
Anatomy Stock Images neckintervertebraldiscdiscusintervertebralisspinousprocessfacet
This review article describes anatomy, physiology, pathophysiology and treatment of intervertebral disc. The intervertebral discs lie between the vertebral bodies, linking them together. The components of the disc are nucleus pulposus, annulus fibrosus and cartilagenous end-plates. The blood supply to the disc is only to the cartilagenous end.
Biology Intervertebral disc
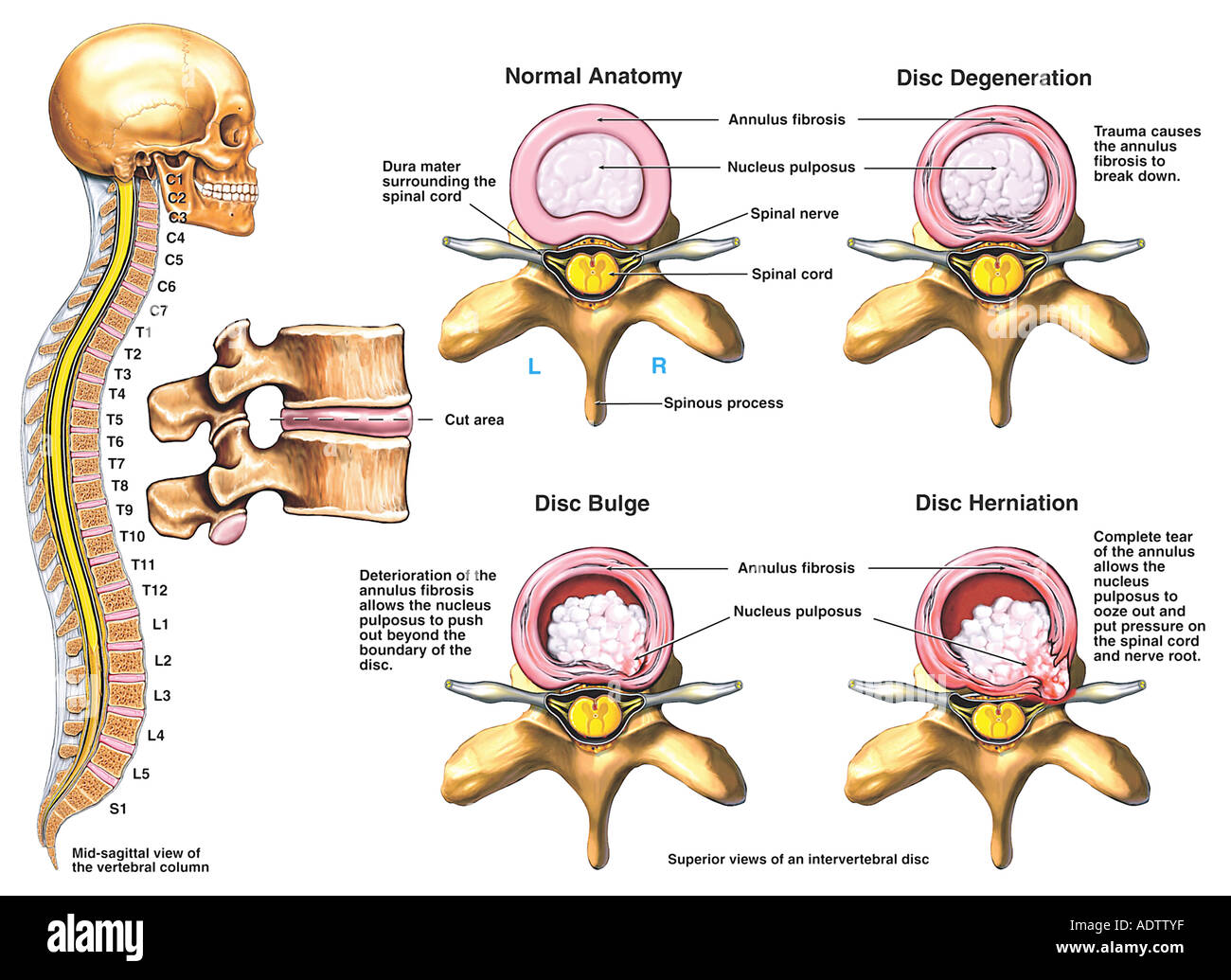
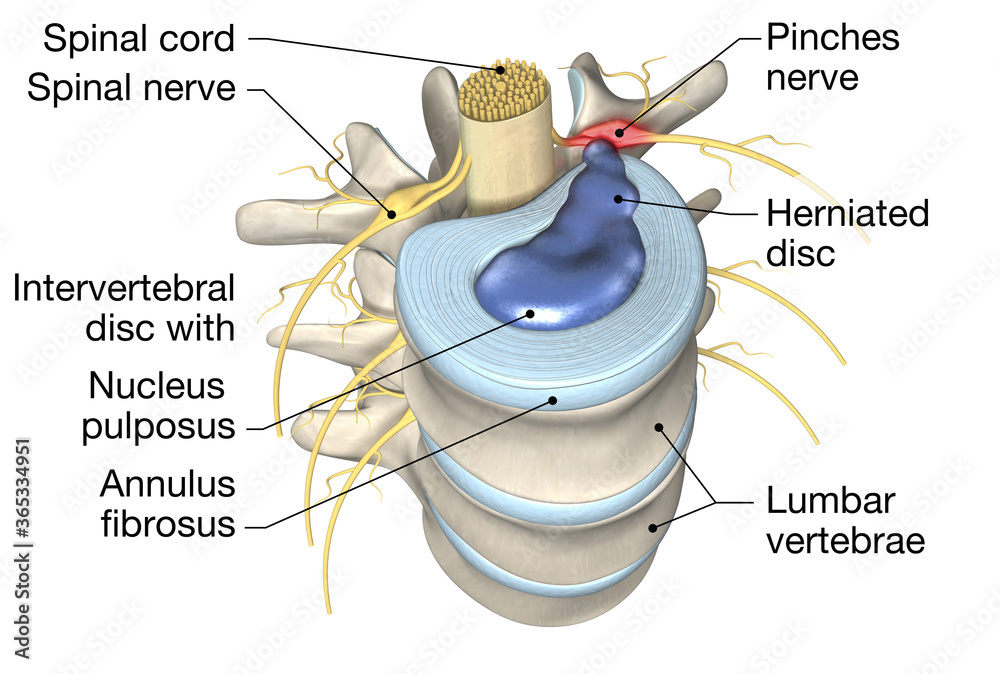
A spinal disc herniation is an injury to the intervertebral disc between two spinal vertebrae, usually caused by excessive strain or trauma to the spine. It may result in back pain, pain or sensation in different parts of the body, and physical disability. The most conclusive diagnostic tool for disc herniation is MRI, and treatment may range.
/images/library/3351/x5Q5Fdrtu4llrJmj9sdg_intervertebral_discs.png)
Intervertebral Discs Anatomy and Embryology Kenhub
More in this Collection. Phone International: 0044 203 289 7147. Indications: Osteochondrosis of the vertebral column, cervical syndrome, prolapsus nucleus pulposus, rheumatic diseases and neuralgia of intervertebral origin. Composition: D10, D30, D200 0.367 ml each.

Diskus intervertebralis II Anatomi og Fysiologi
Diskus Intervertebralis adalah cakram yang membentuk sendi tulang rawan di antara vertebra, memberikan peredam kejut yang sangat efisien. Diskus intervertebralis terdiri dari anulus fibrosus, nukleus pulposus dan tulang rawan di ujung lempengnya. Struktur ini sering rusak dan menjadi penyebab paling umum gangguan tulang punggung bawah.
Intervertebral Disc Anatomy
Definition/Description. The intervertebral disc (IVD) is important in the normal functioning of the spine. It is a cushion of fibrocartilage and the principal joint between two vertebrae in the spinal column. There are 23 discs in the human spine: 6 in the cervical region (neck), 12 in the thoracic region (middle back), and 5 in the lumbar.
