Shapes of molecules
The CTB geometry is identified by donor atoms taking up one apex and three equatorial positions of a trigonal bipyramid (TBP) (Fig. 1).The remaining two coordination sites R 1 and R 2 form the top of a distorted Y shape around the opposite apex, effectively adding a capping atom to a TBP with a R 1 MR 2 angle of 50-80°. The R 2 ML angle (Fig. 1) ideally is close to 180° but in practice can.

Trigonal Bipyramidal Molecular Geometry VSEPR Theory Planar Molecule Ax Transparent PNG
Introduction. Main medical applications of In III complexes are currently related to the use of the isotope 111 In (electron capture with gamma emissions of 171 and 245 keV, t 1/2 = 67.4 h) in diagnostic radiopharmacy, 1-4 where it is frequently used for the imaging of infection and inflammation sites. Additionally, 111 In is under discussion for cancer therapy, since it also emits Auger.
Apicophilicity Trigonal Bipyramidal Molecular Geometry Structure Molecule Monomer, PNG
Other articles where trigonal bipyramidal arrangement is discussed: chemical bonding: Applying VSEPR theory to simple molecules:.and found to be a trigonal bipyramid. The XeF4 (xenon tetrafluoride) molecule is hypervalent with six electron pairs around the central xenon (Xe) atom. These pairs adopt an octahedral arrangement. Four of the pairs are bonding pairs, and two are lone pairs.
Molecular Modeling 1 Chem Lab
The base angles are still 180°, 120°, and 90° while the tweaked angle will now be slightly less in each case due to the extra repulsion from the lone pair. POLARITY: POLAR - The lone pair electrons throw off the perfectly cancelling symmetry of the five trigonal bipyramidal regions thus making the overall molecule polar.
Trigonal bipyramidal structure Science, Chemistry, Molecular Geometry ShowMe
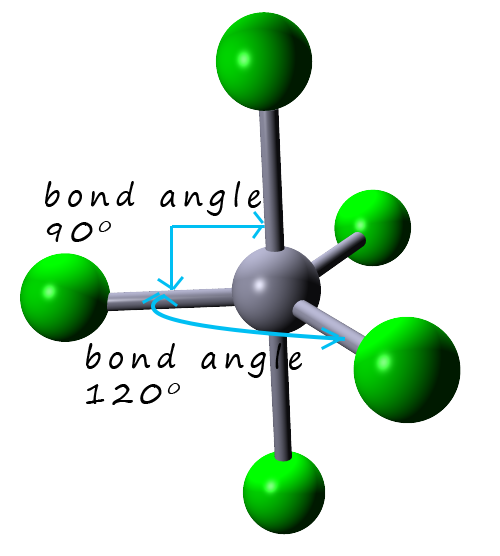
Trigonal Bipyramidal Geometry. Trigonal bipyramidal arrangement of 5 regions of high electron density (white). Three regions of high electron density point at the corners of an equilateral triangle. One region of high electron density is directly above the plane of the triangle, and one is directly below the plane. A trigonal bipyramidal.

Trigonal Bipyramidal Collection
Synthetic chemistry enables a bottom-up approach to quantum information science, where atoms can be deterministically positioned in a quantum bit or qubit. Two key requirements to realize quantum technologies are qubit initialization and read-out. By imbuing molecular spins with optical initialization and readout mechanisms, analogous to solid-state defects, molecules could be integrated into.

