
PPT Coal Mining PowerPoint Presentation ID5218988
Drift mining - horizontal shafts dug into the earth; Slope mining - diagonal shafts dug into the earth; The room and pillar method is the most popular technique for subsurface mining. This type of mining involves cutting networks of open areas (or rooms) into horizontal layers of coal.

PPT Obtaining Raw Materials PowerPoint Presentation, free download
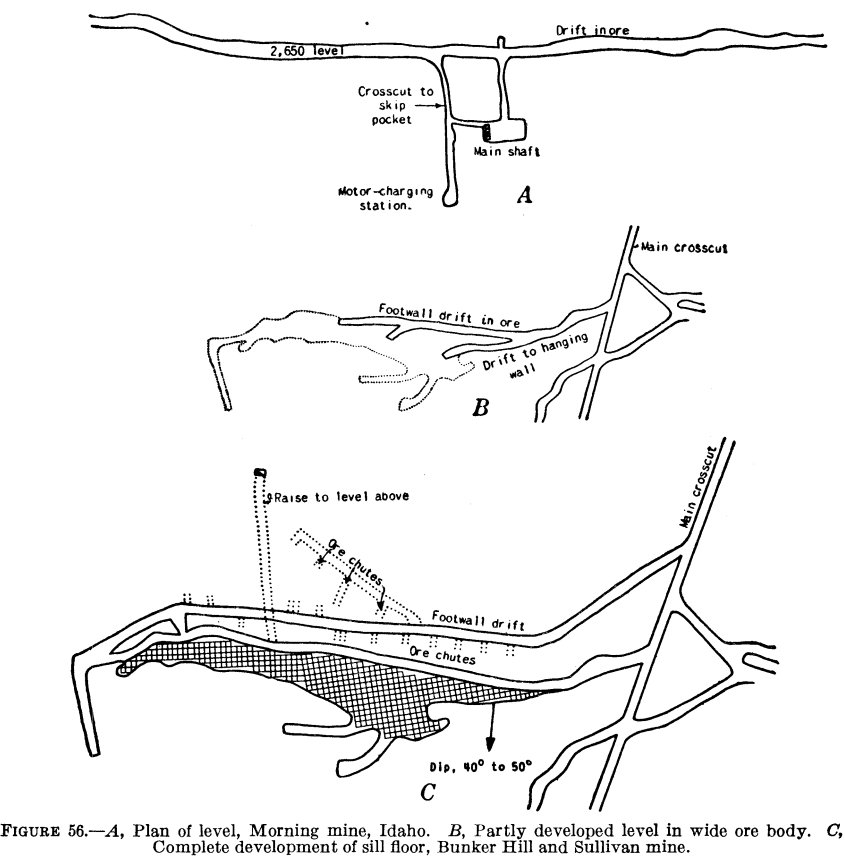
Drifts are 13 by 13 feet in cross section and are timbered with standard drift sets. Where the vein is much wider or flatter, as at the Bunker Hill and Sullivan mine, crosscuts are driven from the shaft or incline to and through the ore, but more than one drift may be required to facilitate. rapid removal of broken ore from the stopes.

Drift Mining At Newman Road 1900 SHEFFIELD HISTORY CHAT Sheffield
Take a tour underground at Mahogany Drift Mine. Ronnie, one of our experienced drift mine engagers, explains its history, some of the ways of cutting coal ou.

What Is a Mining Drift? A Beginners Guide An Underground Miner
Drift mining, a fascinating subterranean world that remains largely unexplored by the average person, is a captivating topic that deserves a closer look. In this blog section, we will embark on a journey to unveil the depths of drift mining, shedding light on its history, techniques, and.