3D illustration showing lumbal vertebra with intervertebral disc, medically 3D illustration
Jika dilakukan pada tulang belakang, istilah discus intervertebralis bisa saja muncul. Punggung kita terdiri dari banyak tulang belakang (vertebrae) yang tiap sela-selanya diisi oleh bantalan yang disebut discus intervertebralis. Tulang yang banyak dan bersela-sela ini penting untuk kita dapat melakukan gerakan membungkuk, membusung, dan.
Intervertebral disc anatomy, function, degeneration, herniation
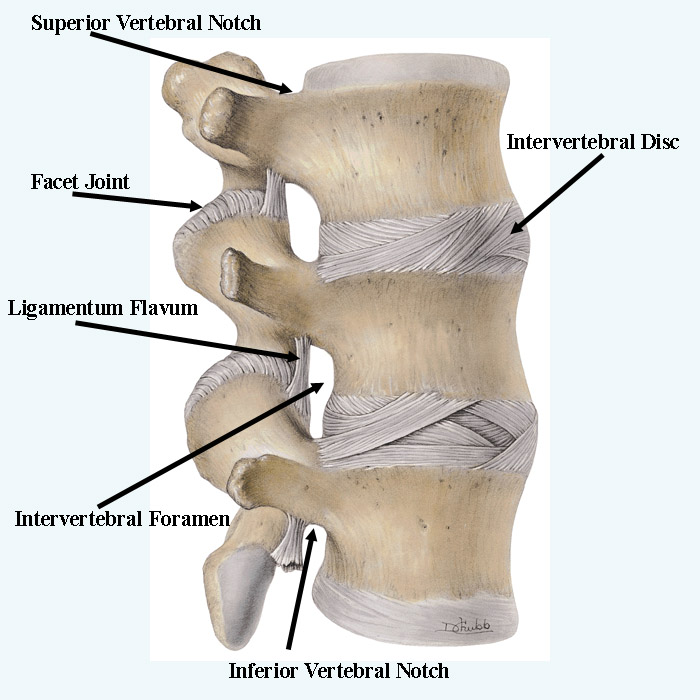
