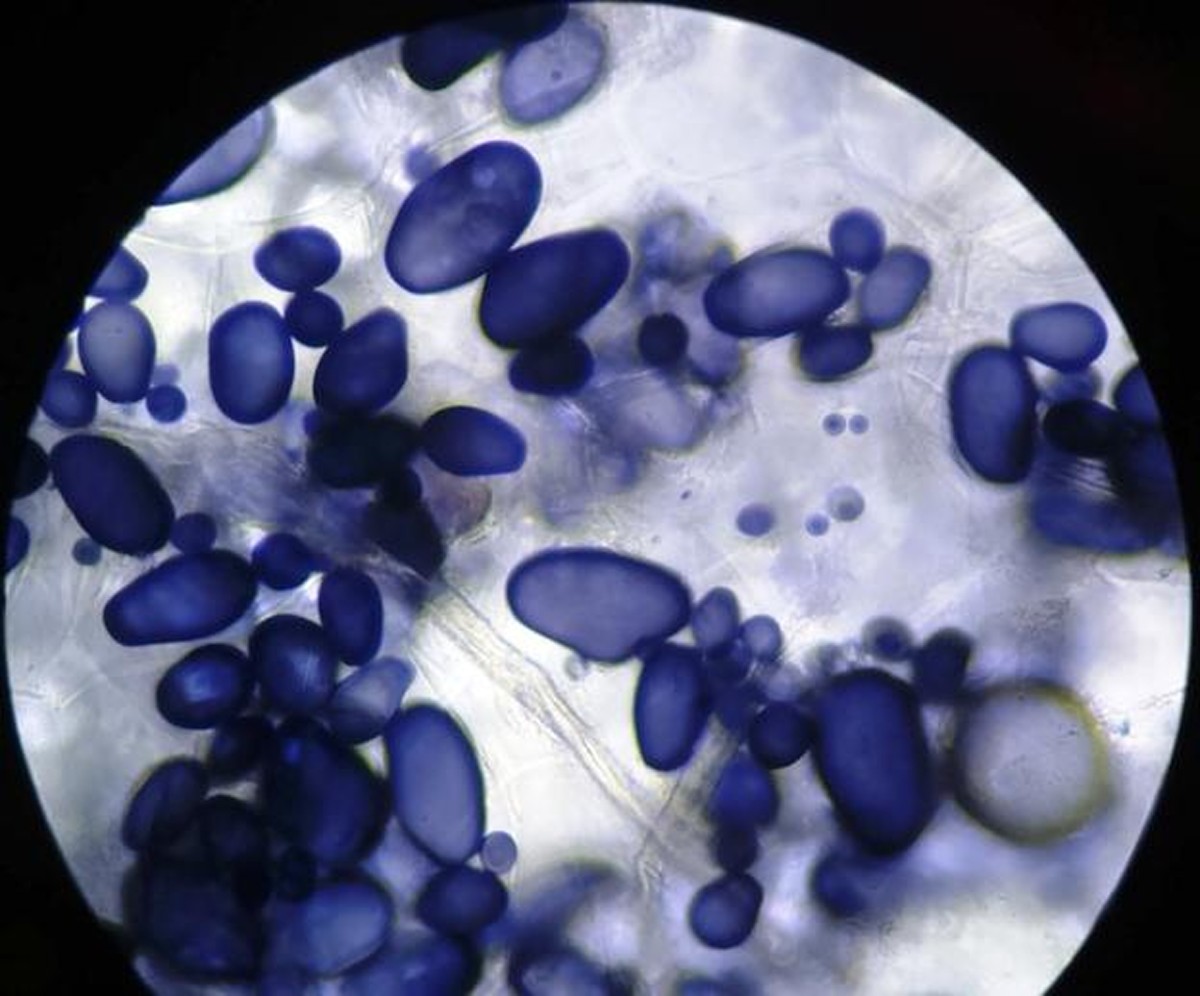
Amiloplastos qué son, características, funciones, estructura
Over 3000 amyloplast-localized proteins were identified, of which >98% were quantified and defined as the kfALP (k iwi f ruit a my l oplast p roteome). The kfALP data were validated by Tandem-Mass-Tag (TMT) labeled proteomics in 'Hort16A'. Analysis of the proteomic data across development and ripening revealed: 1) a conserved increase in.