Scotswood Delaval Drift Mine 01 06 2020 Scotswood Road VIDEO
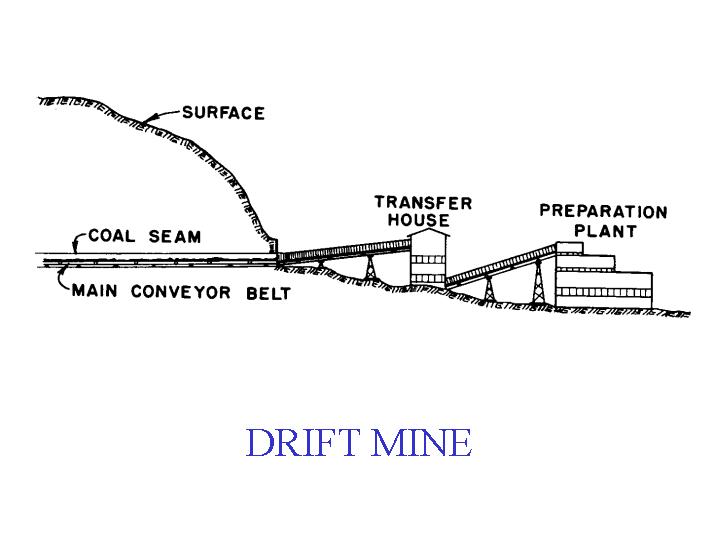
Drift mining can refer to one of two things: mining an ore deposit by underground mining or working coal seams through adits. A mining drift is an underground mine where the entry is above water level and typically on the slope of a hill. It's driven horizontally into the ore seam. Through drift mining, companies can extract precious geological.
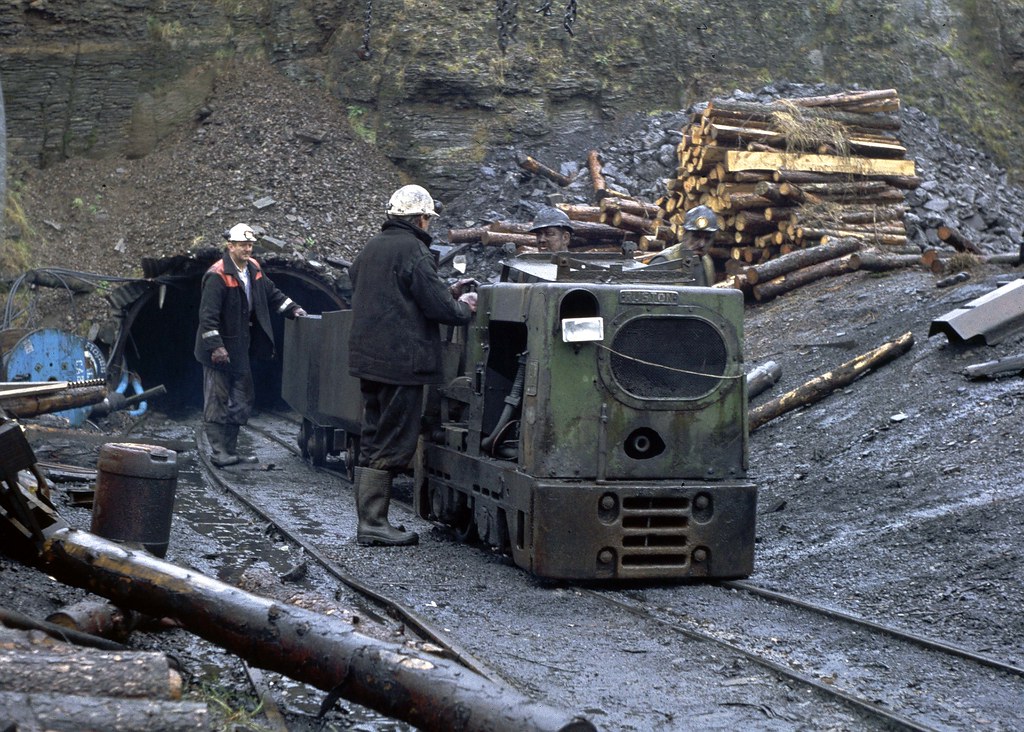

