
Antigen and it's Epitope Biotechfront
Epitop (Inggris: epitope, antigenic determinant) adalah area tertentu pada molekul antigenik, yang mengikat antibodi atau pencerap sel B maupun sel T. Umumnya molekul berukuran besar, seperti protein dan polisakarida dapat menunjukkan sifat antigen.. Banyak antigen mempunyai beragam epitop yang menjadi stimulan produksi antibodi atau sel T, setelah terjadi ikatan pada fragmen pengikat antigen.

Visual representation of the epitopes in their native structural... Download Scientific Diagram
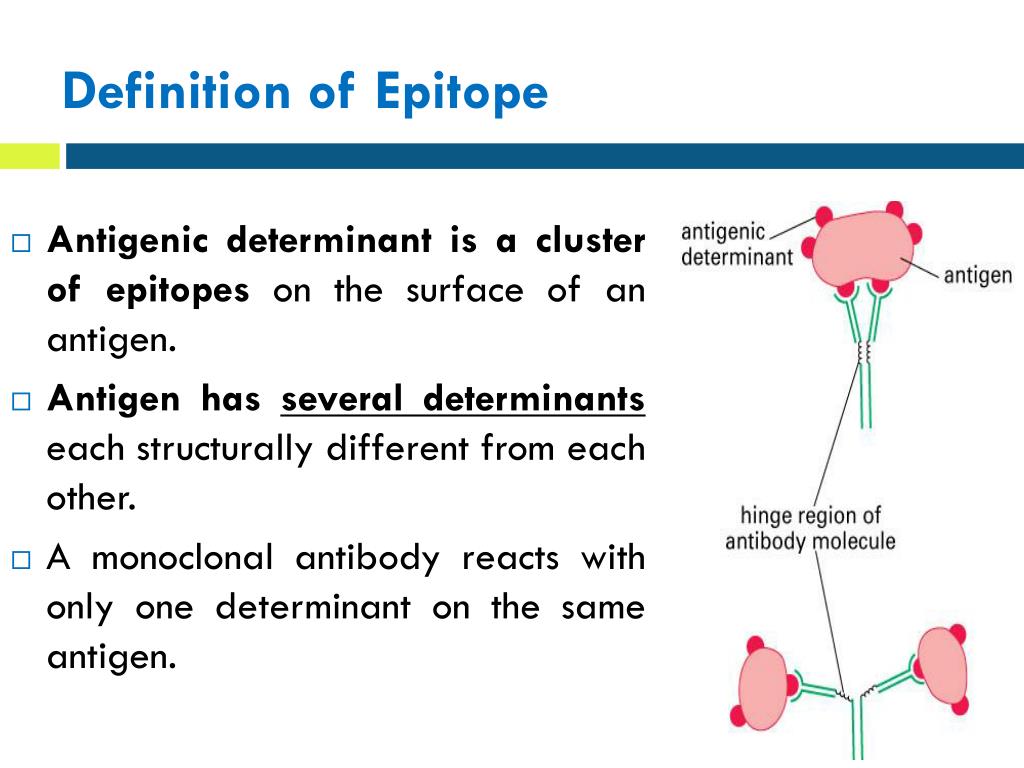
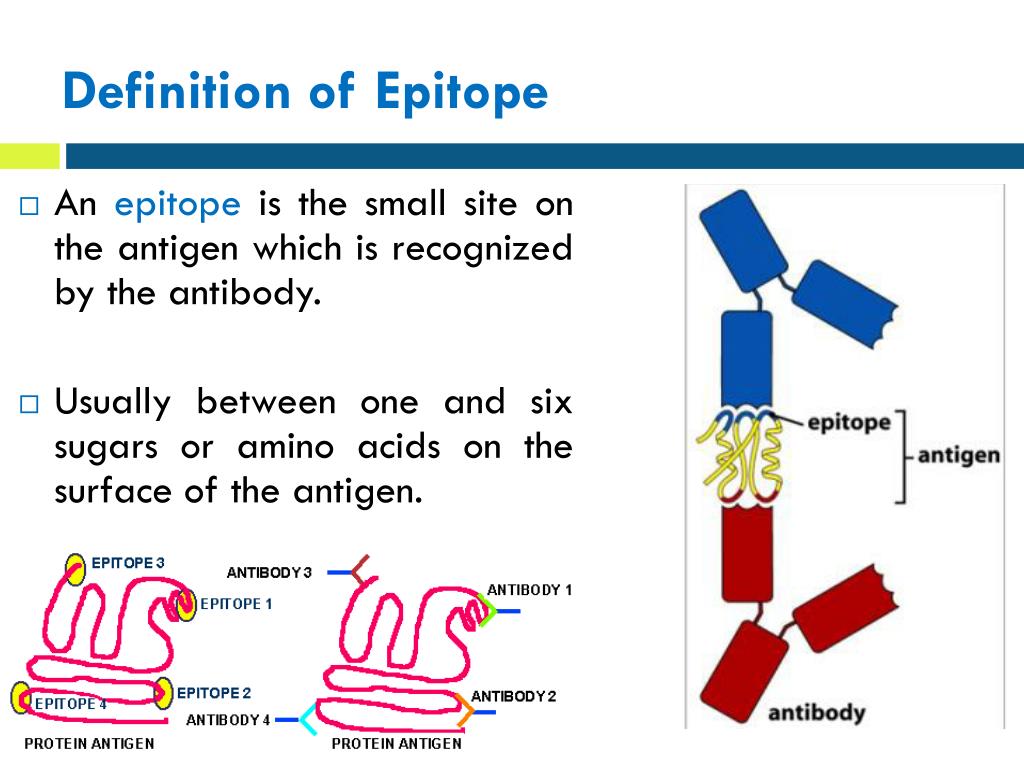
Epitope. An epitope, also known as antigenic determinant, is the part of an antigen that is recognized by an antibody, B-cell receptor or T-cell receptor. Generally an antigen has several or many different epitopes and reacts with many different antibodies, an epitope is approximately five or six amino acids in length. Adjuvant
PPT Dr. Nabil MTIRAOUI, M.Sc, Ph.D PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID6099710
The Immune Epitope Database (IEDB) is a freely available resource funded by NIAID. It catalogs experimental data on antibody and T cell epitopes studied in humans and other animal species in the context of infectious disease, allergy, autoimmunity and transplantation. The IEDB also hosts epitope prediction and analysis tools, and has a.
Epitope Mapping Using Crystallography Creative Biostructure
Epitope, or antigenic determinant, is a small, specific portion of an antigen recognized by the immune system such as antibodies. A single antigen usually has several different epitopes. The region on an antibody which recognizes the epitope is called a paratope. Antibodies fit precisely and bind to specific epitopes.