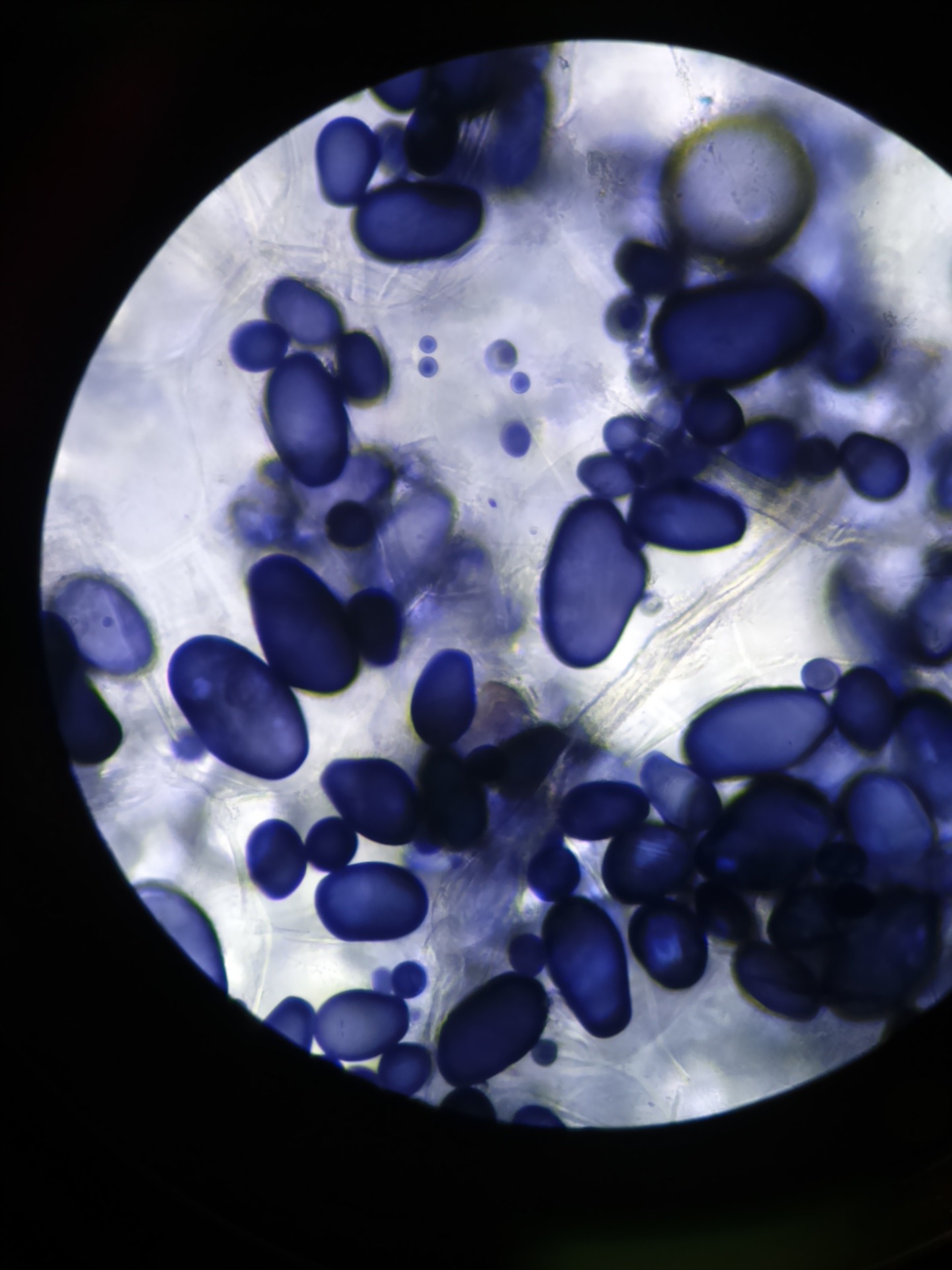
Amiloplastos y almacenamiento de almidón en plantas YuBrain
Amyloplast. Amyloplasts in special tissues in the stem (the endodermis) and the root (the columella of the root cap) perform a mechanical, not a metabolic, function as they sink to the bottom of the cell and signal an upper/lower cell polarity that initiates a gravitropic growth response (Toyota et al., 2013). From: Encyclopedia of Cell Biology.
