿Cuál es su tratamiento?
The two major and three minor NERC interconnections, and the nine NERC Regional Reliability Councils. 735 kV substation near the Robert-Bourassa generating station. Hydro-Québec's electricity transmission system (also known as the Quebec interconnection) is an international electric power transmission system centred in Quebec, Canada.The system pioneered the use of very high voltage 735.
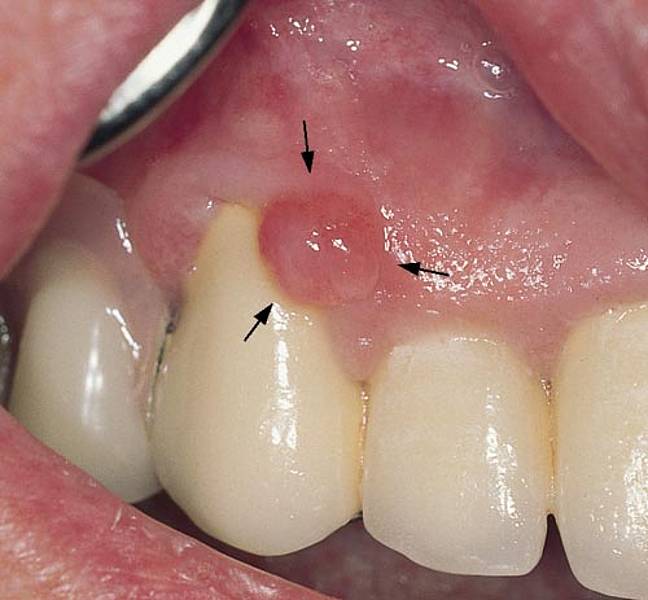
fibroma in mouth pictures, photos
Fibromatosis (Gingival, of Tuberosity) Gingival fibromatosis ( Figure 87-5) is familial or acquired due to treatment with phenytoin, cyclosporine, nifedipine, or other calcium channel blockers. In familial gingival fibromatosis, large connective tissue masses develop and may cover the teeth. The fibrous hyperplasia is found along the alveolar.

Clinical appearance of Hereditary Gingival Fibromatosis in her daughter... Download Scientific
GINGF5 (617626) is caused by mutation in the REST gene (600571) on chromosome 4q12. There is some evidence for a locus on chromosome 2p16-p13 (see MAPPING). Gingival fibromatosis is a rare overgrowth condition characterized by a benign, slowly progressive, nonhemorrhagic, fibrous enlargement of maxillary and mandibular keratinized gingiva.

SciELO Brasil Generalized hereditary gingival fibromatosis in a child clinical
Hereditary gingival fibromatosis (HGF) is characterized by a slow, progressive, benign enlargement of the gingiva. Clinically, the HGF-gingival enlargement is characterized as being of normal color, firm consistency, non-hemorrhagic, and asymptomatic with an equal gender predilection. HGF, which is the most common genetic form of gingival.

