
Anatomical Terminology Anatomy and Physiology I
We recommend at least a 3D sagittal FLAIR sequence (or 2D axial and sagittal FLAIR sequence), and a 2D axial diffusion weighted sequence; post-contrast T1 images may be obtained depending on clinical and radiographic suspicion for PML, and/or PML-related immune reconstitution inflammatory syndromes. Q: Are there any age-limits for MRI scans?
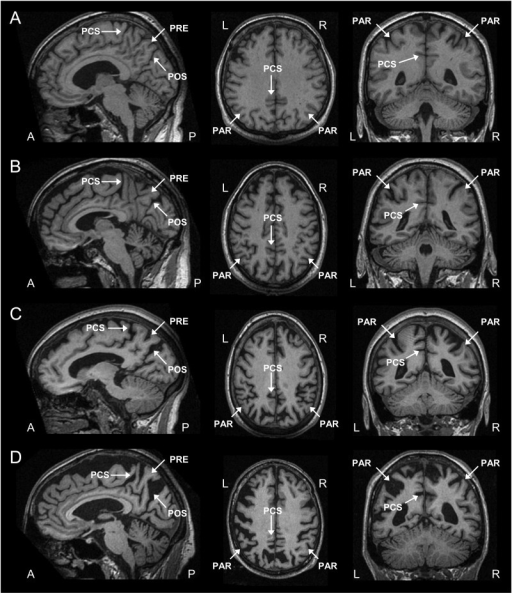
T1weighted sagittal, axial, and coronal images as exam Openi
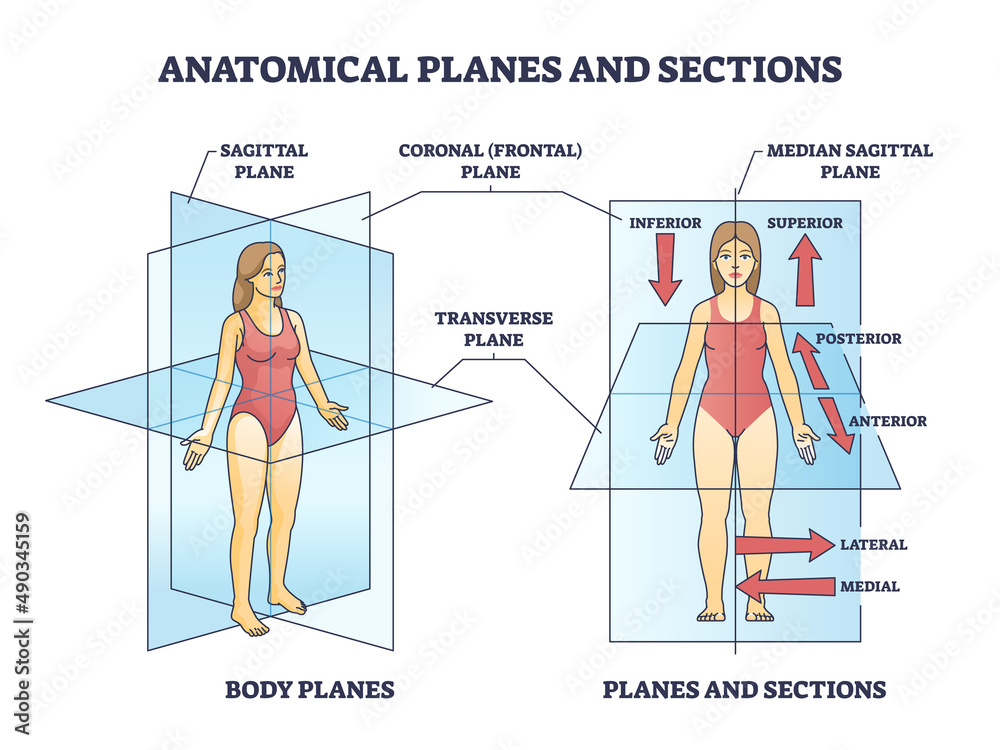
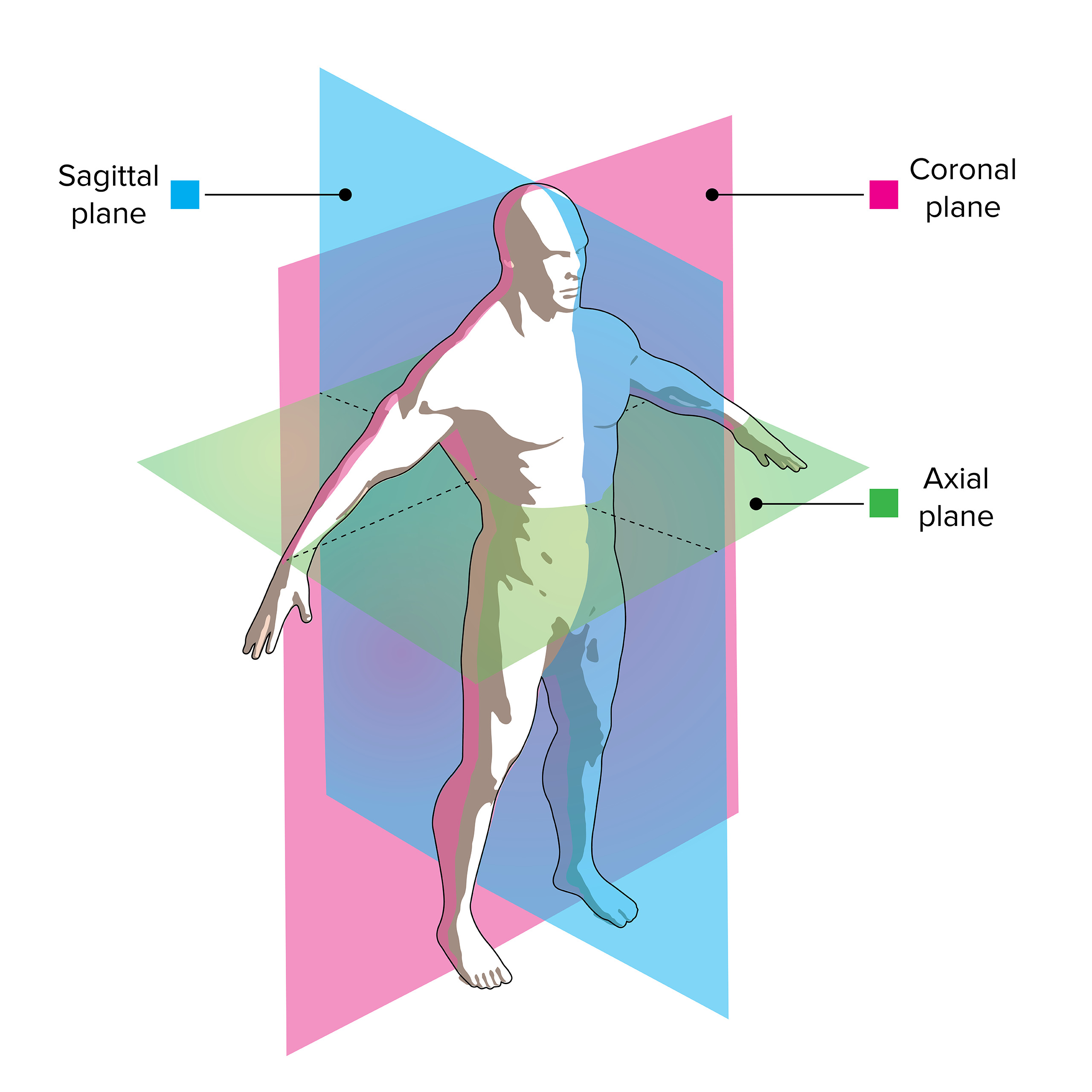
The sagittal plane (/ ˈ s æ dʒ ɪ t əl /; also known as the longitudinal plane) is an anatomical plane that divides the body into right and left sections. It is perpendicular to the transverse and coronal planes. The plane may be in the center of the body and divide it into two equal parts (mid-sagittal), or away from the midline and divide it into unequal parts (para-sagittal).

Identification of anatomical planes applied to brain Diagram Quizlet
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is one of the most commonly used tests in neurology and neurosurgery. MRI provides exquisite detail of brain, spinal cord and vascular anatomy, and has the advantage of being able to visualize anatomy in all three planes: axial, sagittal and coronal (see the example image below).
Anatomical planes or sections for human medical body division outline diagram. Labeled
The coronal or frontal planes divide the body into front and back (also called dorsal and ventral or posterior and anterior) sections and are x-y planes. The transvers planes, also known as the.
