
2n+1)!? +[(2n)!] 61 !? [(2n + 1)!? [(2n)!)2 60 eşitliğini sağlayan n değeri kaçtır? A) 5 B) 6 C
Simplify (2n+2) (2n-2) (2n + 2) (2n − 2) ( 2 n + 2) ( 2 n - 2) Expand (2n+2)(2n− 2) ( 2 n + 2) ( 2 n - 2) using the FOIL Method. Tap for more steps. 2n(2n)+2n⋅−2+2(2n)+ 2⋅−2 2 n ( 2 n) + 2 n ⋅ - 2 + 2 ( 2 n) + 2 ⋅ - 2. Simplify terms. Tap for more steps. 4n2 − 4 4 n 2 - 4. Free math problem solver answers your algebra.

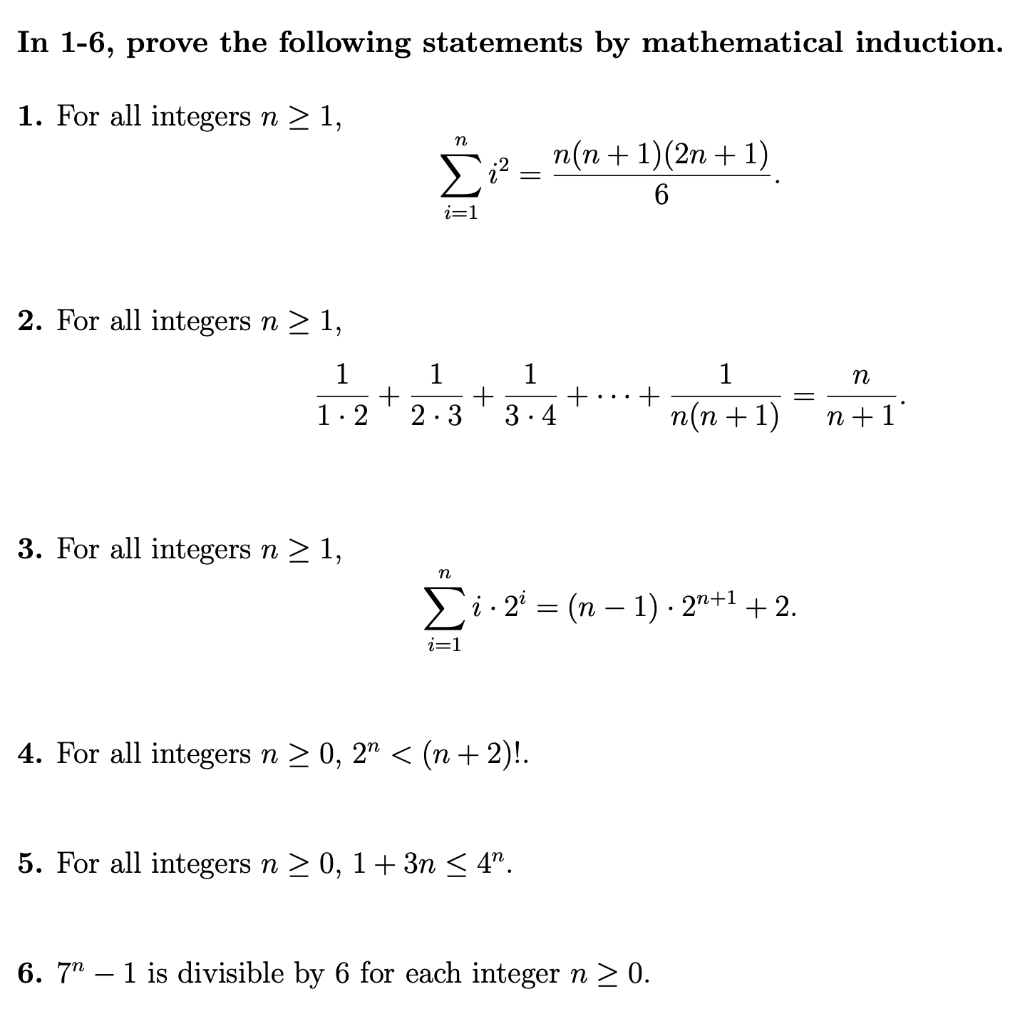
Prove by mathematical induction that the sum of squares of positive integers is n(n+1)(2n+1)/6
2n^{2} - n - 1 = 0. en. Related Symbolab blog posts. Middle School Math Solutions - Equation Calculator. Welcome to our new "Getting Started" math solutions series. Over the next few weeks, we'll be showing how Symbolab. Enter a problem. Cooking Calculators.