Treatment of gingival fibromas using CO laser and electrosurgery in a patient with tuberous
Abstract. Gingival fibromatosis is a rare and heterogeneous group of disorders that develop as slowly progressive, local or diffuse enlargements within marginal and attached gingiva or interdental papilla. In severe cases, the excess tissue may cover the crowns of the teeth, thus causing functional, esthetic, and periodontal problems, such as.
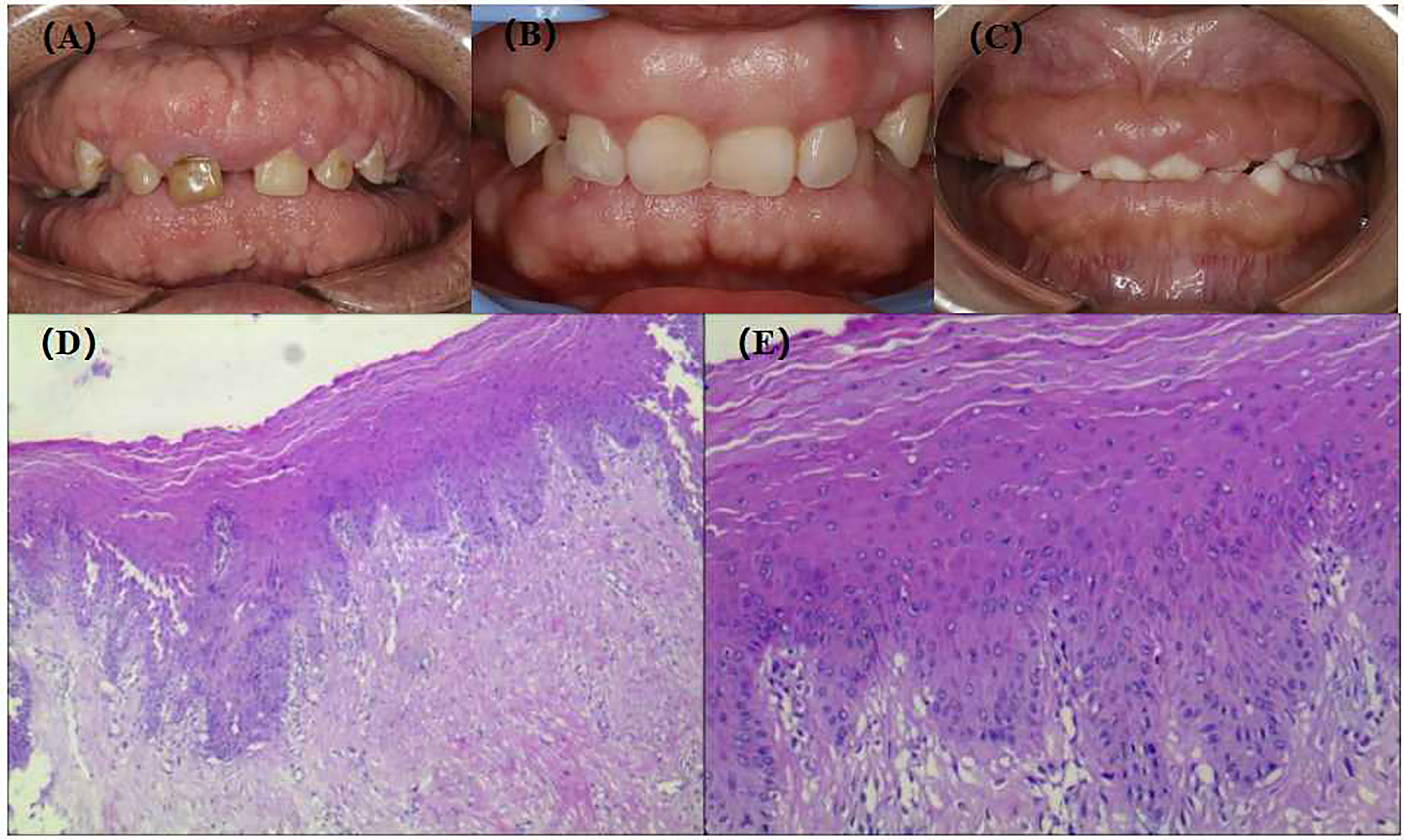
Frontiers Case Report A Case of Hereditary Gingival Fibromatosis With a High Level of Human β
Gingival fibromatosis (GF) is a rare condition character-ized by pathological, diffuse or local growth of