
endosperm Google Search Bi̇tki̇
The endosperm is a tissue that surrounds the embryo of seeds in angiosperms and provides nutrition. Angiosperms are plants that produce flowers and seeds that are enclosed within a fruit.

The Modular Control of Cereal Endosperm Development Trends in Plant Science
The endosperm could inherit maternally derived mRNA and proteins that are located at specific sub-domains in the central cell. Indeed, the central cell shows cytological evidence of polarity, which could prefigure the future endosperm antero-posterior organization [32]. Direct maternal effects that originate from the central cell constitute an.
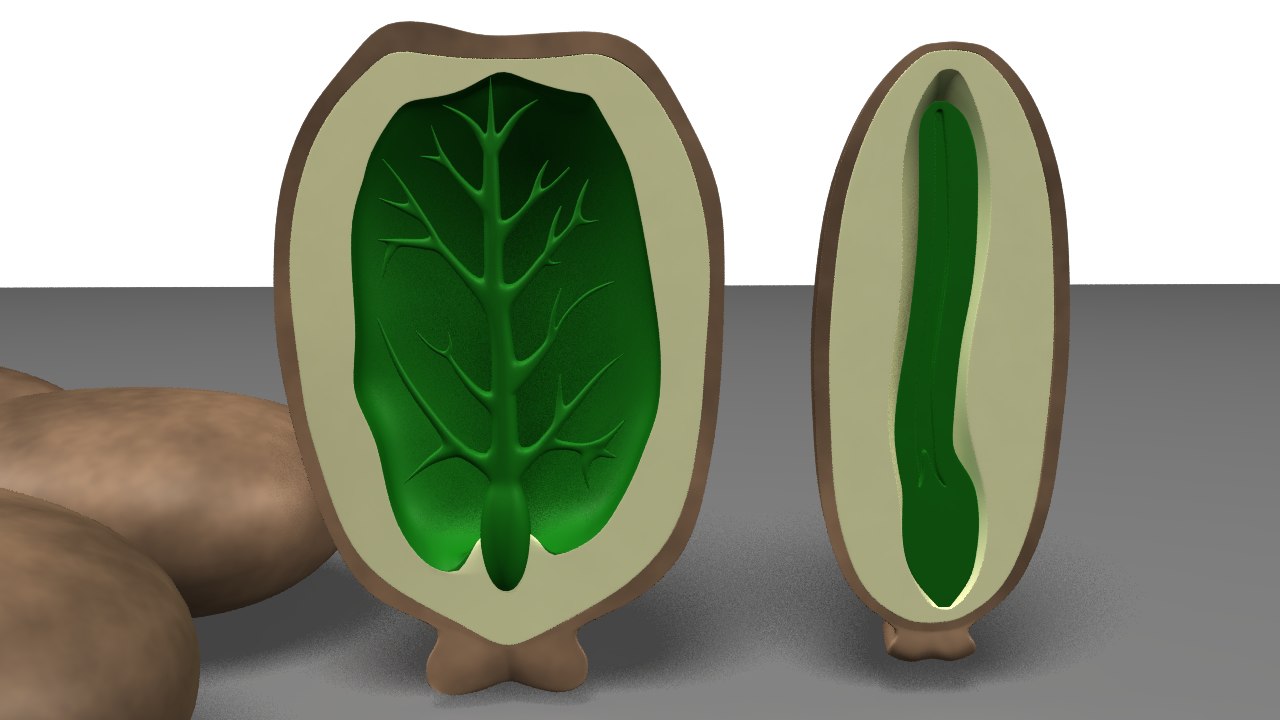
3d obj endosperm seeds
Science & Tech. endosperm, tissue that surrounds and nourishes the embryo in the seeds of angiosperms (flowering plants). In some seeds the endosperm is completely absorbed at maturity (e.g., pea and bean ), and the fleshy food-storing cotyledons nourish the embryo as it germinates. In others, some of the endosperm is present until germination.