Question 10 Find sum of series, nth terms is (2n 1)2
2N, 2N+1, 2N+2 redundancy. N refers to the minimum number of resources (amount) required to operate an IT system. 2N simply means that there is twice the amount of required resources/capacity available in the system. For a simple example, let's consider a server in a data center that has ten servers with an additional ten servers that act as.

Ex 4.1, 7 Prove 1.3 + 3.5 + 5.7 + .. + (2n1) (2n+1) Class 11
Simplify (n-1) (2n-2) (n − 1) (2n − 2) ( n - 1) ( 2 n - 2) Expand (n−1)(2n− 2) ( n - 1) ( 2 n - 2) using the FOIL Method. Tap for more steps. n(2n)+n⋅ −2−1(2n)−1 ⋅−2 n ( 2 n) + n ⋅ - 2 - 1 ( 2 n) - 1 ⋅ - 2. Simplify and combine like terms. Tap for more steps. 2n2 − 4n+2 2 n 2 - 4 n + 2. Free math problem solver.
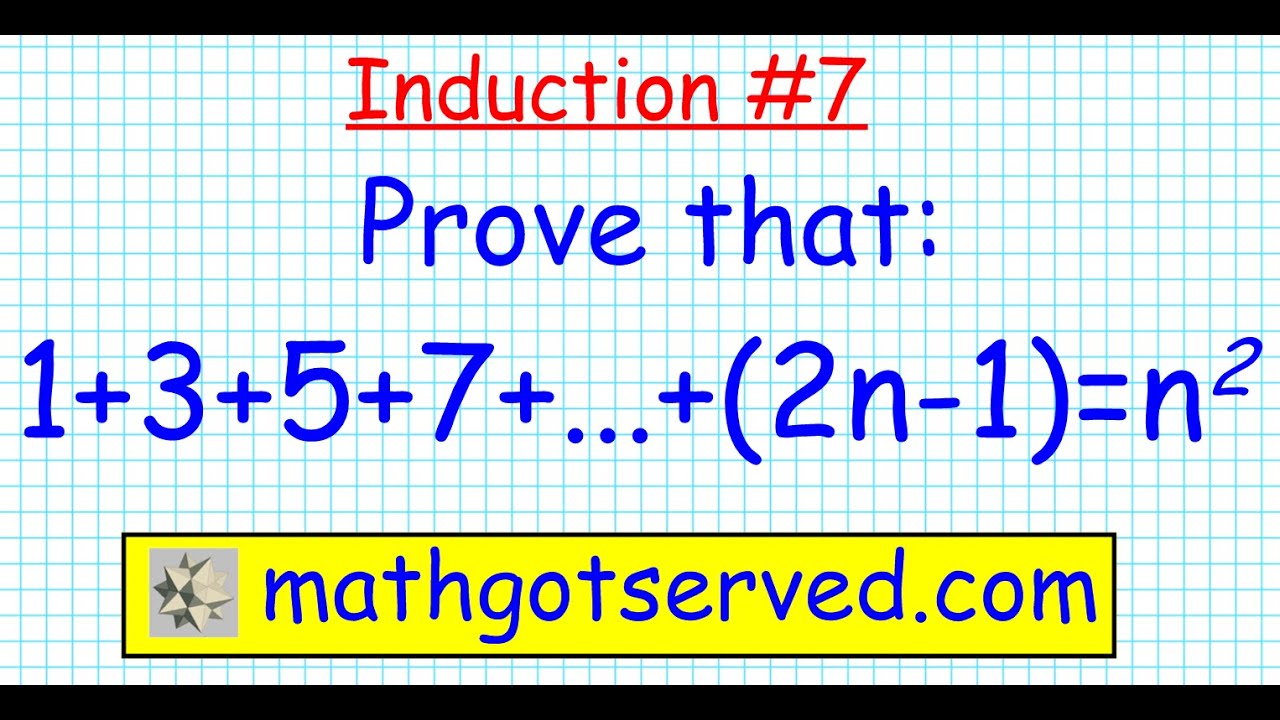
7 Proof by induction 1+3+5+7+...+2n1=n^2 discrete prove all n in N induccion mathgotserved
n 2 = 1 2 + 2 2 + 3 2 + 4 2 = 30 . We can add up the first four terms in the sequence 2n+1: 4.