EPOS™
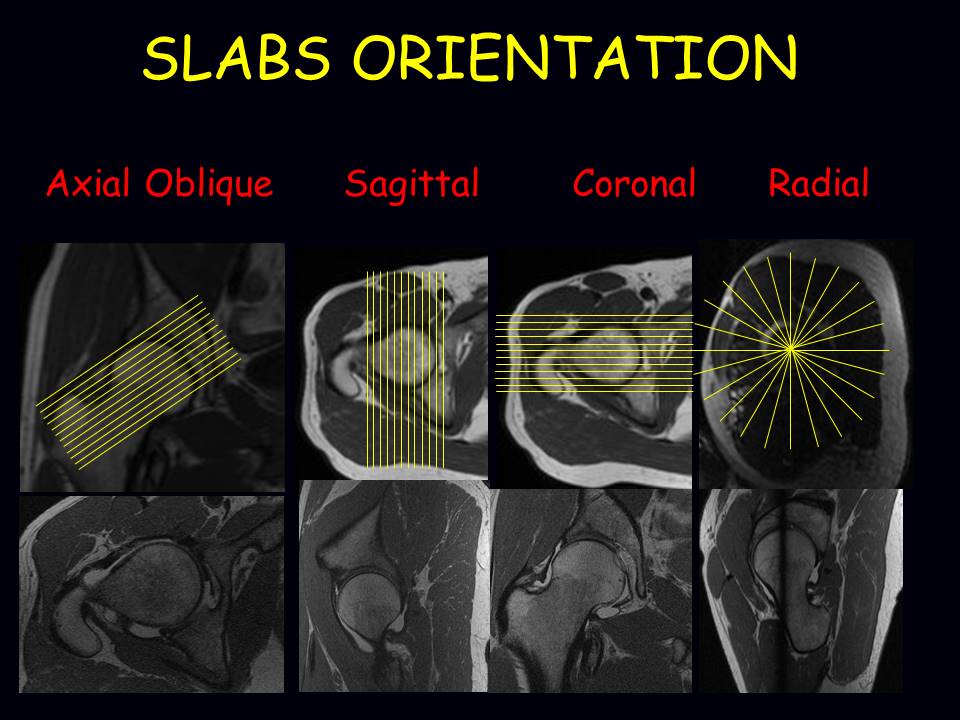
As useful and dramatic as axial computed tomograms are, severe limitations have been encountered. Most of these involve the accurate location of masses and, as in angiography, projections in several planes are essential.. Coronal and sagittal reconstructions are practical and obtained with ease. The computerized tomogram is invaluable in.

Anatomical Terminology Foundations of Neuroscience
Sagittal and coronal planes are also referred to as longitudinal planes as they make a right angle to the transverse plane. Although motion is a combination of different movements, it can be classified depending upon the anatomical plane where it has occurred. To describe these planes, consider a person standing with an upright stance.
Imaging of the Spine and Spinal Cord Concise Medical Knowledge
Check all images planes (axial, coronal, sagittal, or oblique) MRI sequences. Hover on/off image to show/hide findings. Tap on/off image to show/hide findings. Click image to align with top of page. MRI sequences. Look at the fat-sensitive T1 images which often provide good anatomical detail of the area being studied;

Features Used to Classify Animals · Biology
CT evaluation of diffuse infiltrative lung disease: dose considerations and optimal technique. J Thorac Imaging. 2009;24:252-259. HRCT Primer. Image Reconstruction Planes. Review the different image reconstruction planes, which include axial, coronal, and sagittal planes and are made possible using volumetric acquisition CT.

Sagittal T2 weighted resonance image of the female pelvis The BMJ
Anatomical planes are imaginary planes/2D surfaces used to divide the body to facilitate descriptions of location and movement. The anatomical position is used as a reference when describing locations of structures and movements. It is an upright position with arms by the side and palms facing forward. Feet are parallel with toes facing forward.