Ruston 504546 at Parc Level Drift Mine. Photo Taken 11.1… Flickr
Drift mining. Drift mining is a way of mining where tunnels are dug horizontally. It was used by the coal industry in the 1700s. It would follow a coal seam into a hillside. It was not very safe which is why it wasn't used much. It was not safe because water could easily get in. This short article about technology can be made longer.
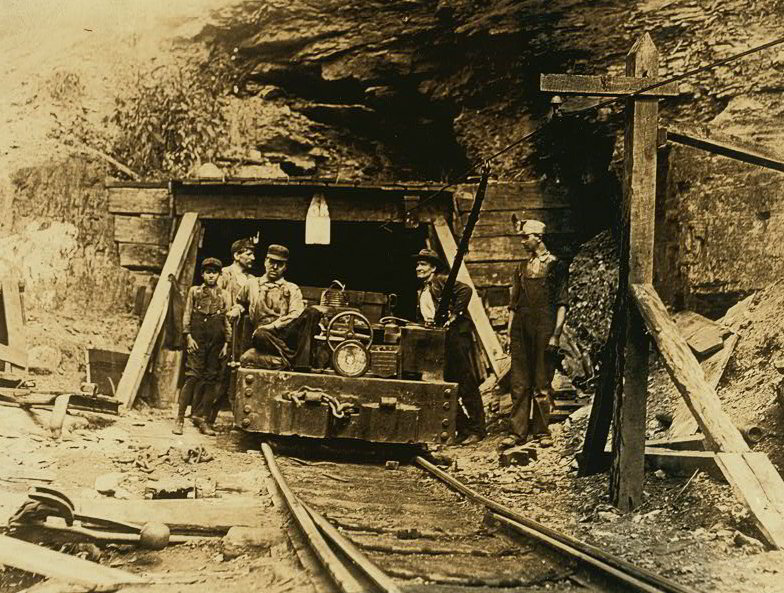

What Is a Mining Drift? A Beginners Guide An Underground Miner
Mining - Drifts, Tunnels, Shafts: All horizontal or subhorizontal development openings made in a mine have the generic name of drift. These are simply tunnels made in the rock, with a size and shape depending on their use—for example, haulage, ventilation, or exploration. A drift running parallel to the ore body and lying in the footwall is called a footwall drift, and drifts driven from the.

Drift mine at National Mining Museum, Yorkshire. YouTube
Drift mining is either the mining of an ore deposit by underground methods, or the working of coal seams accessed by adits driven into the surface outcrop of the coal bed. [1] A drift mine is an underground mine in which the entry or access is above water level and generally on the slope of a hill, driven horizontally into the ore seam.
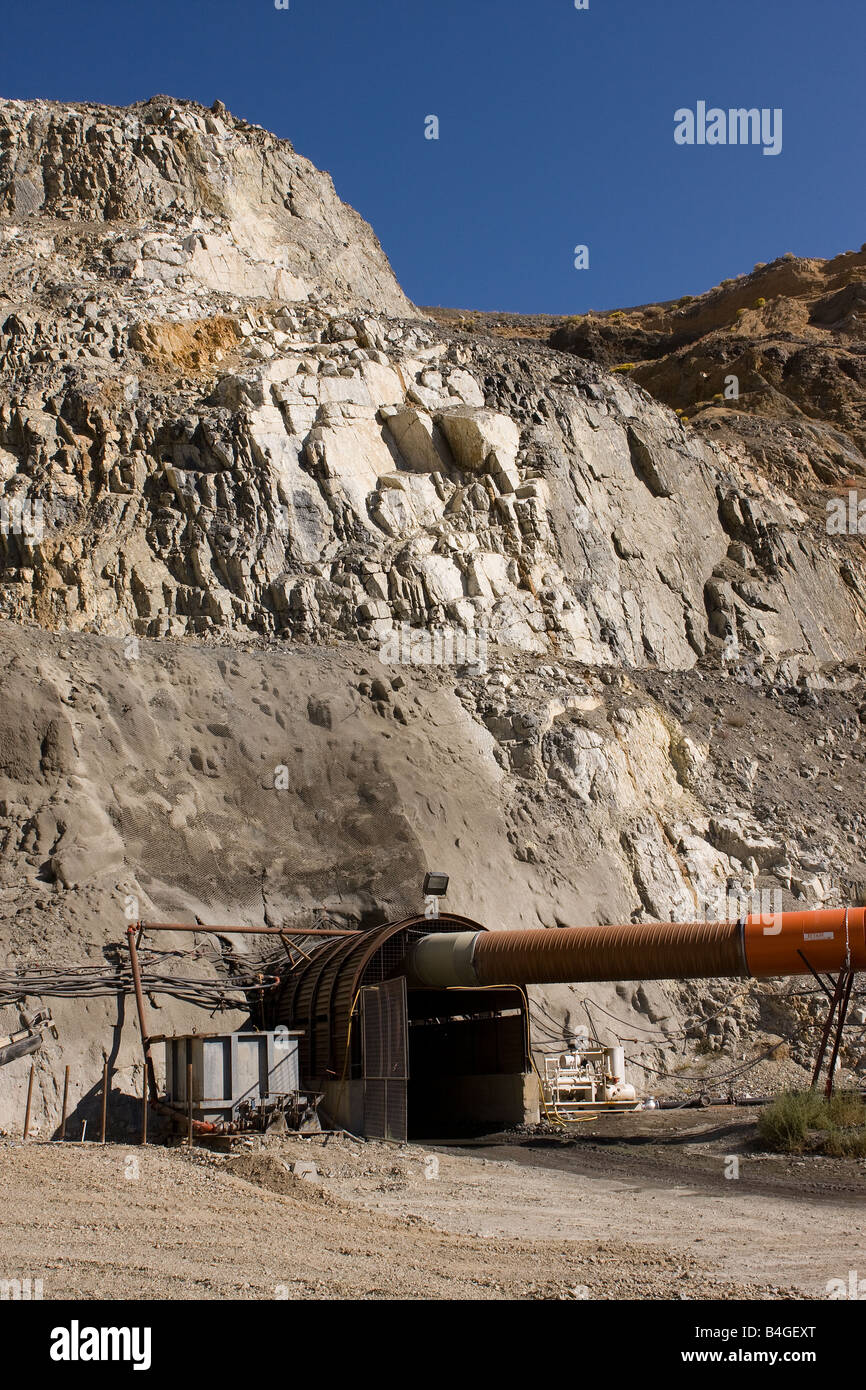