Trigonal Bipyramidal Lewis Structure
Three orbitals are arranged around the equator of the molecule with bond angles of 120 o. Two orbitals are arranged along the vertical axis at 90 o from the equatorial orbitals. The shape of the orbitals is trigonal bipyramidal. Since there is an atom at the end of each orbital, the shape of the molecule is also trigonal bipyramidal.
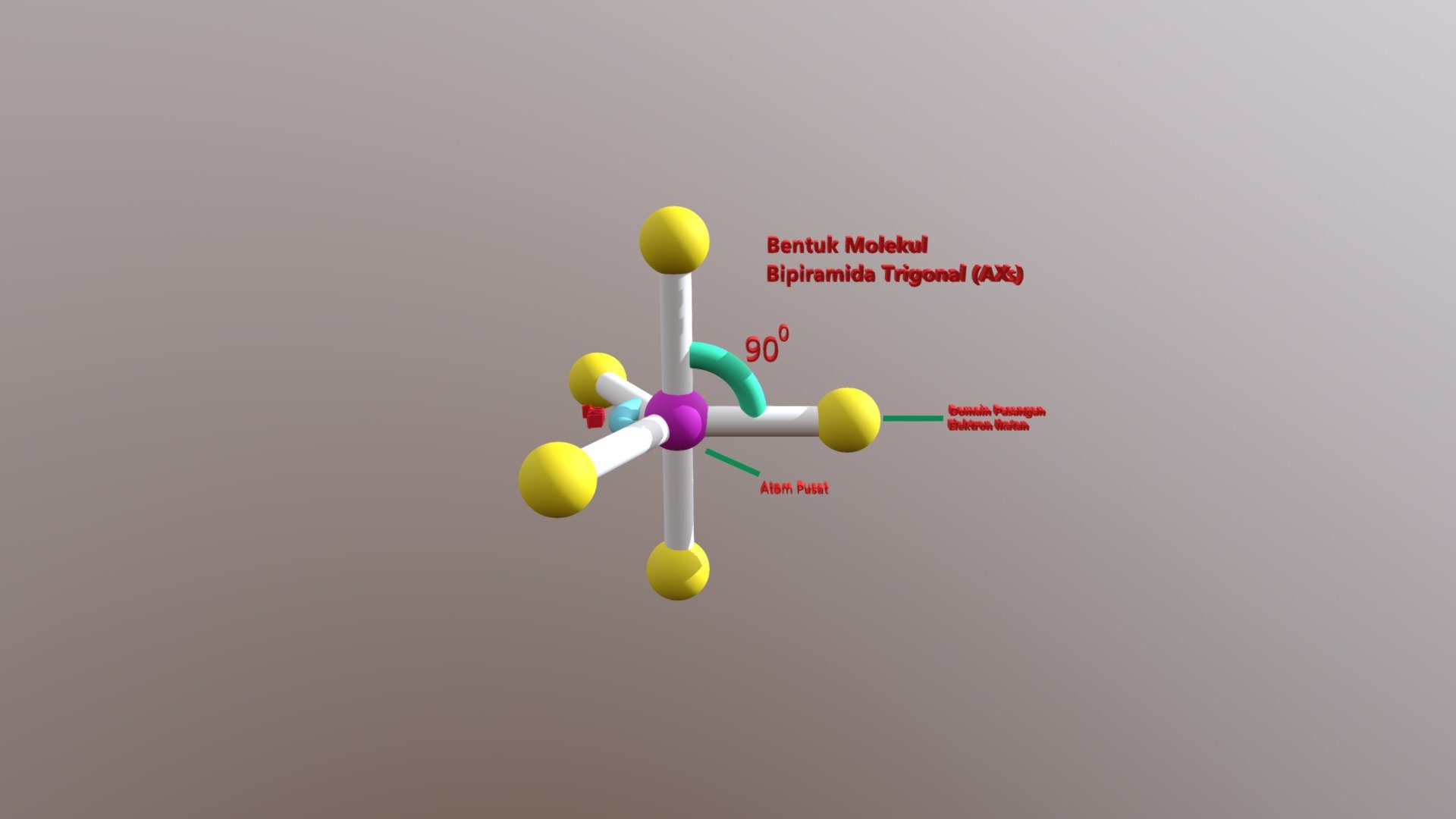
Bipiramida Trigonal Santi 3D model by santi.syafiana [dabcd9b] Sketchfab
Triangular bipyramid. In geometry, the triangular bipyramid is the hexahedron with six triangular faces, constructed by attaching two tetrahedrons face-to-face. The same shape is also called the triangular dipyramid [1] [2] or trigonal bipyramid. [3] If these tetrahedrons are regular, all faces of triangular bipyramid are equilateral.

Trigonal Bipyramidal Geometria Molecular, Trigonal Plana Geometria Molecular, Pentagonal
Trigonal bipyramidal molecular geometry. In chemistry, a trigonal bipyramid formation is a molecular geometry with one atom at the center and 5 more atoms at the corners of a triangular bipyramid. [1] This is one geometry for which the bond angles surrounding the central atom are not identical (see also pentagonal bipyramid ), because there is.