PPT Early Development PowerPoint Presentation ID371787
The endosperm cell walls are composed of pentosans, other hemicelluloses, and beta-glucans, but not cellulose. The pentosans in them absorb large amounts of water. The endosperm cells are packed with starch granules embedded in a protein matrix. Starch is the major component of wheat endosperm, comprising approximately 64-75% of milled endosperm.
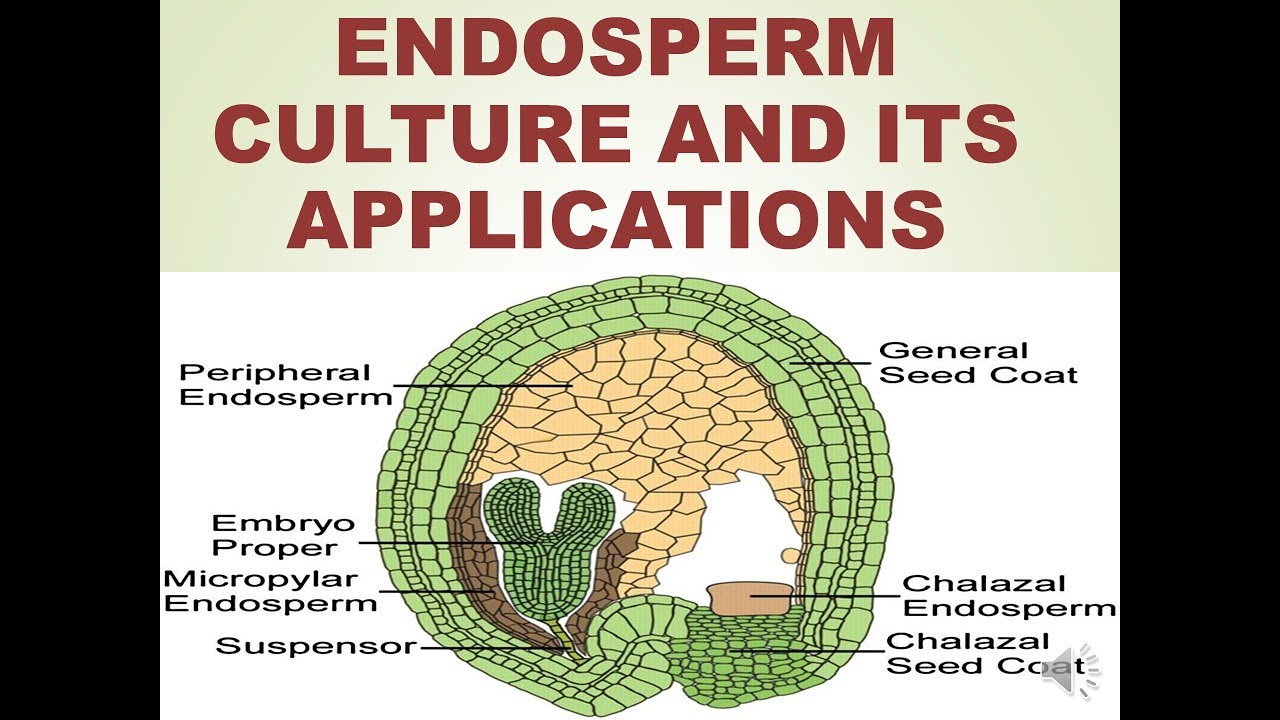
ENDOSPERM CULTURE AND IT'S APPLICATIONS YouTube
Functions of Endosperm: Endosperm stores the food reserve and is important for the growth of an embryo. They provide protection to the developing embryo and supply nutrients. They have the capability to regulate gene expression and seed germination. Endosperm induces signals according to environmental conditions and regulates embryonic growth.