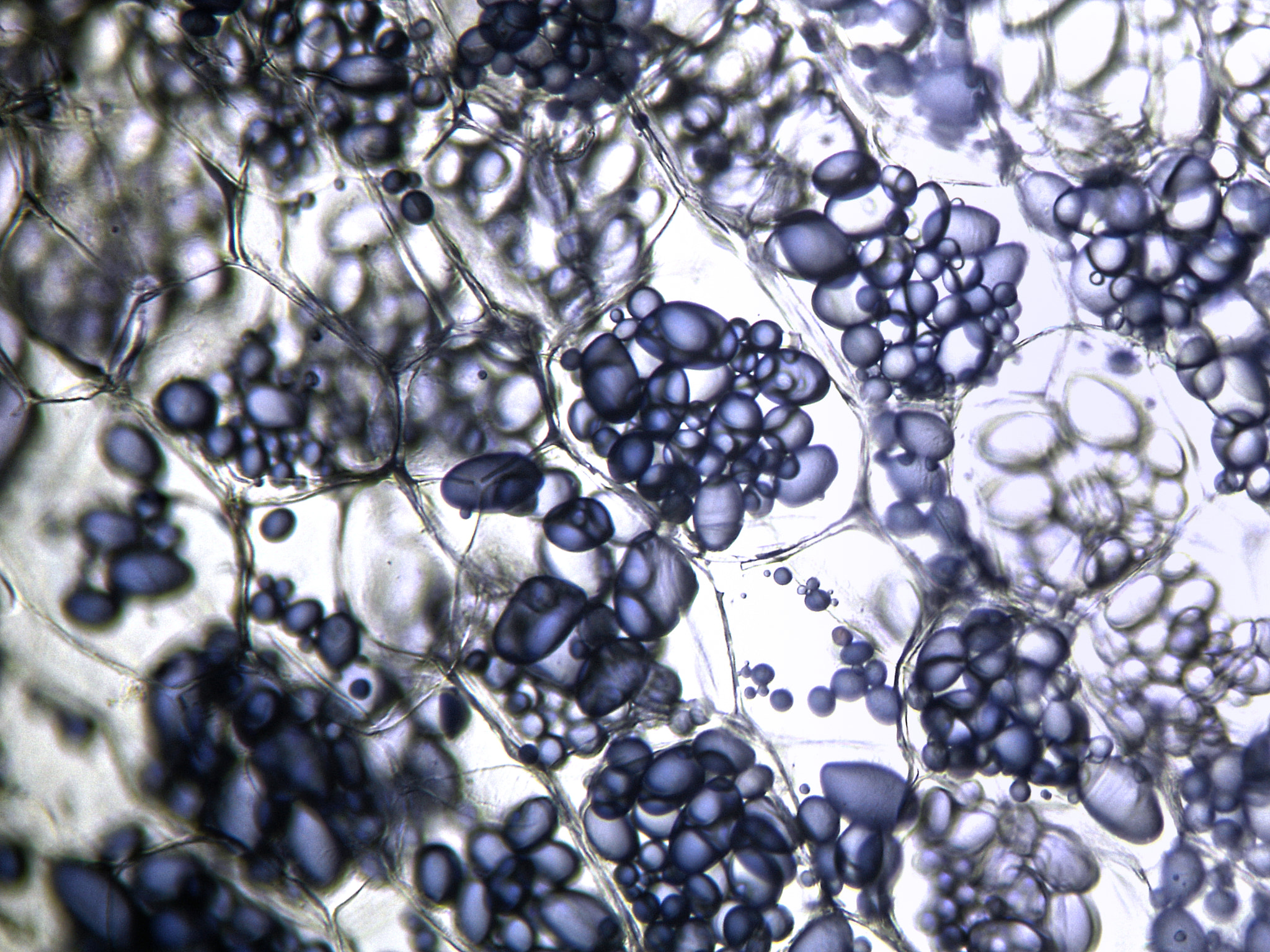
Amyloplasts in Potato Cells by Hernán Toro / 500px
As well as their storage functions, the amyloplast from Arabidopsis roots were reported to contribute to gravitropism signaling (Chen et al., 1999; Nakamura et al., 2019). Elaioplast. Elaioplasts are characterized by ultrastructures filled with hydrophobic contents such as lipids and terpenoids. They are specialized for biosynthesis and the.