The basic trigonal bipyramidal molecular
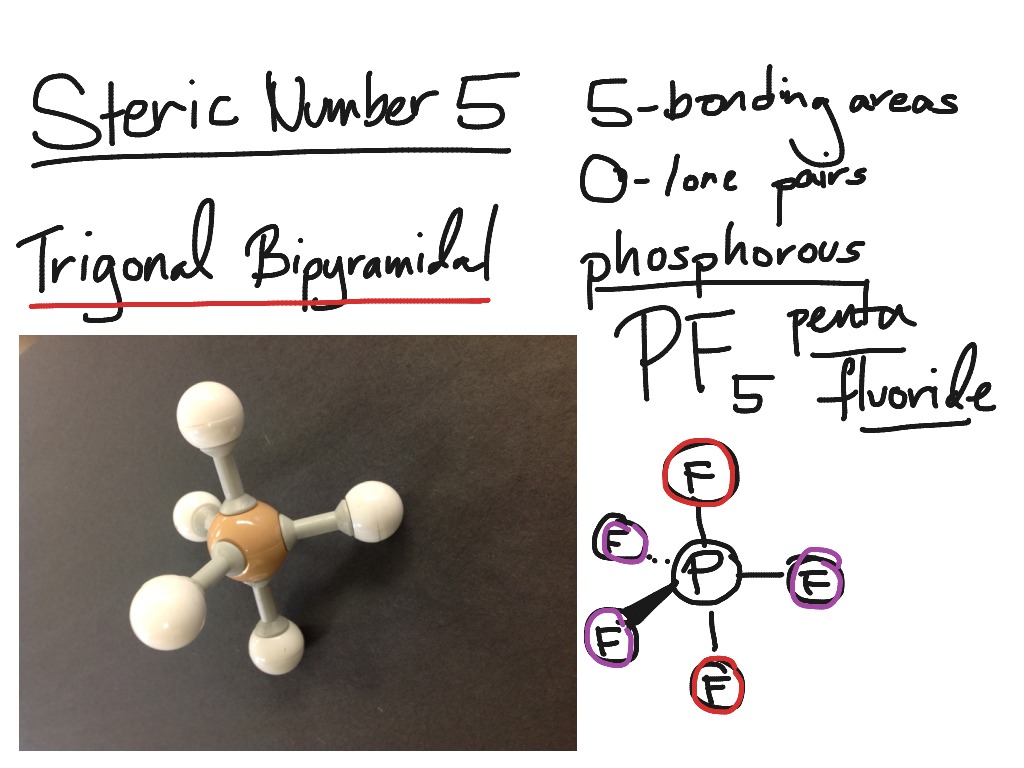
2.9.1: Trigonal Bipyramidal Species. Page ID. Trigonal Bipyramidal Species are those that have a central p-block atom and are attached to 5 other atoms. It is classified as a EX5 molecule, where E stands for the central atom, and X stands for the atoms that are attached. It makes sense, then, to classify this molecule a 5-coordinate system.

Trigonal Bipyramidal Molecular Geometry/Shape and Bond Angles YouTube
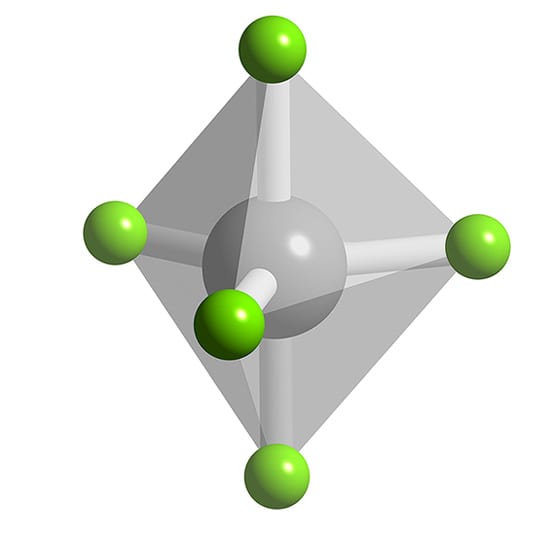
AB2U 3. Molecular Geometry. AB 6, AB5U, and AB4U 2. Some examples of molecules with this geometry are: SF 6, SeF 6, SCl 6, etc. These molecules are examples of central atoms with six bonding pairs of electrons. Molecules are octahedral and nonpolar when all six substituents are the same. If the six substituents are not the same polar.
MA5 trigonal bipyramid
Note that the largest angle is ~103 degrees, but the F-P-F angles in the basal plane are all ~87 degrees. Here's the trigonal bipyramidal geometry: Now the angles are exactly what we expect from VSEPR. We see 90 degree angles between the equatorial plane and the axial F atoms. And the F-P-F in the plane are all 120 degrees.