Quinoa micropylar endosperm (at the torpedo stage). cn, crushed... Download Scientific Diagram
The endosperm is a very vital part of a fertilized embryo. It forms the surrounding tissue of the growing embryo. The endosperm is primarily a storage tissue and its main function is to provide starch and other nutrients to the growing embryo. There are two types of seeds: Albuminous seed and Exalbuminous seed.
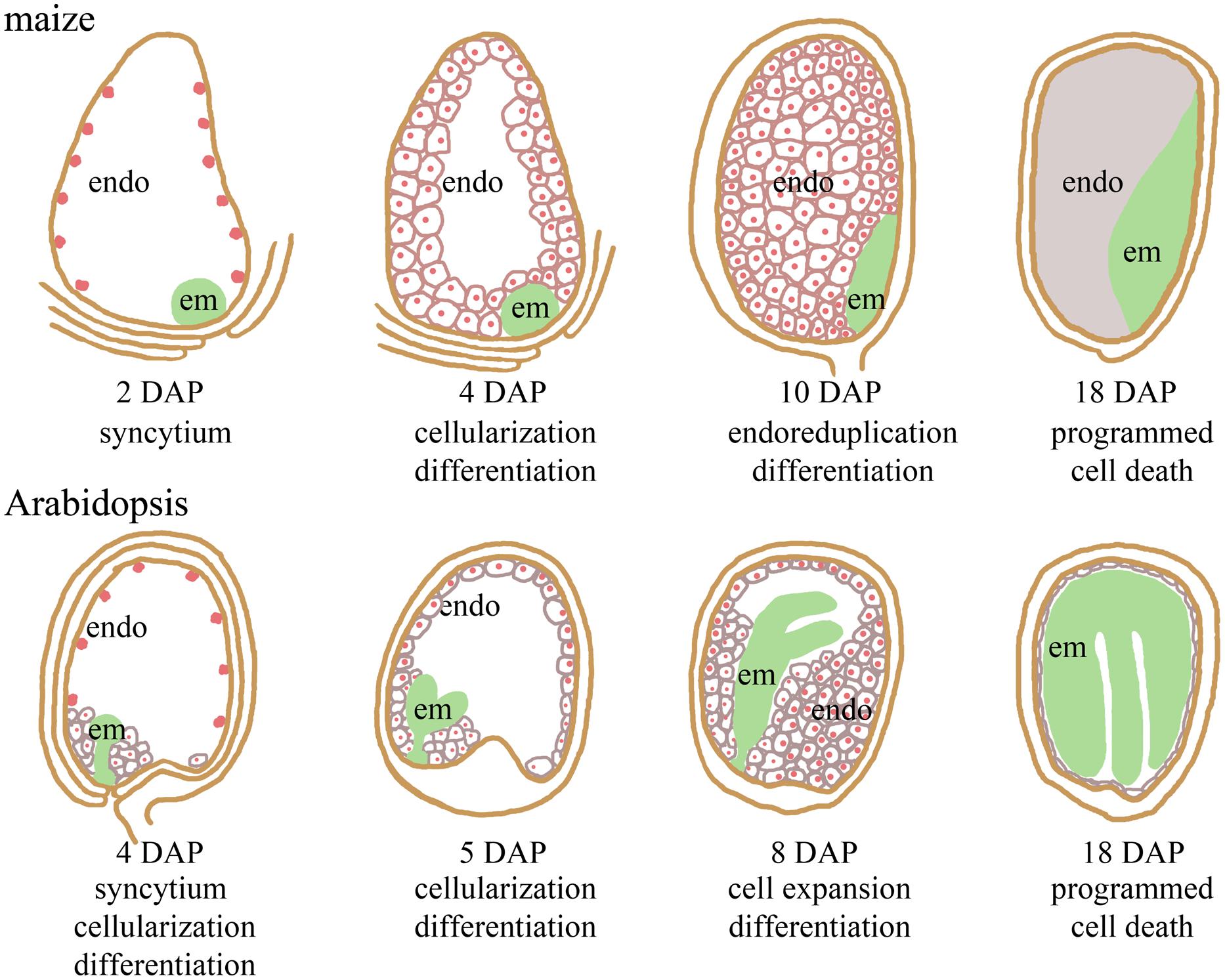
What is endosperm?
Abstract. Endosperm is a seed storage tissue formed within the angiosperm embryo sac from a second fertilization of the central cell. Generally, endosperm cells are triploid, rich in cellular reserves, and are compactly arranged without intercellular spaces. Reserves are stored in the form of carbohydrates, protein, and lipids, although.

Endosperm ।। Endosperm development, Types & Function ।। BotanyTv YouTube
If the nutrition is stored as endosperm, the cotyledons are generally small and undeveloped; whereas when the cotyledons are enlarged, there is little endosperm in the mature seed. Most of us are familiar with nutrient-containing cotyledons. When you eat beans, peanuts or walnuts you are largely consuming cotyledons containing the stored nutrients.