gingiva. In severe cases functional, periodontal, esthetic and psycho-logical problems may occur. The condition may be related to hereditary factors and occurs as a non-syndromic her-editary gingival fibromatosis (HGF) or as a part of a syn.
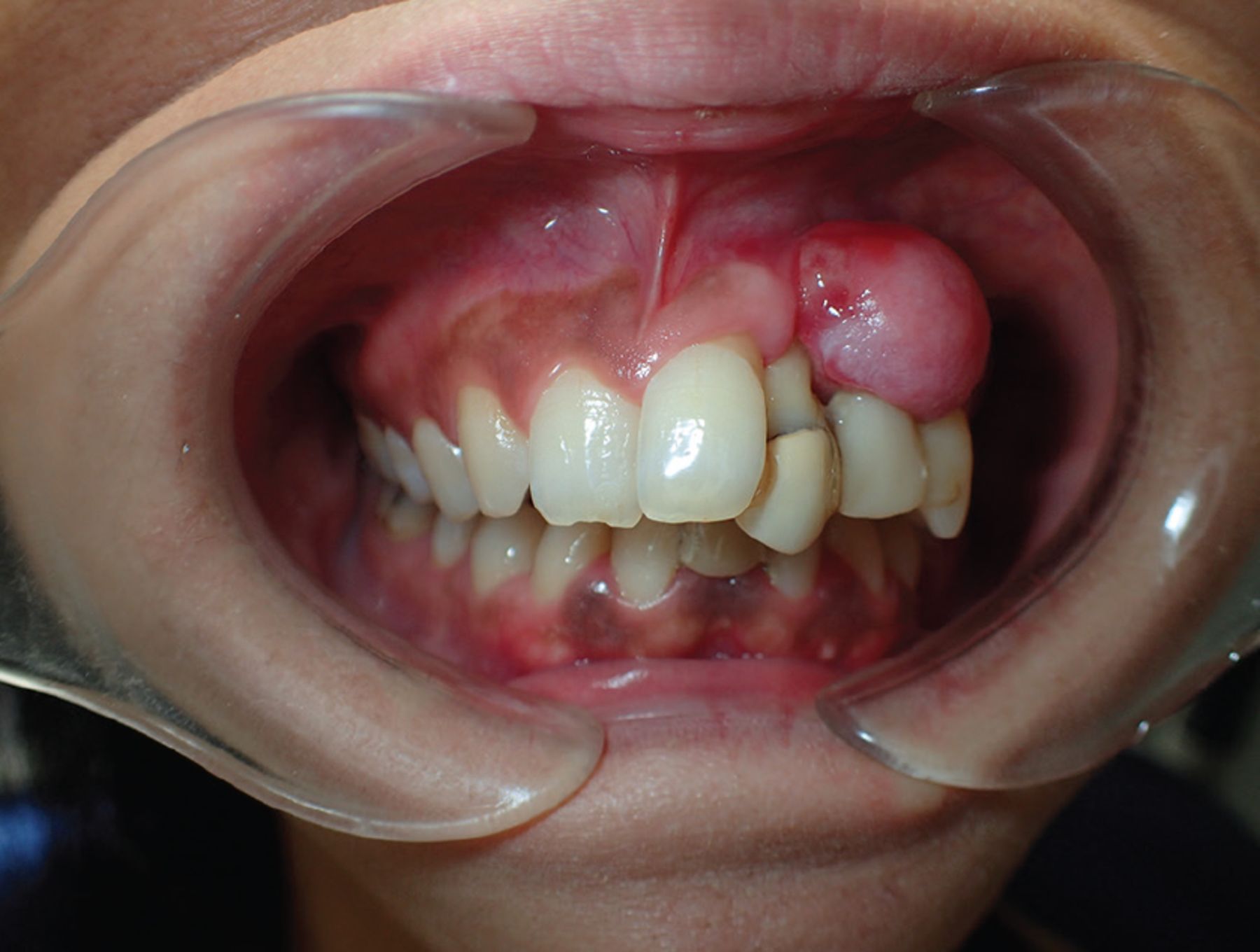
Fibrous epulis A tumorlike gingival lesion Cleveland Clinic Journal of Medicine
Gingival fibromatosis (GF) is the overgrowth of the gingival characterized by the expansion and accumulation of the connective tissue with the occasional presence of an increased number of cells ( 1 ). It is a hereditary condition or due to side effect of medications including phenytoin, cyclosporin, and nifedipine ( 2 ).