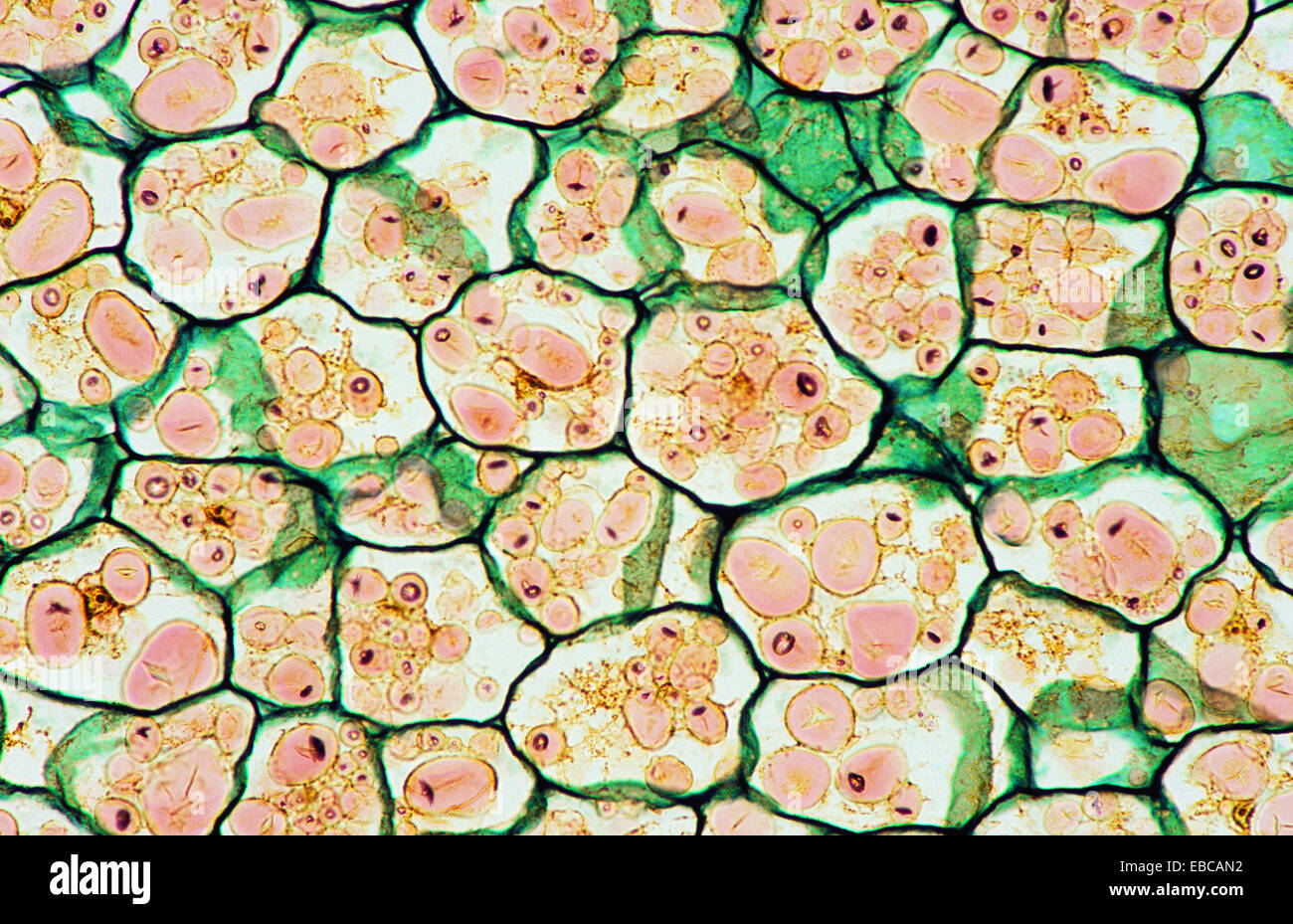
Potato amyloplasts, ESEM Stock Image B100/0048 Science Photo Library
For example, during amyloplast-to-chromoplast conversion in the developing tobacco nectary, chromoplast differentiation is associated with the production of nectar sugars as well as starch catabolism (Horner et al. 2007). In fact, other studies suggested that carbohydrates, such as sucrose and hexose, could regulate chromoplast differentiation.