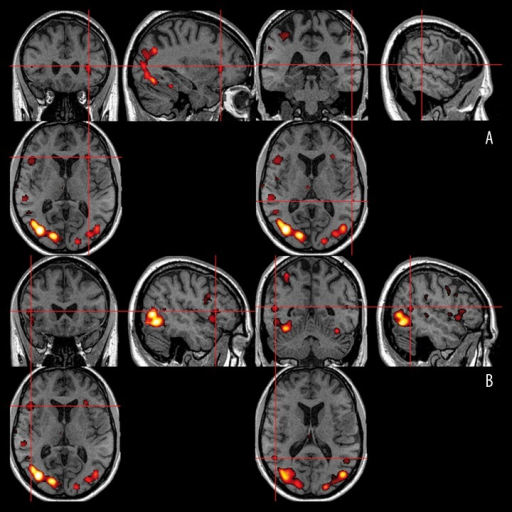
Sagittal, coronal and axial views of the Broca’s and Openi
820 Jorie Blvd., Suite 200 Oak Brook, IL 60523-2251 U.S. & Canada: 1-877-776-2636 Outside U.S. & Canada: 1-630-571-7873
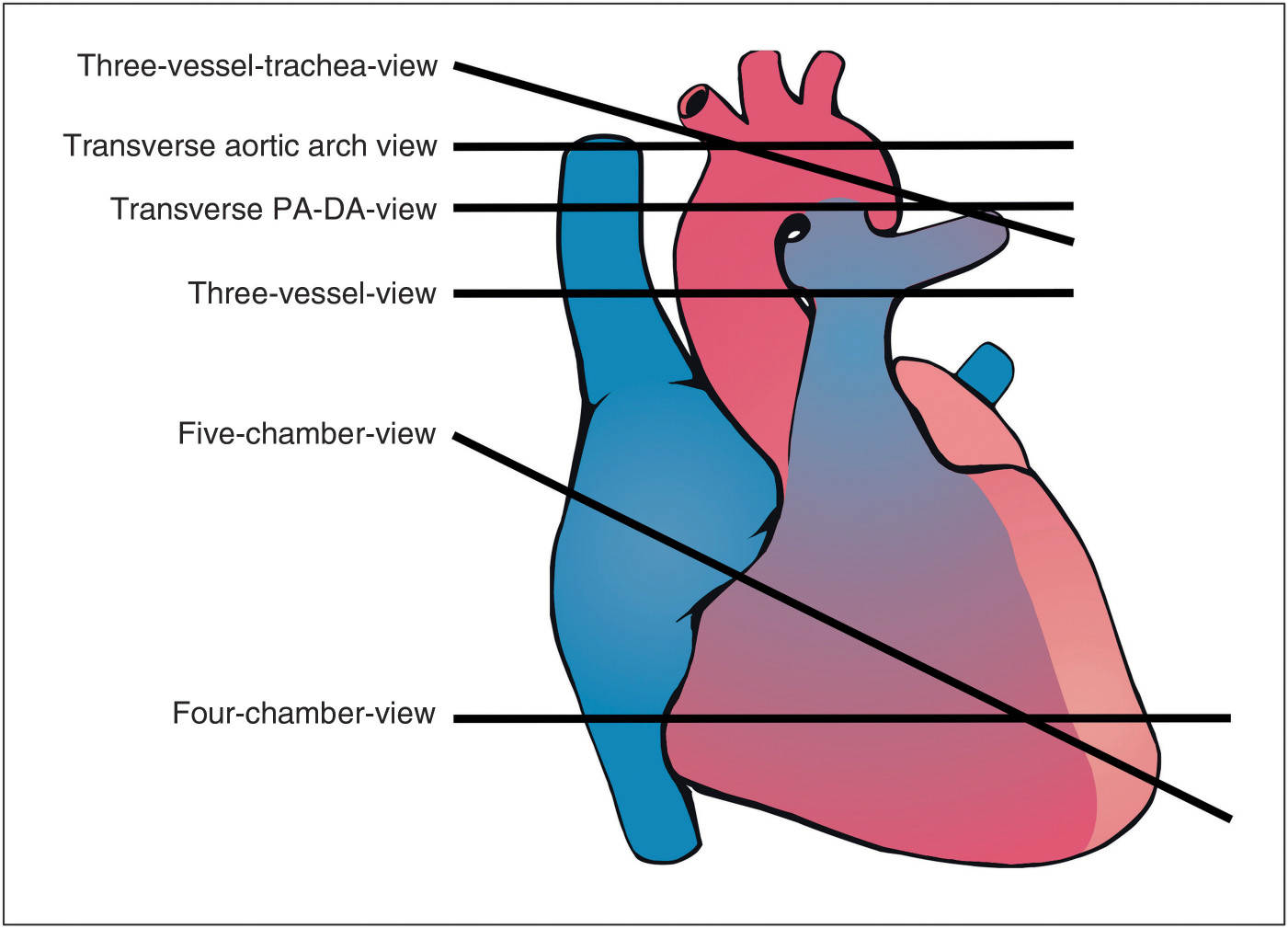
The Great Vessels Axial, Oblique, and Sagittal Views Obgyn Key
Coronal (frontal) plane: separates the front (anterior) and back ( posterior) of the body. Sagittal (longitudinal) plane: separates the left and right sides of the body. Transverse (axial) plane.