Drift mining hires stock photography and images Alamy
Drift mine - An underground coal mine in which the entry or access is above water level and generally on the slope of a hill, driven horizontally into a coal seam. Drill - A machine utilizing rotation, percussion (hammering), or a combination of both to make holes. If the hole is much over 0.4m in diameter, the machine is called a borer.
Jordan Saunders Underground Mining
Other articles where drift is discussed: mining: Horizontal openings: drifts: All horizontal or subhorizontal development openings made in a mine have the generic name of drift. These are simply tunnels made in the rock, with a size and shape depending on their use—for example, haulage, ventilation, or exploration. A drift running parallel to the…

Drift Mine. Yorkshire Nov 2013. Pit Heavy.
Drift mining is either the mining of an ore deposit by underground methods, or the working of coal seams accessed by adits driven into the surface outcrop of the coal bed. A drift mine is an underground mine in which the entry or access is above water level and generally on the slope of a hill, driven horizontally into the ore seam. Random House dictionary says the origin of the term "drift.

Exploring the Blaentillery Drift Mine Part 1 YouTube
Drift Mining. Drift mining is a process of accessing precious geological material, like coal, by cutting into the side of the earth, rather than tunneling directly downwards. Drift mines have flat entries into the coal seam from a hillside. Drift mines are different from slope mines, which have a tending opening from the surface to the coal vein.

What Is a Mining Drift? A Beginners Guide An Underground Miner
November 24, 2011. When its -40° F. above ground, its only +28° F. underground. I had a mining engineer friend who, knowing I was interested in modern mining as well as mining history, invited me to see an operating placer drift mine operation in the Chatanika Valley. In placer drift mines, vertical or diagonal shafts are sunk into alluvial.

High Moor Drift Mine. Photograph courtesy of Joe Wheelhouse (2002
Drift (Horizontal Roadway) Chen He &. Xu Kuangdi. Living reference work entry. First Online: 24 January 2023. 4 Accesses. Download reference work entry PDF. Drift is a horizontal or approximately horizontal roadway, called also horizontal roadway. It is the most common form of tunnel engineering in the underground mines.

Sectional views of the DLSOS mining system with backfilling. Download
Historical US drift mining (coal) Coal miner standing in a drift portal at Fork Mountain, Tennessee, 1920. Colorado. The Boulder-Weld Coal Field beneath Marshall Mesa in Boulder, Colorado was drift mined from 1863 to 1939. Measurements in 2003, 2005, and 2022 showed that the mine has an active coal-seam fire.It was investigated as a possible cause of the 2021 Marshall Fire.
Mining Levels Stations, Drifts, & Crosscuts
This approach is called drift mining (the horizontal tunnel is the drift). These shafts and tunnels were typically dug in winter so that frozen ground would not melt and collapse on the miners. Even so, the practice was arduous and dangerous. In the spring and summer, a defrosting pile of gold-rich gravel called paydirt could be processed using.