Arabidopsis Amyloplasts Stock Image C021/9809 Science Photo Library
Chloroplasts and Other Plastids. Chloroplasts, the organelles responsible for photosynthesis, are in many respects similar to mitochondria. Both chloroplasts and mitochondria function to generate metabolic energy, evolved by endosymbiosis, contain their own genetic systems, and replicate by division. However, chloroplasts are larger and more.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/starch_grains-57f7c1173df78c690f635fe2.jpg)
Amyloplast Definition and Function
You Might Also Like. amyloplast (ăm´əlōplăst´), also called leucoplast, a nonpigmented organelle, or plastid, occurring in the cytoplasm of plant cells. Amyloplasts transform glucose, a simple sugar, into starch through the process of polymerization, and store starch grains within their stretched membranes.

Starch Grains Or Amyloplasts Photograph by Dr Jeremy Burgess/science Photo Library. Pixels
An amyloplast is an organelle found in plant cells. Amyloplasts are plastids that produce and store starch within internal membrane compartments. They are commonly found in vegetative plant tissues, such as tubers (potatoes) and bulbs. Amyloplasts are also thought to be involved in gravity sensing ( gravitropism) and helping plant roots grow in.
Amyloplast High Resolution Stock Photography and Images Alamy
Amyloplast: Amyloplast is a colourless plastid found in plants that is responsible for starch storage and synthesis. Amyloplasts can be found in a variety of tissues, the most common of which are storage tissues. They're found in both photosynthetic and parasitic plants, implying that they're also prevalent in non-photosynthetic ones.
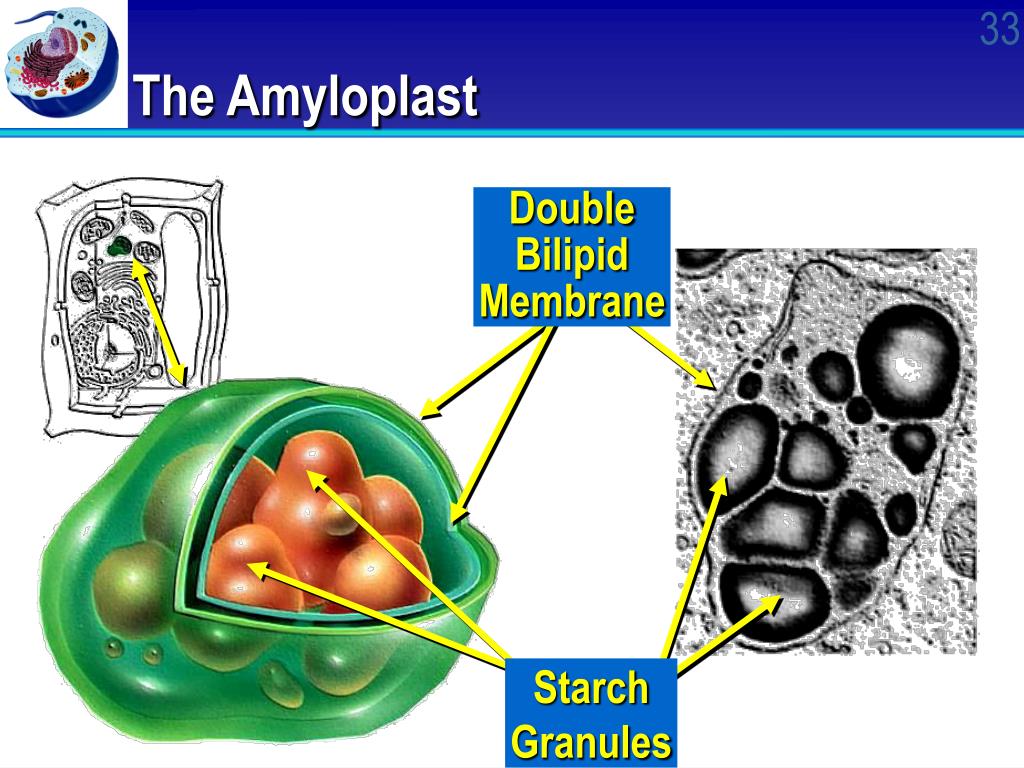
PPT Cell Structure & Function PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID5488471
Amiloplas memiliki arti dalam bidang ilmu biologi. Dikutip buku Anatomi dan Fisiologi Tumbuhan (2021) oleh Arwin Arif, amiloplas menyimpan pati yang tidak terpigmentasi. Istilah umumnya leukoplas yang artinya plastida yang tidak terpigmentasi, tetapi bukan sebagai istilah untuk amiloplas, yang mengidentifikasi apa yang tersimpan di dalam plastid.

Diagrama De La Estructura Del Ejemplo Del Vector Del Amiloplasto Esquema Médico Etiquetado Con