Antigen and Factors Affecting Immunogenicity • Microbe Online
A epitop, juga dikenal sebagai penentu antigenik, adalah situs spesifik pengikatan antigen atau imunogen dengan antibodi atau reseptor sel sistem kekebalan tubuh. Untuk memahami konsep ini, harus dijelaskan bahwa imunogen adalah makromolekul dengan kapasitas untuk menginduksi respons imun, yaitu, merupakan zat eksogen atau endogen yang diakui organisme sebagai zat asing atau tidak, mampu.

Polyclonal and Monoclonal Antibody Production Microbiology
Epitope identification using high-performance immuno-analytic tools can be very useful in various applications in the field of epitope mapping, including the design of peptide-based vaccines, identification of immunological processes, prediction of epitopes used in the diagnosis of diseases, determination of features of antibodies in various.
PPT Dr. Nabil MTIRAOUI, M.Sc, Ph.D PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID6099710
Epitope-based vaccines would contribute to overcoming this problem. It is envisaged that epitopes would be selected for their ability to elicit potent neutralization rather than their natural surface accessibility. Such epitopes are most likely to correspond to conserved aspects of the pathogen that cannot tolerate modification and through.

Epitopes B and T Cell Epitopes Immunology B Cell Education YouTube
Although neoantigen load and occurrence have been widely studied, a detailed pan-cancer analysis of the occurrence and characterization of neoepitopes is missing. We investigated the proteome-wide.

Bcell epitope recognition. Bcell epitopes are solventexposed... Download Scientific Diagram
Introduction. The Immune Epitope Database and Analysis Resource (IEDB) is a freely available resource that contains an extensive collection of experimentally measured immune epitopes and a suite of tools for predicting and analyzing epitopes (Figure 1).The IEDB includes antibody and T cell epitopes for infectious diseases, allergens, autoimmune diseases, and transplant/alloantigens studied in.

PPT Chapter 21 Immune System PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2364494
Molecular mimicry is the theoretical possibility that sequence similarities between foreign and self-peptides are enough to result in the cross-activation of autoreactive T or B cells by pathogen-derived peptides.Despite the prevalence of several peptide sequences which can be both foreign and self in nature, just a few crucial residues can activate a single antibody or TCR (T cell receptor).

PPT Epitope Tagging PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID4639059
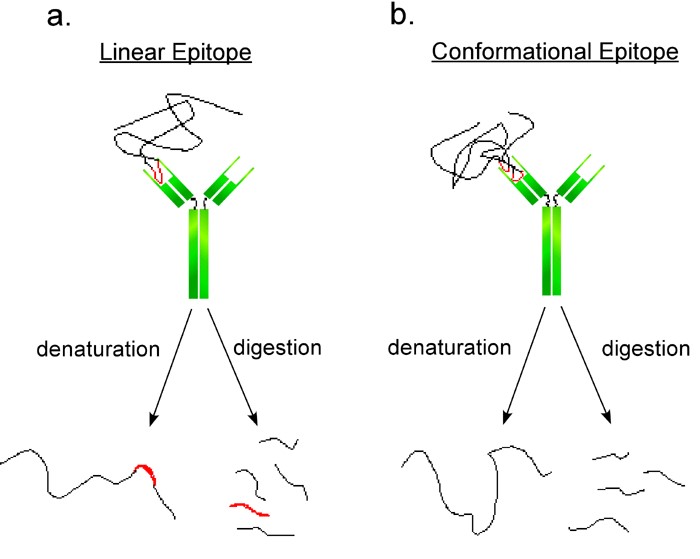
Epitopes of an antigen. The actual portions or fragments of an antigen that react with receptors on B-lymphocytes and T-lymphocytes, as well as with free antibody molecules, are called epitopes or antigenic determinants. The size of an epitope is generally thought to be equivalent to 5-15 amino acids or 3-4 sugar residues.