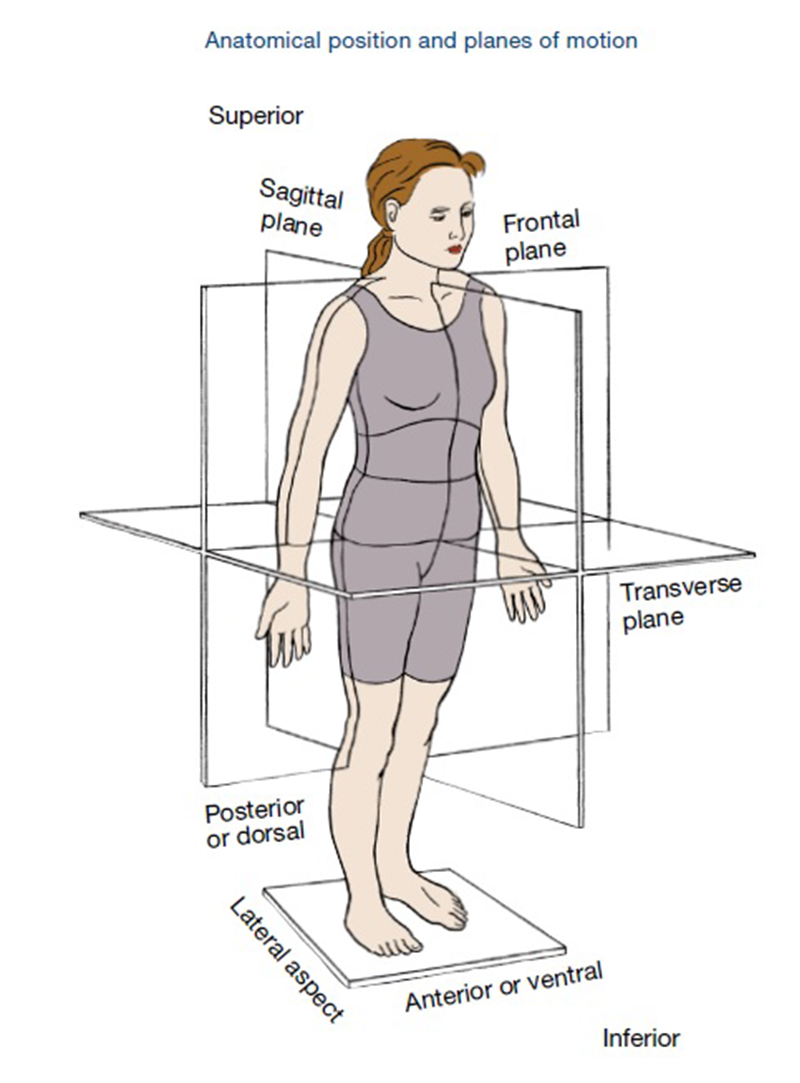
Planes of Motion Explained ACE Blog
The captured 2D images are instantaneously conveyed to the computer, which reconstructs them, using modified Feldkamp algorithm into the anatomical volume for viewing at 1:1 ratio in axial, coronal, and sagittal planes (orthogonal planes) (Figure 3a,3b,3c,3d) . The data is in the Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine (DICOM) format.

Pediatric Craniosynostosis UF Pediatric Neurosurgery » Pediatric Craniosynostosis » Lillian S
A coronal or frontal plane divides the body into dorsal and ventral (back and front, or posterior and anterior) portions. A transverse plane, also known as an axial plane or cross-section, divides the body into cranial and caudal (head and tail) portions. A sagittal plane divides the body into sinister and dexter (left and right) portions.

Imaging of the Head and Brain Concise Medical Knowledge
Anatomical position for a human is when the human stands up, faces forward, has arms extended, and has palms facing out. Figure 1.2.1 1.2. 1 : These two people are both in anatomical position. (CC-BY, Open Stax ) When referencing a structure that is on one side of the body or the other, we use the terms "anatomical right" and "anatomical.

Anatomical plane Wikipedia
Axial Coronal Sagittal *On axial & coronal images, the RIGHT side of the patient is on the LEFT side of the image. Head CT Anatomy and Basic Interpretation. Surface Anatomy of the Brain. Vertex Level Superior frontal gyrus Middle frontal gyrus Precentral gyrus (Frontal lobe) Central sulcus Postcentral gyrus

Anatomical Terminology Basics Facty Health
The sagittal suture extends posteriorly from the coronal suture, running along the midline at the top of the skull in the sagittal plane of section (see Figure 7.9). It unites the right and left parietal bones. On the posterior skull, the sagittal suture terminates by joining the lambdoid suture. The lambdoid suture extends downward and.