Adjacent vertebrae articulate through zygapophyseal joints between the respective superior and inferior facets of the vertebral articular processes as well as through the joints of the vertebral bodies. While the former serves to limit the spine's range of motion, the latter increases it and provides the majority of the spine's weight-bearing capacity. The inferior surface of the superior.
Lumbar vertebra with intervertebral disc, medically 3D illustration ilustração do Stock Adobe
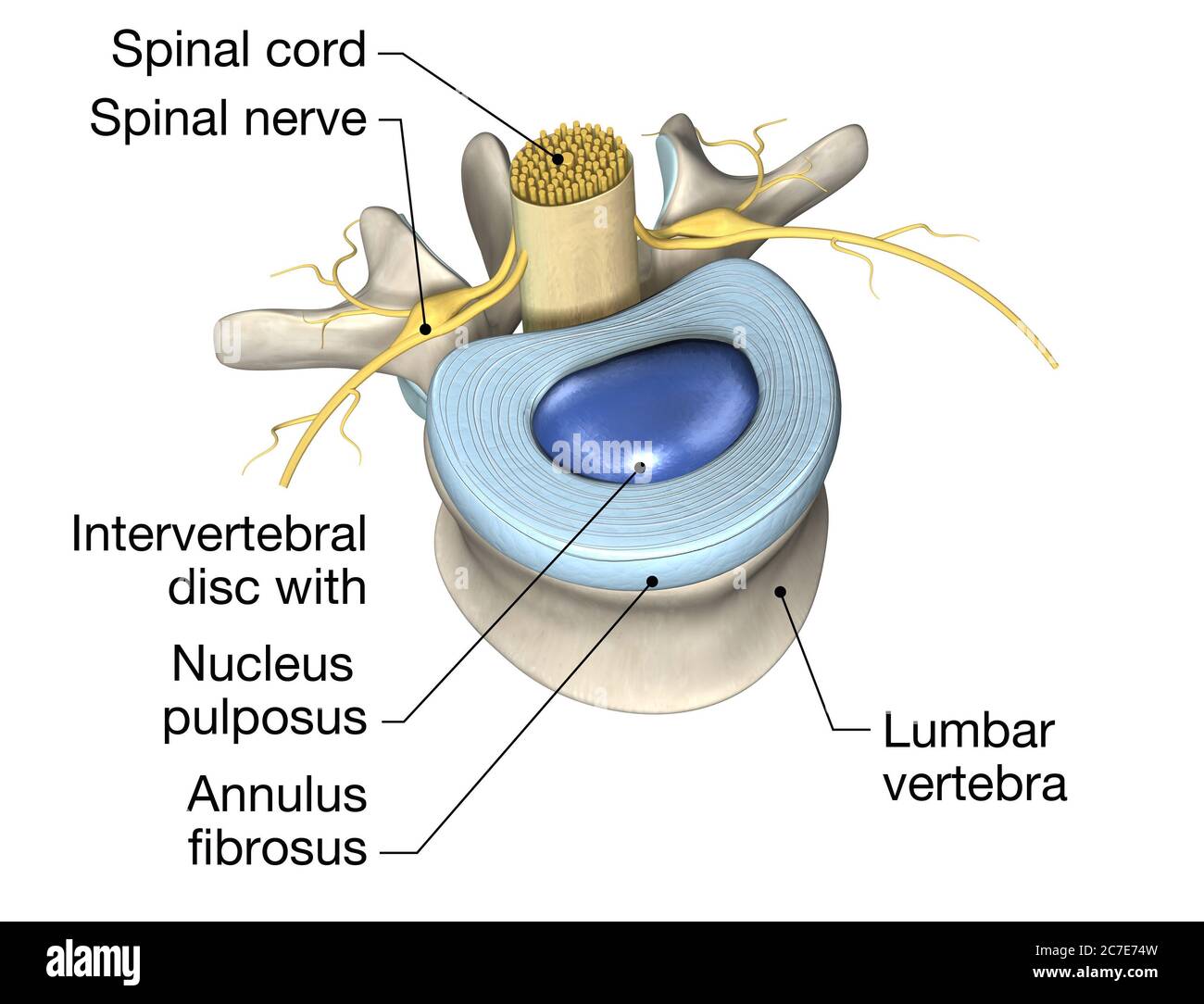
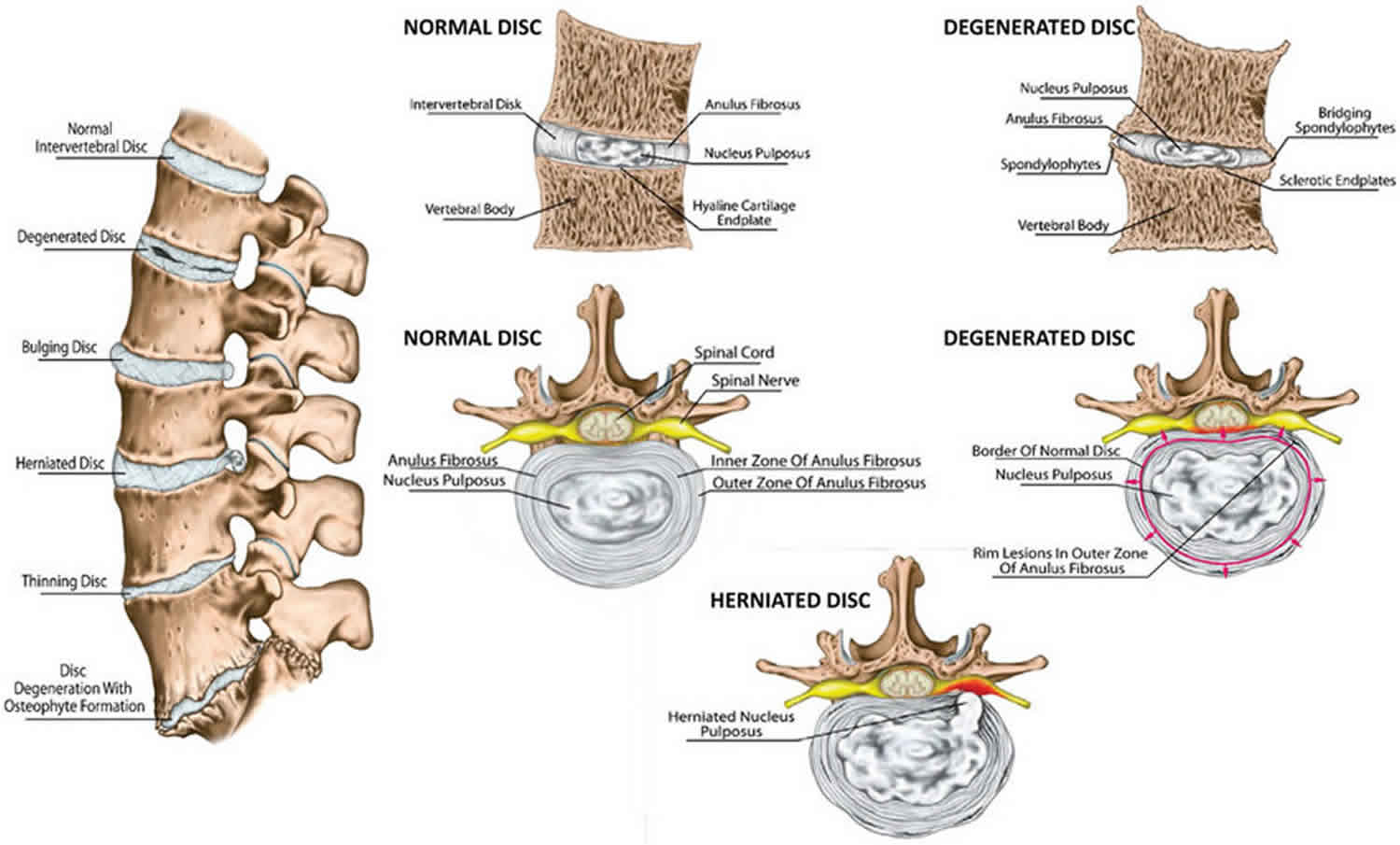
An intervertebral disc is a structure located between adjacent vertebrae of the spine. It consists of a tough outer layer called the