Mathematical Induction with Divisibility 3^(2n + 1) + 2^(n + 2) is Divisible by 7 YouTube
6. In example to get formula for 1 2 + 2 2 + 3 2 +. + n 2 they express f ( n) as: f ( n) = a n 3 + b n 2 + c n + d. also known that f ( 0) = 0, f ( 1) = 1, f ( 2) = 5 and f ( 3) = 14. Then this values are inserted into function, we get system of equations solve them and get a,b,c,d coefficients and we get that. f ( n) = n 6 ( 2 n + 1) ( n + 1)
6=12n+5 3740016=12n+5 multi step equations
Compute answers using Wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions of students & professionals. For math, science, nutrition, history.
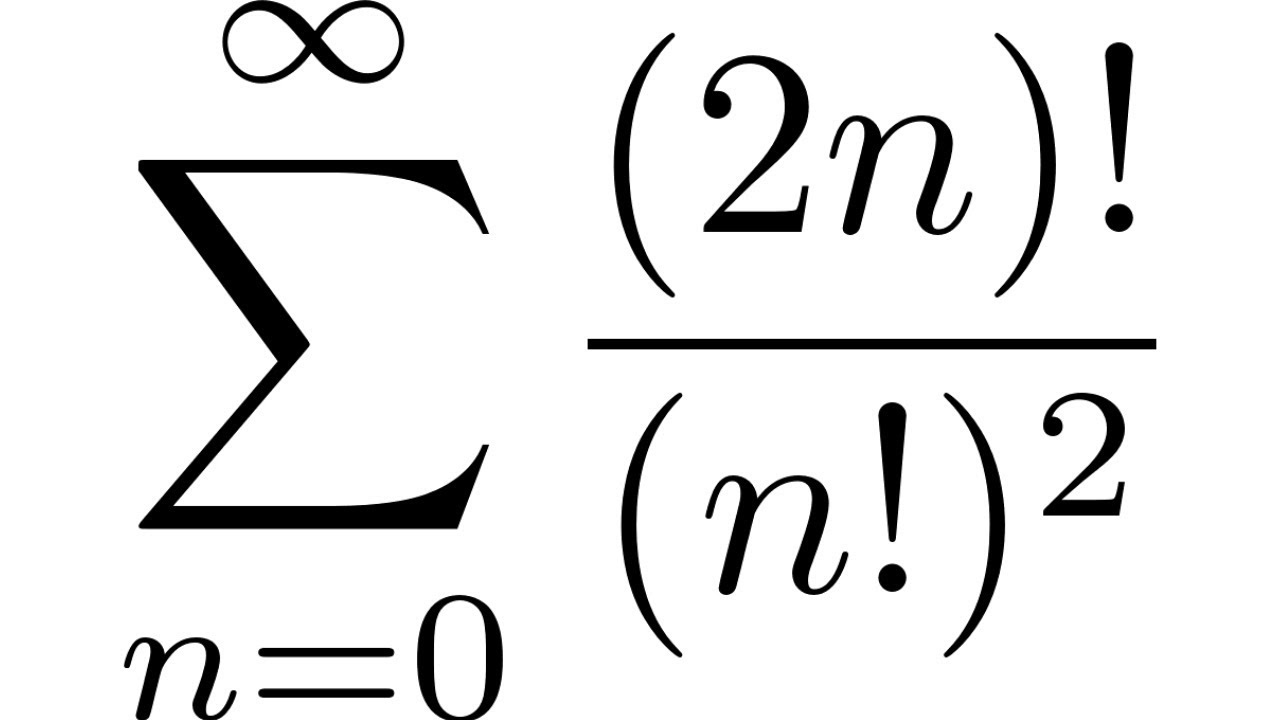
Infinite Series Convergence and Divergence Example with SUM((2n)!/(n!)^2) Ratio Test YouTube
Let's break down the solution to the given problem step by step. Problem Statement: Prove that \ (1 + 2 + 2^2 +. + 2^n = 2^ {n+1} - 1\). Solution: Step 2/5. Understand the Series The series given is a geometric series where the first term \ (a = 1\) and the common ratio \ (r = 2\). Each term in the series is twice the previous term, and we.