Trigonal Bipyramidal Molecular Geometry Download Free 3D model by orgoly [8a7db40] Sketchfab
In this video we'll look at the Trigonal Bipyramidal Molecular Geometry and Bond Angles. We'll use the example of PCl5 to understand the molecular shape..
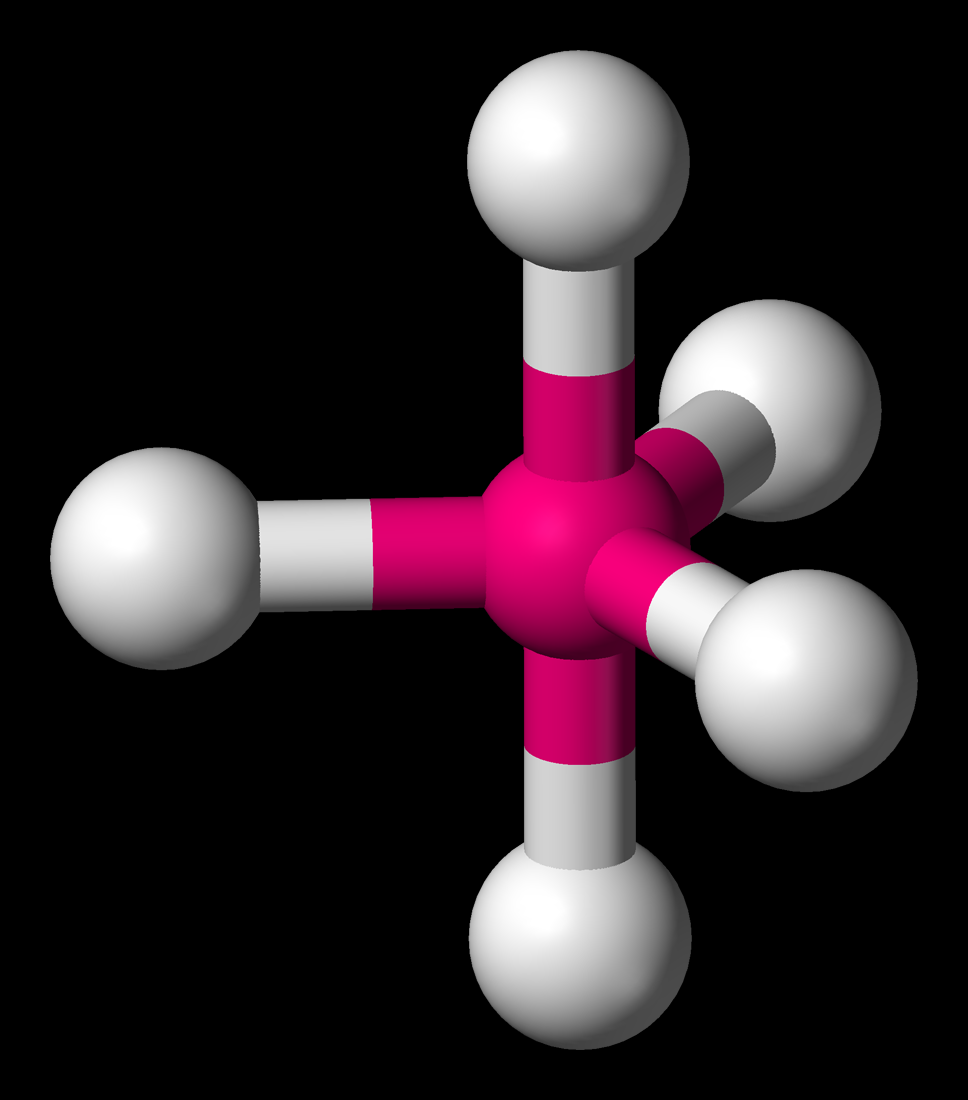
Image Trigonalbipyramidal3D.png Engineering
The stereoisogram approach, which has originally been developed to rationalize organic stereochemistry (Fujita in J Org Chem 69:3158-3165, 2004; Fujita in Tetrahedron 62:691-705, 2006; 65:1581-1592, 2009), is extended and applied to inorganic stereochemistry by using trigonal bipyramidal compounds as examples. The point group D 3h of a trigonal bipyramidal skeleton is extended into the.

Seesaw Molecular Geometry VSEPR Theory Trigonal Bipyramidal Molecular Geometry, PNG, 1100x858px
A trigonal bipyramidal molecule is a bit more complicated, mostly because it has more atoms and bonds to take into account. As the name implies, a trigonal bipyramidal shape looks like two three.
Trigonal Bipyramidal 3D model by EfrenR [f9ebad4] Sketchfab
Molecular Geometry of the Trigonal Bipyramidal Structures. The order of most repulsion to least repulsion among bonding and lone pair electrons are: Lone pair-Lone pair > Lone pair-Bond pair > Bond pair-Bond pair. To decide where to place lone pairs on the parent Trigonal Bipyramidal structure, we must place lone pairs far away from each other.