a-c Amyloplast staining and quantification of the root apexes of Col-0, smb-3, ss4-3, adg1-1, ss4-3 smb-3 and adg1-1 smb-3 seedlings that were transferred to split-agar medium with or without.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/amyloplast-5b6c5498c9e77c0050442e0c.jpg)
Amyloplast Definition and Function
Amyloplasts are special organelles found in plant cells that store starch. In potatoes, they hold around 80% of the total starch content and give potatoes their distinct texture. Amyloplasts regulate sugar levels by storing glucose molecules and serve a structural support role throughout potato development. Potatoes are an excellent source of.

Amyloplast with starch grains UWDC UWMadison Libraries
statolith: a specialized form of amyloplast involved in graviperception by plant roots and most invertebrates gravitropism : a plant's ability to change its growth in response to gravity This page titled 30.20: Plant Sensory Systems and Responses - Plant Responses to Gravity is shared under a CC BY-SA 4.0 license and was authored, remixed.

TEM of an amyloplast Stock Image B100/0080 Science Photo Library
Amyloplast. Potato storage tissue containing amyloplasts by Krishna satya 333, CC0, via Wikimedia Commons. Amyloplast is one of the best-studied plastids. It's a type of leucoplast primarily involved in the synthesis and storage of starch (the word Amylo means starch).
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/leaf_cross-section-5b6c51af46e0fb0025c81ef5.jpg)
Amyloplast Definition and Function
amyloplast: [noun] a colorless plastid that forms and stores starch.

Amyloplast membrane localization of SSG6GFP in various tissues.... Download Scientific Diagram
Flexi Says: An amyloplast is an organelle found in plant cells. Amyloplasts are plastids that produce and store starch within internal membrane compartments. They are commonly found in vegetative plant tissues, such as tubers (potatoes) and bulbs. Discuss further with Flexi.

Plant cell anatomy and crosssection of Amyloplast Stock Vector Adobe Stock
Amyloplast. Amyloplasts are a type of plastid, double-enveloped organelles in plant cells that are involved in various biological pathways. Amyloplasts are specifically a type of leucoplast, a subcategory for colorless, non-pigment-containing plastids. [1] [2] Amyloplasts are found in roots and storage tissues, and they store and synthesize.