Endosperm Definition, Description, & Importance Britannica
Endosperm. Endosperm is present in the seeds of most of the angiosperms. It provides nourishment to the growing embryo. Endosperm is replaced by fleshy cotyledons in dicotyledons. In monocotyledons, endosperm persists in the mature seeds too and stores the food. Endosperm tissue is rich in carbohydrates and also contains proteins and lipids.
AD Syncytial stage of endosperm development in longitudinal sections... Download Scientific
Endosperm. The endosperm is a tissue produced inside the seeds of most of the flowering plants following double fertilization. It is triploid (meaning three chromosome sets per nucleus) in most species, [1] which may be auxin -driven. [2] It surrounds the embryo and provides nutrition in the form of starch, though it can also contain oils and.
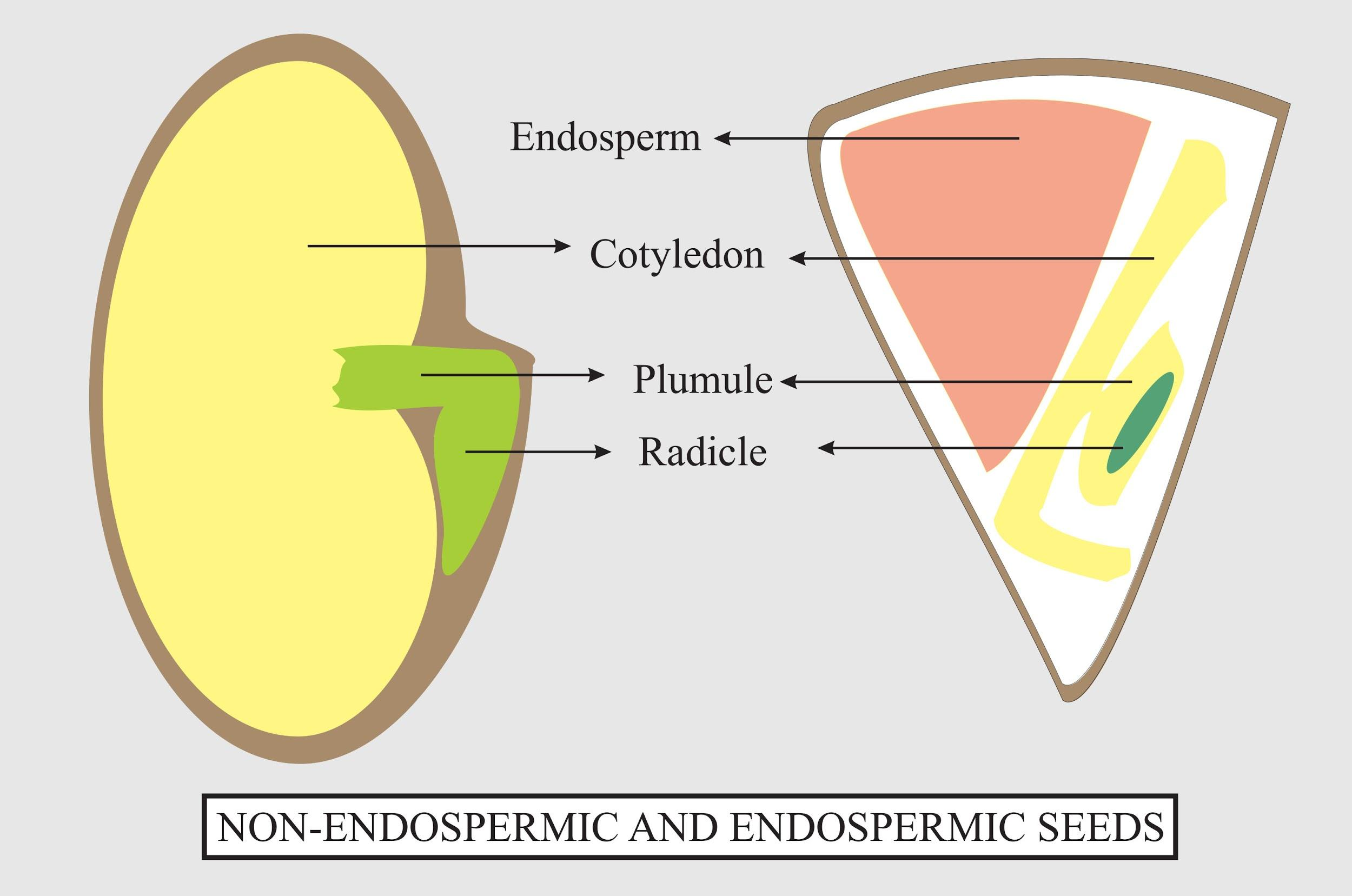
Give any two examples of each endospermic (albuminous) seeds and nonendospermic seeds
Endosperm. nutritive tissue surrounding the embryo within seeds. of flowering plants.A tissue found in many seeds which. supplies nutrients to the embryo.

Endosperm cellularization failure correlates with embryo arrest in fis2... Download Scientific
Whether the endosperm is haploid and a continuation of the gametophytic tissue, a diploid or triploid tissue, or a second embryo of abnormal size and shape, is still debatable. Strasburger (1900) even called the fusion of the two polar nuclei with the second male gamete as vegetative fertilization. The families which lack endosperm are.