annulus fibrosus and a gel-like center called the nucleus pulposus. The intervertebral disc acts as a cushion, allowing the spine to bend and twist without damaging the vertebrae.
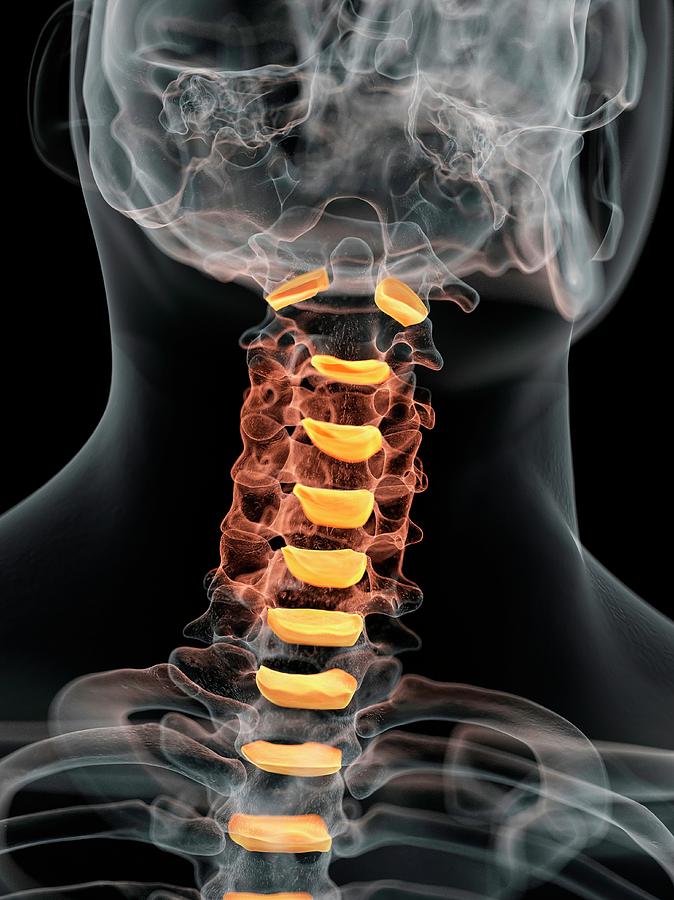
Human Intervertebral Discs Of Neck Photograph by Sciepro Pixels
Diskus intervertebralis sebagian besar avaskuler atau tidak ada pembuluh darah. Struktur di diskus intervertebra mendapat nutrisi dan oksigen secara difusi dari pembuluh darah di sekitarnya. Seiring dengan bertambahnya usia seseorang maka organ dalam tubuh akan mengalami penuaan atau degenerasi, termasuk juga diskus intervertebra.