Epitopes Types, Function, Epitope Spreading • Microbe Online
The size of an epitope is generally thought to be equivalent to 5-15 amino acids or 3-4 sugar residues. Some antigens, such as polysaccharides, usually have many epitopes, but all of the same specificity. This is because polysaccharides may be composed of hundreds of sugars with branching sugar side chains, but usually contain only one or two.
EpitopePredikt aibiologics
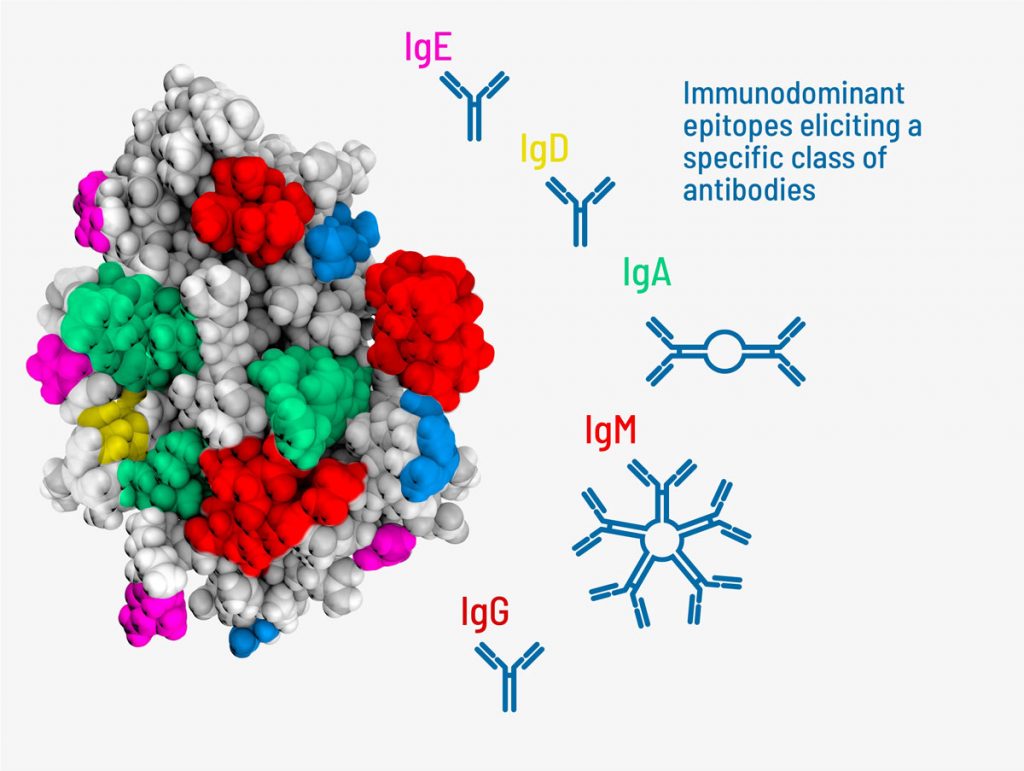
Functions of Epitopes. Epitope recognition by B-cell and T-cell is central to humoral and cell-mediated immune response. The humoral branch (B cells) recognizes an enormous variety of epitopes (also referred to as B-cell epitopes): those displayed on the exposed regions of bacteria or viral particles, as well as those displayed on soluble proteins, glycoproteins, polysaccharides, or.

Discovering Antibodies with Broader Epitope Specificities
Epitope spreading is defined as the diversification of epitope specificity from the initial focused, dominant epitope-specific immune response, directed against a self or foreign protein, to.

Epitope prediction on a betalactamase unbound structure (PDB ID... Download Scientific Diagram
An epitope is the part of the antigen that binds to a specific antigen receptor on the surface of a B cell. Binding between the receptor and epitope occurs only if their structures are complementary. If they are, epitope and receptor fit together like two pieces of a puzzle, an event that is necessary to activate B-cell production of antibodies.

(A) Principle of epitope matching. Example of two different potential... Download Scientific
An epitope, also known as antigenic determinant, is the part of an antigen that is recognized by the immune system, specifically by antibodies, B cells, or T cells.The part of an antibody that binds to the epitope is called a paratope.Although epitopes are usually non-self proteins, sequences derived from the host that can be recognized (as in the case of autoimmune diseases) are also epitopes.