Hereditary gingival fibromatosis associated with the missense mutation of the KCNK4 gene Oral
Gingival fibromatosis is a rare and heterogeneous group of disorders that develop as slowly progressive, local or diffuse enlargements within marginal and attached gingiva or interdental papilla. In severe cases, the excess tissue may cover the crowns of the teeth, thus causing functional, esthetic, and periodontal problems, such as bone loss and bleeding, due to the presence of pseudopockets.

(PDF) Idiopathic Gingival Fibromatosis
La fibromatosis gingival idiop⁄tica (FGI), comprende un grupo hetero-g"neo de patolog™as de causas no determinadas. La FGI es sinŠnimo de nomenclaturas tales como hiperplasia gingival, elefantiasis gingival, fibromatosis gingival hereditaria, fibroma difuso, gigantismo de la gingiva, fibromatosis familiar cong"nita (Newman et al., 2002).
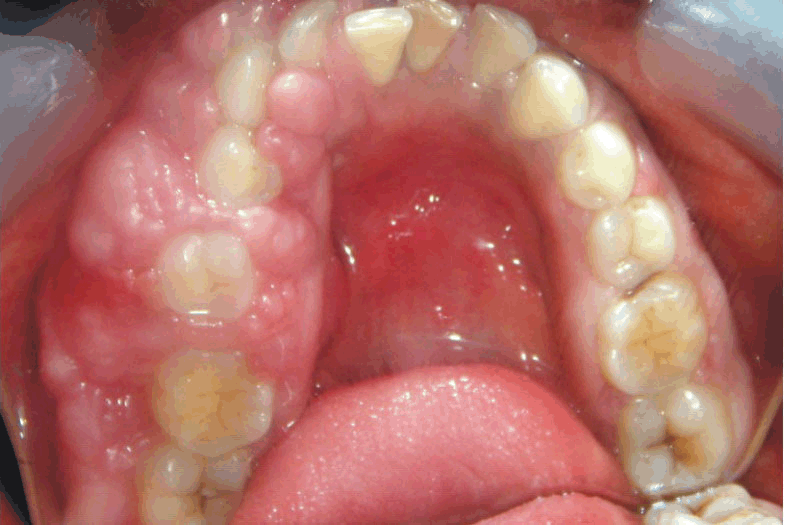
Fibromatosis gingival
Idiopathic gingival fibromatosis is a rare heriditary condition characterized by slowly progressive, nonhemorrhagic, fibrous enlargement of maxillary and mandibular keratinized gingiva caused by increase in submucosal connective tissue elements. This case report gives an overview of gingival fibromatosis in a 11-year-old female patient who.

The phenotypic overlap of syndromes associated with hereditary gingival fibromatosis followup
Hereditary gingival fibromatosis (HGF) is a rare, hereditary, benign disease characterized by slow and progressive fibrous hyperplasia of the gingiva [1, 2] and was initially reported by Goddard and Gross in 1856 [].It has a prevalence of 1:175,000 according to phenotype and 1:350,000 according to genotype, and it can affect both mandibular and maxillary gingiva [].

6b Idiopathic gingival fibromatosis Download Scientific Diagram
Idiopathic gingival fibromatosis (IGF) is an uncommon, benign, hereditary, slowly progressive, nonhemorrhagic fibrous enlargement of keratinized gingiva. It usually begins at the time of eruption of permanent teeth, but can develop with the eruption of deciduous dentition and rarely present at birth. [ 1] The hyperplastic gingival tissue is.

Figure 1 from Idiopathic Gingival Fibromatosis Semantic Scholar
Nord-du-Québec (French pronunciation: [nɔʁ dy kebɛk]; English: Northern Quebec) is the largest, but the least populous, of the seventeen administrative regions of Quebec, Canada.With nearly 750,000 square kilometres (290,000 sq mi) of land area, and very extensive lakes and rivers, it covers much of the Labrador Peninsula and about 55% of the total land surface area of Quebec, while.

Figure 1 from Idiopathic Gingival Fibromatosis with Generalized Aggressive Periodontitis A Rare
Hereditary gingival fibromatosis (HGF) is a rare disorder characterized by a benign, slowly progressive, fibrous gingival overgrowth that can appear as an isolated disorder (non-syndromic) or as part of a syndrome (syndromic) and it may be localized or generalized [].Non-syndromic form is the most common genetic form of gingival fibromatosis with both autosomal dominant and recessive modes of.

The phenotypic overlap of syndromes associated with hereditary gingival fibromatosis followup
Hereditary gingival fibromatosis (HGF) is a benign, non-hemorrhagic, fibrous gingival overgrowth that can cover all or part of the teeth. In the current periodontal diseases and conditions classification developed by Armitage in 1999, HGF is one of the categories of Gingival lesions of genetic origin in the Gingival Diseases section (1-5). The.

(PDF) Idiopathic Gingival Fibromatosis
Background Hereditary gingival fibromatosis (HGF) is a rare condition characterized by slowly progressive overgrowth of the gingiva. The severity of overgrowth may differ from mild causing phonetic and masticatory issues, to severe resulting in diastemas or malposition of teeth. Both, autosomal-dominant and autosomal-recessive forms of HGF are described. The aim of this review is a clinical.