Discus intervertebralis with tears and fissures in the annulus... Download Scientific Diagram
flexibility, the intervertebral discs allow the spine to twist and bend. throughout a wide range of postures. In addition to allowing. flexibility, the intervertebral discs function in both absorbing energy. and distributing loads applied to the spine. The unique structure and. composition of the intervertebral disc allow for a wide array of.
Intervertebral disc; Disk, Intervertebral; Intervertebral Disk
Background. Depending on the location of the herniated disc at the shoulder, axilla, or ventral side of the compression nerve root, various puncture sites and channel entrances were selected so that the goal of targeted removal of the herniated disc could be achieved by a full-endoscopic technique.

Classification of Joints · Anatomy and Physiology
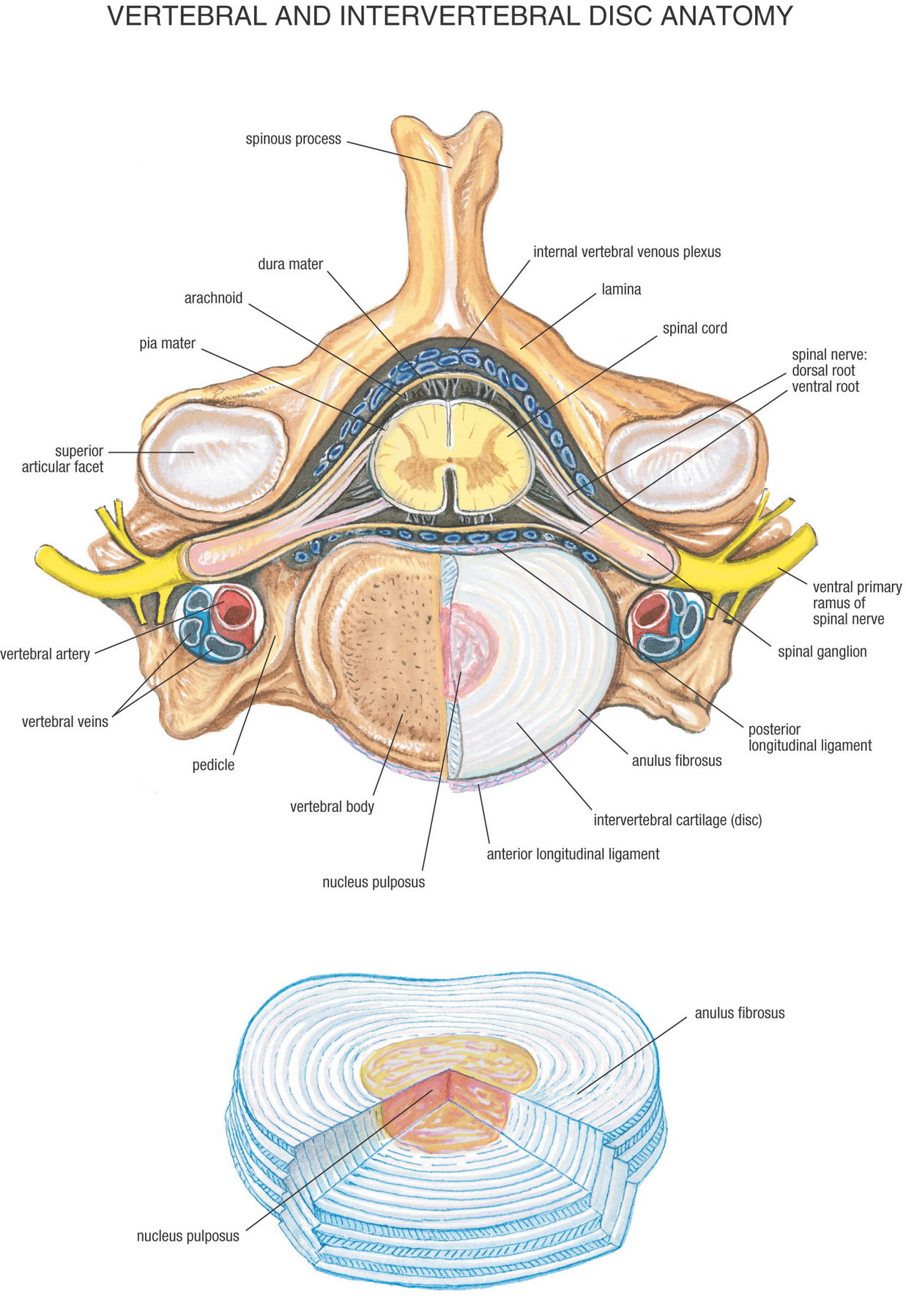
Intervertebral discs consist of an outer fibrous ring, the anulus (or annulus) fibrosus disci intervertebralis, which surrounds an inner gel-like center, the nucleus pulposus. The anulus fibrosus consists of several layers (laminae) of fibrocartilage made up of both type I and type II collagen.Type I is concentrated toward the edge of the ring, where it provides greater strength.
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/article/en/the-intervertebral-discs/s7NeTocKheeOY6q2XMZeg_discus_intervertebralis_large_UcRX3hmxLtk5W9lJvS4hSQ.png)
Intervertebral discs Anatomy and embryology Kenhub