ENDOSPERM
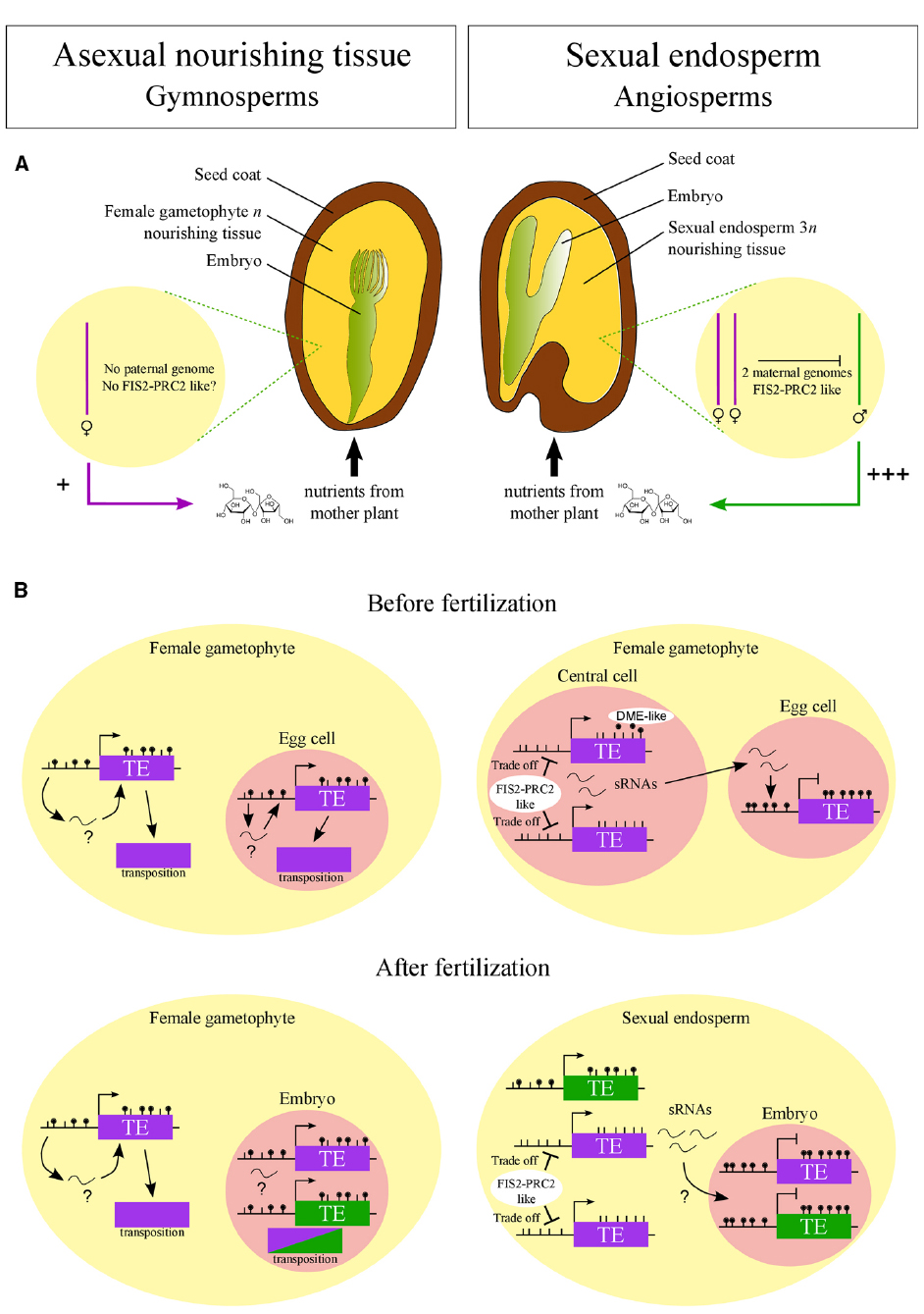
The endosperm makes the main source of food for the embryo. In gymnosperms, the endosperm is haploid (n) and forms a continuation of the female gametophyte. On the other hand, in angiosperms it is formed mostly as the result of a fusion of the two polar nuclei and one of the male gametes. Since all the three nuclei taking part in the fusion are.

Seeds, Gymnosperm Endosperm Female Gametophyte
All whole grain kernels contain three parts: the bran, germ, and endosperm. Each section houses health-promoting nutrients. The bran is the fiber -rich outer layer that supplies B vitamins, iron, copper, zinc, magnesium, antioxidants, and phytochemicals. Phytochemicals are natural chemical compounds in plants that have been researched for their.
Frontiers Evolution and function of processes in the endosperm Plant Science
Whole Grains are Healthier. Whole grains contain all three parts of the kernel. Refining normally removes the bran and the germ, leaving only the endosperm. Without the bran and germ, about 25% of a grain's protein is lost, and are greatly reduced in at least seventeen key nutrients. Processors add back some vitamins and minerals to enrich.

Cross section of a coffee seed showing the folding of the endosperm and... Download Scientific
The resulting triploid endosperm tissue develops by successive nuclear divisions and varying degrees of cellularization throughout its short life, to envelop and provide a nurturing environment to.