Question 8 Prove 1.2 + 2.22 + 3.23 + .. + n.2n = (n1) 2n+1 + 2
Factor n^2-2n+1. n2 − 2n + 1 n 2 - 2 n + 1. Rewrite 1 1 as 12 1 2. n2 − 2n+12 n 2 - 2 n + 1 2. Check that the middle term is two times the product of the numbers being squared in the first term and third term. 2n = 2⋅n ⋅1 2 n = 2 ⋅ n ⋅ 1. Rewrite the polynomial. n2 − 2⋅n⋅1+12 n 2 - 2 ⋅ n ⋅ 1 + 1 2. Factor using the perfect.

Convert the following products into factorials (n + 1)(n + 2)(n + 3)....(2n)
\sum_{n=0}^{\infty} \frac{1}{2n-1} en. Related Symbolab blog posts. The Art of Convergence Tests. Infinite series can be very useful for computation and problem solving but it is often one of the most difficult. Enter a problem. Cooking Calculators.

For all positive integers n , show that ^2nCn + ^2nCn 1 = 12( ^2n + 2Cn + 1)
Free Pre-Algebra, Algebra, Trigonometry, Calculus, Geometry, Statistics and Chemistry calculators step-by-step

Find the radius and interval of convergence of series {(1)^n x^(2n +1)/(2n+1)! Ratio Test YouTube
13. This question already has answers here : Closed 12 years ago. Possible Duplicate: Proof the inequality n! ≥ 2n by induction. Prove by induction that n! > 2n for all integers n ≥ 4. I know that I have to start from the basic step, which is to confirm the above for n = 4, being 4! > 24, which equals to 24 > 16.

Question 10 Find sum of series, nth terms is (2n 1)2
Simplify by multiplying through. Tap for more steps. (n2 + n)(2n+1) ( n 2 + n) ( 2 n + 1) Expand (n2 +n)(2n+1) ( n 2 + n) ( 2 n + 1) using the FOIL Method. Tap for more steps. n2(2n) +n2 ⋅1+n(2n)+n⋅1 n 2 ( 2 n) + n 2 ⋅ 1 + n ( 2 n) + n ⋅ 1. Simplify and combine like terms. Tap for more steps. 2n3 + 3n2 +n 2 n 3 + 3 n 2 + n.

Prove that (2n + 1)!n! = 2^n1.3.5... (2n 1)(2n + 1)
Solve for n 1/(n^2)+1/n=1/(2n^2) Step 1. Find the LCD of the terms in the equation. Tap for more steps. Step 1.1. Finding the LCD of a list of values is the same as finding the LCM of the denominators of those values. Step 1.2. Since contains both numbers and variables, there are two steps to find the LCM.

Solved Show that sigma^n_k = 1 k^2 = n(n + 1) (2n + 1)/6
The solution to ((2(n+1))!)/((2n)!) is (2n+2)(2n+1) Study Tools AI Math Solver Popular Problems Study Guides Practice Cheat Sheets Calculators Graphing Calculator Geometry Calculator Company About Symbolab Blog Help Contact Us

Induction Help prove 2n+1
Which means $$(2n+2)! = (2n+2) \cdot (2n+1) \cdot (2n)!$$ So when dividing $(2n+2)!$ by $(2n)!$ only those first two factors of $(2n+2)!$ remain (in this case in the denominator). Share