Discus intervertebralis. Definition. The intervertebral discs (intervertebral fibrocartilages) are interposed between the adjacent surfaces of the bodies of the vertebræ, from the axis to the sacrum, and form the chief bonds of connection between the vertebræ. They vary in shape, size, and thickness, in different parts of the vertebral column
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/3352/QOYKBd3SZINF9jv0r8q9GQ_cPpqRfAgns_Anulus_fibrosus_1.png)
Intervertebral Discs Anatomy and Embryology Kenhub
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data. Vacuum phenomena involving the intervertebral discs is usually a result of an accumulation of gas, principally nitrogen , within the crevices of the intervertebral discs or adjacent vertebrae. This is a joint-specific example of the vacuum phenomenon.
Spine Basics OrthoInfo AAOS
Synonyms: none. The intervertebral joints connect directly adjacent vertebrae of the vertebral column. Each intervertebral joint is a complex of three separate joints; an intervertebral disc joint (intervertebral symphysis) and two zygapophyseal (facet) joints. This article will describe the anatomy and function of the intervertebral joints.
/images/anatomy_term/discus-intervertebralis-txii-li/CURgswBvGHt6z0rGFu8ww_Discus_intervertebralis_TXII-LI_01.png)
Intervertebral disc T12L1 (Discus intervertebralis TXIILI) Kenhub
Understanding Spinal Anatomy: Intervertebral Discs. Between each vertebral body is a cushion called an intervertebral disc. Each disc absorbs the stress and shock the body incurs during movement and prevents the vertebrae from grinding against one another. The intervertebral discs are the largest structures in the body without a vascular supply.